The healthcare quality professional is tasked with monitoring the monthly fall rates. The fall rate that requires the most immediate investigation is
A team at a large ambulatory surgery center is working to improve patient safety and plans to leverage technology as a strategy. Which of the following best illustrates that this is occurring?
The greatest motivator for organization leaders to use a balanced scorecard is that it
The purpose of sentinel event review of never events is to
A healthcare quality professional has been informed of a significant medication error resulting in patient harm. A multidisciplinary team should be selected to conduct a
A new pediatric psychiatric unit will open in one year. The utilization coordinator is responsible for developing the utilization management program. The program's success will depend on which of the following factors?
The desired outcome of peer review Is to
For which incident would a process improvement manager be required to perform a root cause analysis (RCA)?
Complaint analysis is most useful in identifying which of the following?
A consistent and effective communication plan for a process improvement initiative facilitates
A quality professional has been asked to assist with prioritizing quality performance Initiatives In the surgery department. Given the Information In the matrix below, which of the following performance Initiatives should take priority?
An organization has compiled the scatter plots below:
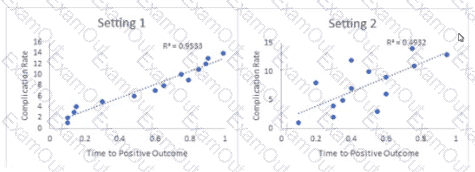
Based on these plots, which of the following conclusions can be made by the quality professional?
Which of the following Is an example of a population health strategy?
Cold-spotting involves identifying populations that
A nurse inadvertently hung an IV medication on the wrong patient’s IV pump, but discovered the error prior to initiating the infusion. Patient harm was averted, and the nurse disclosed the error to a healthcare quality professional. The quality professional should

