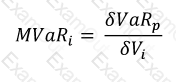A bank extends a loan of $1m to a home buyer to buy a house currently worth $1.5m, with the house serving as the collateral. The volatility of returns (assumed normally distributed) on house prices in that neighborhood is assessed at 10% annually. The expected probability of default of the home buyer is 5%.
What is the probability that the bank will recover less than the principal advanced on this loan; assuming the probability of the home buyer's default is independent of the value of the house?
Which of the following statements are correct:
I. A training set is a set of data used to create a model, while a control set is a set of data is used to prove that the model actually works
II. Cleansing, aggregating or ensuring data integrity is a task for the IT department, and is not a risk manager's responsibility
III. Lack of information on the quality of underlying securities and assets was a major cause of the collapse in the CDO markets during the credit crisis that started in 2007
IV. The problem of lack of historical data can be addressed reasonably satisfactorily by using analytical approaches
Which of the following best describes a 'break clause ?
Which of the following are ordered correctly in the order of debt seniority in a bankruptcy situation?
I. Equity, Subordinate debt, Senior debt
II. Senior debt, Preferred stock, Equity
III.Secured debt, Accounts payable, Preferred stock
IV. Secured debt, DIP financing, Equity
Which of the following can be used to reduce credit exposures to a counterparty:
I. Netting arrangements
II. Collateral requirements
III. Offsetting tradeswith other counterparties
IV. Credit default swaps
CreditRisk+, the actuarial model for calculating portfolio credit risk, is based upon:
If a borrower has a default probability of 12% over one year, what is the probability of default over a month?
Which of the following statements is true
I. If no loss data is available, good quality scenarios can be used to model operational risk
II. Scenario data can be mixed with observed loss data for modeling severity and frequency estimates
III. Severity estimates should not be created by fitting models to scenario generated loss data points alone
IV. Scenario assessments should only be used as modifiers to ILD or ELD severity models.
The risk that a counterparty fails to deliver its obligation upon settlement while having received the leg owed to it is called:
Which of the following best describes the concept of marginalVaR of an asset in a portfolio: