Which of the following workload services are offered as part of HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise? (Choose two.)
Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machines
VMware ESXi virtual machines
Google Distributed Cloud Hosted
serverless functions
Bare Metal servers
The Answer Is:
C, FExplanation:
HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise is a fully managed cloud service that delivers a unified self-service infrastructure provisioning experience to IT and application administrators and developers1. It supports the deployment of bare metal, containers, and virtual machines workloads across datacenters, colocation facilities, or edge locations1. It also provides a consistent cloud experience across any application or workload, whether traditional or cloud-native1.
One of the workload services offered as part of HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise is VMware ESXi virtual machines. VMware ESXi is a hypervisor that enables the creation and management of virtual machines on a physical server2. VMware ESXi virtual machines can run various operating systems and applications, and can be migrated, cloned, or backed up using VMware tools2. HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise integrates with VMware vCenter Server to provide a seamless user interface for provisioning and managing VMware ESXi virtual machines3. Users can also leverage VMware vRealize Automation and vRealize Operations for advanced automation and orchestration capabilities3.
Another workload service offered as part of HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise is Bare Metal servers. Bare Metal servers are physical servers that are dedicated to a single tenant and do not run any hypervisor or virtualization layer4. Bare Metal servers can offer higher performance, security, and customization than virtual machines, as they eliminate the overhead and complexity of virtualization4. HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise enables users to provision and manage Bare Metal servers using a self-serviceportal or an API5. Users can also choose from various server models, configurations, and operating systems to suit their workload needs5.
The other options, such as Microsoft Azure Stack HCI, Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machines, Google Distributed Cloud Hosted, and serverless functions, are not workload services offered as part of HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise. Microsoft Azure Stack HCI and Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machines are alternative virtualization solutions that are not supported by HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise1. Google Distributed Cloud Hosted is a cloud service that extends Google Cloud Platform to customer premises or edge locations, but it is not integrated with HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise. Serverless functions are a cloud computing model that executes code without requiring users to provision or manage servers, but they are not available as a workload service in HPE GreenLake Private Cloud Enterprise1.
References:
1: HPE GreenLake for Private Cloud Enterprise
2: What is VMware ESXi? - Definition from WhatIs.com
3: HPE GreenLake for Private Cloud Enterprise: Scaling and orchestrating modern applications for the enterprise
4: What is a bare metal server? | IBM
5: HPE GreenLake for Private Cloud Enterprise
: Google Distributed Cloud | Google Cloud
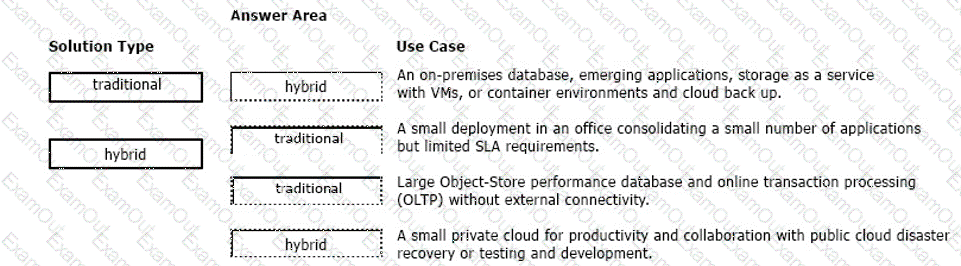
For each use case, identify whether it is a traditional solution or a hybrid solution.

The Answer Is:

Explanation:
According to the HPE Edge-to-Cloud Adoption Framework, page 5, a traditional solution is a cloud deployment model where the cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization comprising multiple consumers (e.g., business units). It may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or somecombination of them, and it may exist on or off premises. A traditional solution offers the organization more control, security, and customization over their cloud resources, but it also requires more investment, maintenance, and expertise.
A hybrid solution is a cloud deployment model where the cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities, but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud bursting for load balancing between clouds). A hybrid solution offers the consumers more choice, agility, and innovation over their cloud resources, but it also requires more integration, management, and complexity.
Based on these definitions, the following use cases are hybrid solutions:
An on-premises database, emerging applications, storage as a service with VMs, or container environments and cloud back up. = Hybrid solution. This use case involves a combination of on-premises and cloud resources, and requires data and application portability between them.
A small private cloud for productivity and collaboration with public cloud disaster recovery or testing and development. = Hybrid solution. This use case involves a combination of private and public cloud resources, and requires data and application portability between them.
The following use cases are traditional solutions:
A small deployment in an office consolidating a small number of applications but limited SLA requirements. = Traditional solution. This use case involves a single organization using a cloud infrastructure for exclusive use, and does not require data and application portability to other clouds.
Large Object-Store performance database and online transaction processing (OLTP) without external connectivity. = Traditional solution. This use case involves a single organization using a cloud infrastructure for exclusive use, and does not require data and application portability to other clouds

