Refer to the exhibit.
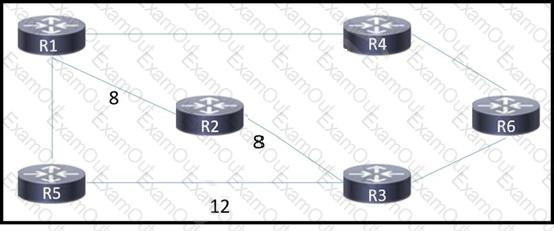
A network engineer configured routers R1 and R5 to run in IS-IS Level 1 mode and router R6 to run in IS-IS Level 2 mode. All other routers are running as Level 1 / Level 2 routers. An engineer expects traffic from R1 to R6 to pass via R2, but IS-IS routing has calculated the best path via R4. Which action corrects the problem?
Refer to the exhibit.
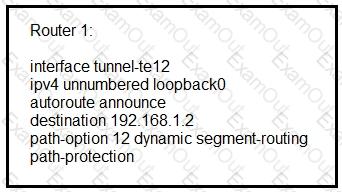
Router 1 has established an SR-TE tunnel with router 2. Which statement describes this
configuration?
Refer to the exhibit.
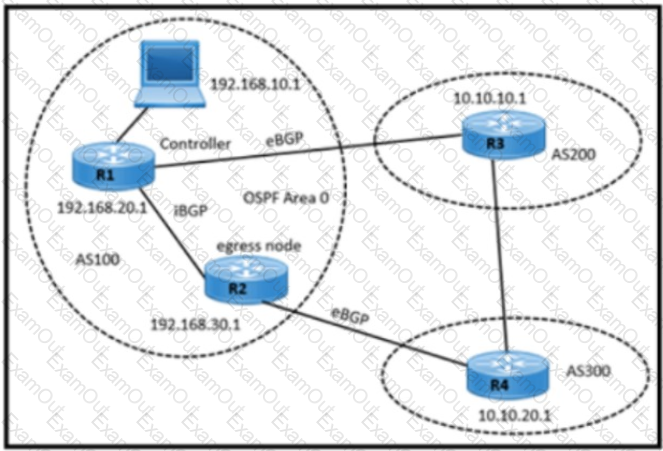
A network engineer must enable segment routing between the three autonomous systems with these requirements:
·OSPF link-state data for area 0 routers must be distributed to the controller via BGP LS.
·EPE must be enabled on the egress node in AS 100.
·Routers must advertise peer node SIDs to the controller R1 via BGP LS.
Which configuration must the engineer apply?
A)

B)

C)

D)

Refer to the exhibit.
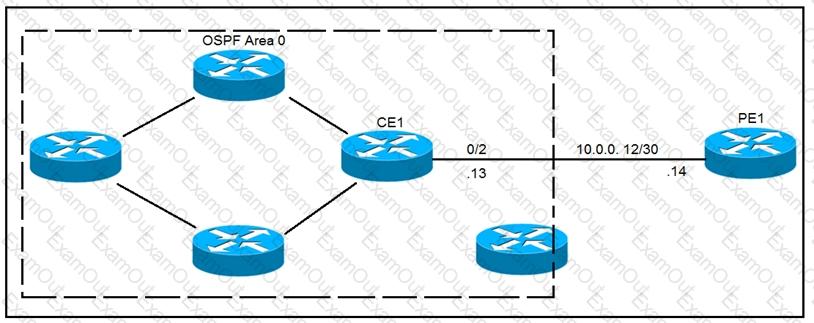
CE1 is the gateway router into the provider network via PE1. A network operator must
inject a default route into OSPF area 0. All devices inside area 0 must be able to reach PE1. Which configuration achieves this goal?

Refer to the exhibit
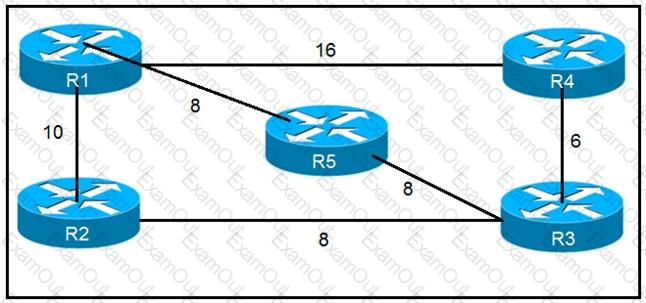
Which router does R1 install as an alternate next hop when trying to reach R3 if LFA is
enabled?
ION NO: 91
What are two major differences between OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is sending data traffic to R6 using the same SRGB range as the other routers in the topology, but it is also using a non-default SRLB range. Which two configuration tasks must the engineer perform to enable normal SRGB and SRLB operations on this network? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.
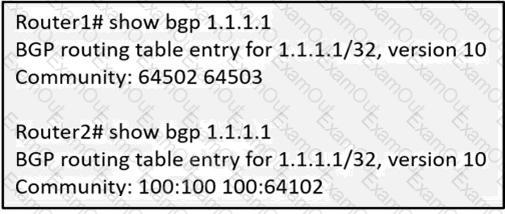
An engineer working on a client’s network is trying to solve the BGP community issue on R1 and R2 routers. After displaying the BGP entries, the engineer notices that both routers still have different outputs. Which action must the engineer perform to any of the routers to correct the problem and get the same output?
Which difference should be considered when intradomain or interdomain multicast routing is implemented?
What are two features of dual-stack? (Choose two.)

