A company is wholly equity funded. It has the following relevant data:
• Dividend just paid $4 million
• Dividend growth rate is constant at 5%
• The risk free rate is 4%
• The market premium is 7%
• The company's equity beta factor is 1.2
Calculate the value of the company using the Dividend Growth Model.
Give your answer in $ million to 2 decimal places.
$ ? million
A company plans to acquire new machinery.
It has two financing options; buy outright using a bank loan, or a finance lease.
Which of the following is an advantage of a finance lease compared with a bank loan?
Country X's short-term interest rates are slightly higher than its long-term rates. Which THREE of the following statements are correct?
An entity prepares financial statements to 31 December each year. The following data applies:
1 December 20X0
• The entity purchased some inventory for $400,000.
• In order to protect the inventory against adverse changes in fair value the entity entered into a futures contract to sell the inventory for a fixed price on 31 January 20X1.
• The entity designated this contract as a fair value hedge of the value of the inventory.
31 December 20X0
• The inventory had a fair value of $480,000 and the futures contract had a fair value of $75,000 (a financial liability).
What will be the impact on the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the year ended 31 December 20X0 in respect of the change in the value of the inventory and the futures contract?
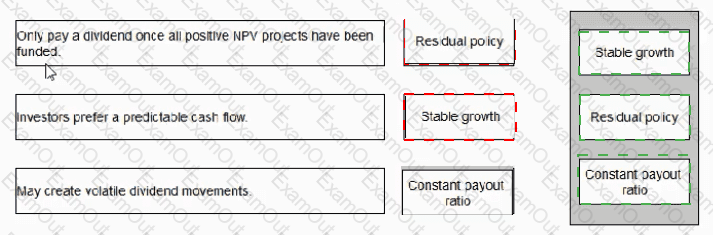
The Board of Directors of a small listed company engaged in exploration are currently considering the future dividend policy of the company. Exploration is considered a high-risk business and consequently the company has a low level of debt finance.
Forecasts indicate a period of profit fluctuation in the next few years as the company is planning to embark on a major capital investment project. Debt finance is unlikely to be available due to the project's high business risk.
Which THREE of the following are practical considerations when determining the company's dividend/retention policy?
A venture capitalist invests in a company by means of buying:
• 9 million shares for $2 a share and
• 8% bonds with a nominal value of $2 million, repayable at par in 3 years' time.
The venture capitalist expects a return on the equity portion of the investment of at least 20% a year on a compound basis over the first 3 years of the investment.
The company has 10 million shares in issue.
What is the minimum total equity value for the company in 3 years' time required to satisify the venture capitalist's expected return?
Give your answer to the nearest $ million.
$ million.
Select the most appropriate divided for each of the following statements:
The Senior Management Team of ABC, an owner-managed, capital intensive start-up engineering business, is considering the options for its dividend policy. It has so far been a successful business and is expanding quickly Once in place, the Senior Management Team anticipates that its current investment plans will yield returns for many years to come The first agenda item at every meeting currently concerns arranging and funding new equipment and premises.
Which of the following dividend policies is likely to be the most suitable?
Company AD is planning to acquire Company DC. It is evaluating two methods of structuring the terms of the bid, which will be ether a debt-funded cash offer or a share exchange
The following Information is relevant
• The two companies are of similar size and in related industries
• AB's gearing ratio measured as debt to debt plus equity, is currently 30% based on market values. This Is the company's optimum capital structure set to reflect the risk appetite of shareholders.
• The combined company is expected to generate savings and synergies
Which THREE of the following are advantages to AB's shareholders of a debt-funded cash offer compared with a share exchange?
A company wishes to raise new finance using a rights issue to invest in a new project offering an IRR of 10%
The following data applies:
• There are currently 1 million shares in issue at a current market value of $4 each.
• The terms of the rights issue will be $3.50 for 1 new share for 5 existing shares.
• The company's WACC is currently 8%.
What is the yield-adjusted theoretical ex-rights price (TERP)?
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
$ ?