Refer to the following scenario to answer the question below.
You need to configure a Core Connector: Candidate Outbound integration for your vendor. The connector requires the data initialization service (DIS).
The vendor needs the file to only include candidates that undergo a candidate assessment event in Workday.
How do you accomplish this?
What is the task used to upload a new XSLT file for a pre-existing document transformation integration system?
Refer to the scenario. You are configuring a Core Connector: Worker integration with the Data Initialization Service (DIS) enabled. The integration must extract worker contact details and job information, including a calculated field override that determines phone allowance eligibility.
While testing, the output contains no records, and the Messages tab shows exception logs stating you don't have access to the Exempt field. You note this is the same field being used for Population Eligibility in the integration.
What must you configure to resolve this security issue?
Refer to the following XML data source to answer the question below.
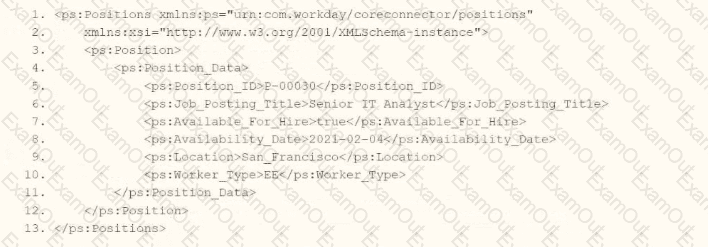
You need the integration file to format the ps:Position_ID field to 10 characters, truncate the value if it exceeds, and align everything to the left.
How will you start your template match on ps:Position to use Document Transformation (DT) to do the transformation using XTT?
Refer to the following scenario to answer the question below.
You need to configure a Core Connector: Candidate Outbound integration for your vendor. The connector requires the data initialization service (DIS).
The vendor requests additional formatting of the candidate Country field. For example, if a candidate's country is the United States of America, the output should show USA.
What steps do you follow to meet this request?
Refer to the scenario. You are configuring a Core Connector: Worker integration with the Data Initialization Service (DIS) enabled. The integration must extract worker contact details and job information, including a calculated field override that determines phone allowance eligibility.
When testing, you run the Test Security Related Action from the Configure Integration Field Override step. Several field overrides display “No” in the Available by User column.
To ensure the ISSG has access to these field overrides and that “Yes” is displayed in the Test Security step, what configuration should you review?
A vendor needs an EIB that uses a custom report to output a list of new hires and their child dependent(s). You have been asked to create a calculated field that will be used to add only child dependent(s).
Which calculated field functions do you need to accomplish this?
Refer to the scenario. You are configuring a Core Connector: Worker integration to extract worker demographic and contact information. The integration uses the Data Initialization Service (DIS) and must include worker fields such as name, address, and a calculated field identifying workers eligible for a phone allowance.
During a Full File test run, the output file is missing all address-related information, even though the Address Line Data, Municipality, Region, and Postal Code fields were configured in the Configure Integration Field Attributes step. You also confirmed that the Worker Personal Data Section is marked as Include in Output.
What should you do to resolve this issue?
How does an XSLT processor identify the specific nodes in an XML document to which a particular transformation rule should be applied?
You have successfully configured an ISU and an ISSG with the correct security policies and have assigned them to an EIB.
What task do you need to run before you can launch the EIB?





