A company has budgeted to produce 5,000 units of Product B per month. The opening and closing inventories of Product B for next month are budgeted to be 400 units and 900 units respectively. The budgeted selling price and variable production costs per unit for Product B are as follows:

Total budgeted fixed production overheads are $29,500 per month.
The company absorbs fixed production overheads on the basis of the budgeted number of units produced. The budgeted profit for Product B for next month, using absorption costing, is $20,700.
Prepare a marginal costing statement which shows the budgeted profit for Product B for next month.
What was the marginal costing profit for the next month?
TP makes wedding cakes that are sold to specialist retail outlets which decorate the cakes according to the customers’ specific requirements. The standard cost per unit of its most popular cake is as follows:
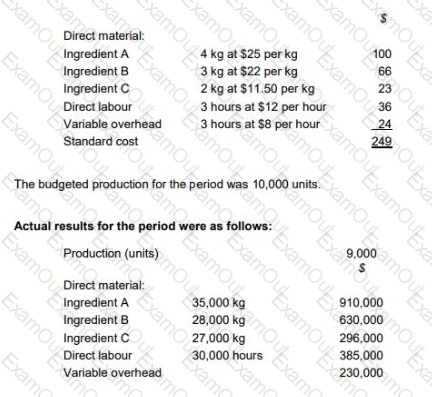
The general market prices at the time of purchase for Ingredient A and Ingredient B were $23 per kg and $20 per kg respectively. TP operates a JIT purchasing system for ingredients and a JIT production system; therefore, there was no inventory during the period.
What was the material price planning variance for ingredient B?
What type of budget is prepared on an annual basis taking current year operating results and adjusting them for expected growth and inflation?
CH is a building supplies company that sells products to trade and private customers.
Budget data for each of the six months to March are given below:
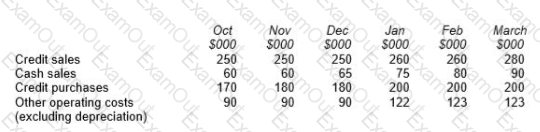
80% of the value of credit sales is received in the month after sale, 10% two months after sale and 8% three months after sale. The balance is written off as a bad debt.
75% of the value of credit purchases is paid in the month after purchase and the remaining 25% is paid two months after purchase.
All other operating costs are paid in the month they are incurred.
CH has placed an order for four new forklift trucks that will cost $25,000 each. The scheduled payment date is in February.
The cash balance at 1 January is estimated to be $15,000.
Prepare a cash budget for each of the THREE months of January, February and March.
Select All the correct answers.
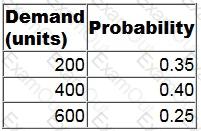
The daily demand for a perishable product has the following probability distribution:
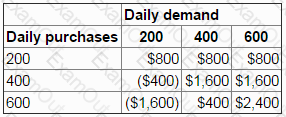
Each unit of the product costs $6 and is sold for $10.
Unsold items are thrown away at the end of the day.
Orders must be placed each morning before the daily demand is known.
The payoff table below shows the profit that would be earned for each of the combinations of purchases and demand.
The number of units that should be purchased at the beginning of each day in order to maximize expected profit is:
Traditional absorption costing is more suitable than activity-based costing when:
Explain why sensitivity analysis is useful when dealing with uncertainty in project
appraisal.
Select all the true statements.
The maximum availability of a material is 8,000 kg.
Product A requires 5 kg of this material and Product B requires 7 kg of this material which is in short supply.
The correct constraint to include for the material when formulating the linear programming problem is:
5c0e02ae-e691-41dd-b436-d41e2edaf83f: A company is using relevant costing to evaluate a make or buy decision.
The company already has a machine on an operating lease which can be used to make the product.
How would the lease rental cost be classified?
Sales volumes reported for the latest period are used by managers as the basis to forecast sales for the forthcoming period. The forecasts are compared with the budgeted sales and plans are adjusted to ensure that the budgeted sales are achieved.
This is an example of:

