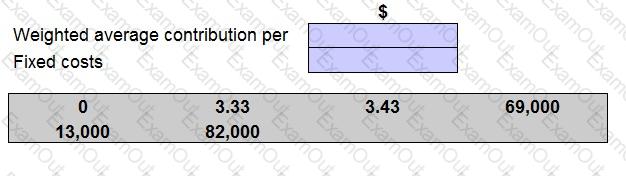
A company sells three products A, B and C in a ratio of 2:2:3.
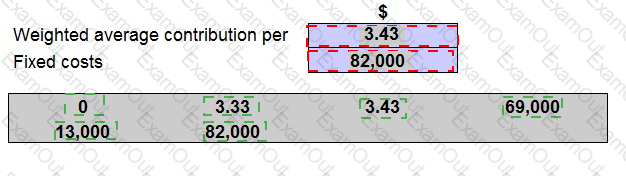
Each unit of A,B and C earns a contribution of $4.00, $2.00 and $4.00 respectively. Production fixed costs are $69,000 each month and selling fixed costs are $13,000 each month.
The company holds no inventory. The management accountant wants to know the total number of units needed to break-even. However, he is unsure about how to calculate the weighted average contribution per unit or what category of fixed cost to use.
Place the amounts given to complete the table in order to calculate the total number of units to break even.
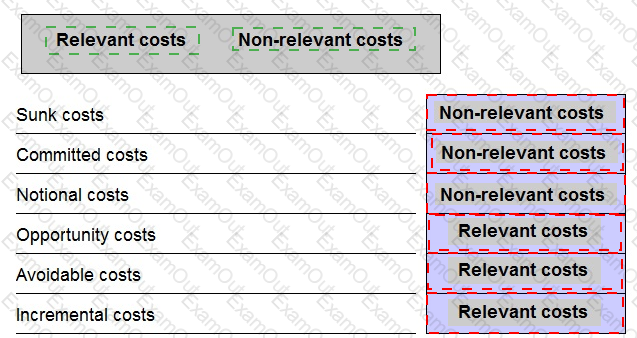
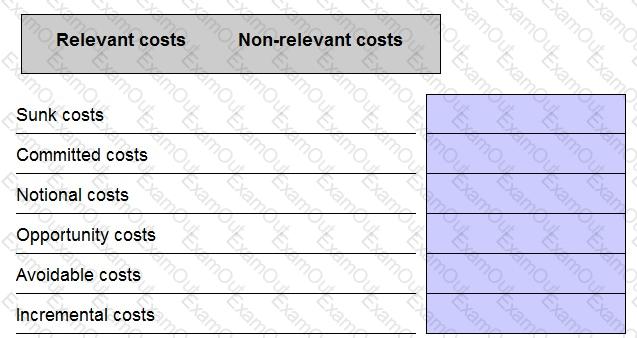
State whether the following costs are relevant or non-relevant in the context of short-term decision making scenarios.
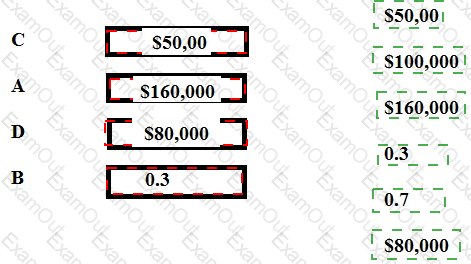
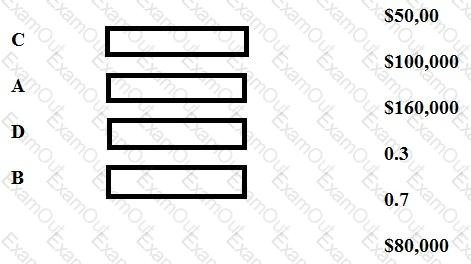
A company is forecasting its revenue for May and has established that sales will be either high, medium or low. The expected value of sales revenue for May has been calculated as $160,000. The following table includes data which relate to the potential sales in May.
Revenue Probability Expected Value
High $250,000 0.2 C
Medium A 0.5 D
Low $100,000 B $30,000
Place the figures given in to the spaces marked with the letters A, B, C and D, to complete the above table.
A company makes and sells three products A, B and C.
The selling prices and costs of the three products, using a traditional absoprtion costing system, are shown in the table below.
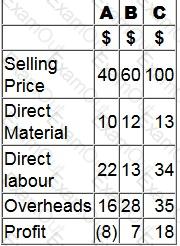
The company has undertaken an analysis of overhead costs using activity-based costing (ABC).
The revised overhead costs for products A, B and C are $6, $32 and $55 respectively.
When comparing the figures obtained under the two costing methods, which of the following statements are true?
Select ALL that apply.
QR uses an activity based budgeting (ABB) system to budget product costs. It manufactures two products, product Q and product R. The budget details for these two products for the forthcoming period are as follows:

The total budgeted cost of setting up the machines is $74,400.
What was the budgeted machine set up cost per unit of product Q?
A manager is deciding which one of four services to provide next period.
The contribution earned by each service will depend on the weather conditions as follows.
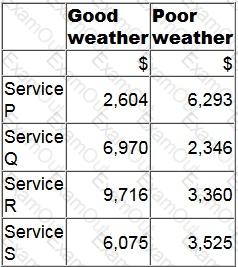
Using the maximin criterion, which service will the manager provide?
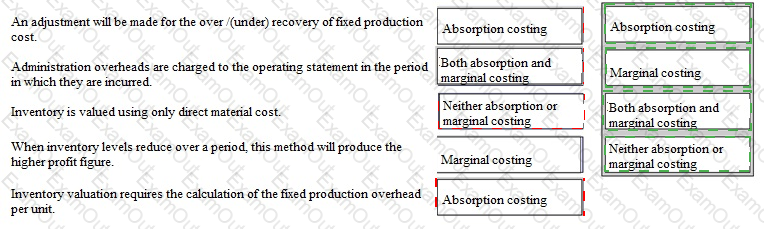
The following 5 statements apply the principles of either, both or neither absorption costing and marginal costing.
Place the option labels against the relevant statements.

A company is preparing its annual budget and is estimating the number of units of Product W that it will sell in each quarter of year 2. Past experience has shown that the trend for sales of the product is represented by the following relationship:

Calculate the expected unit sales of Product W for each quarter of year 2, after adjusting for seasonal variations using the multiplicative model.
TP makes wedding cakes that are sold to specialist retail outlets which decorate the cakes according to the customers’ specific requirements. The standard cost per unit of its most popular cake is as follows:
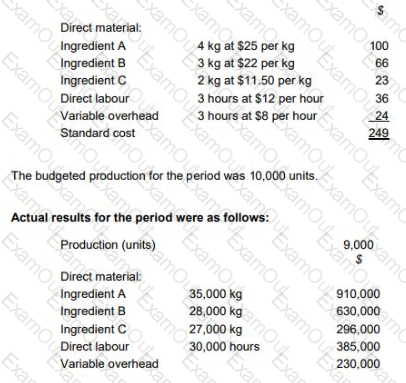
The general market prices at the time of purchase for Ingredient A and Ingredient B were $23 per kg and $20 per kg respectively. TP operates a JIT purchasing system for ingredients and a JIT production system; therefore, there was no inventory during the period.
Discuss the usefulness of the planning and operational variances calculated for TP’s management.
Select ALL the TRUE statements.
A manufacturing company has more units of finished goods inventory at the end of a period than at the beginning of the period.
Which of the following statements is true?