Refer to the exhibit.

The standard variable cost per unit of Product W is $26. The budgeted sales of Product W in April was 3,300 units. The company recorded the following variances for the month of April:
During April 3,600 units of Product W were actually sold.
The budgeted contribution for Product W in April was to the nearest $000:
In a manufacturing company which produces a range of products, the wages of a machine operator in the factory would be classified as a:
Refer to the exhibit.
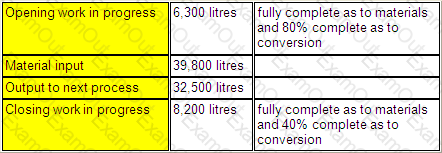
A company operates a process costing system. The following data relates to Process X for the month of September.
Normal loss is 5% of input and all losses occur at the end of the process.
The number of equivalent units, using an average cost basis of valuation, was:
Conversion:
Which THREE of the following costs would normally be classified as semi-variable?
Which THREE of the following statements could explain why an adverse material price variance has arisen?
JB has fixed costs of $120,000 per annum. It manufactures a single product which it sells for $12 per unit. It has a profit/volume ratio of 60%.
JB’s break-even point is
Refer to the exhibit.
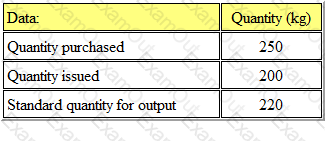
Xpert Ltd uses a standard costing system and therefore values all inventory at standard cost. During period 7, the price paid for material 'Z' was £2 per kg more than the standard price.
The following information for material 'Z' relates to period 7:
What was the material price variance for 'Z' in period 7?
A company operates a flexible budget system. A budget for direct material cost is set at £12500 for 2500 kgs of material.
It is budgeted that all materials will be obtained at a 5% discount when total production is in excess of 2700 kgs.
What variance is reported if actual material usage is 3000 kgs and the actual cost is £13500?
Which of the following are NOT behavioural aspects of budgetary controls? (Select ALL that apply.)
Refer to the exhibit.
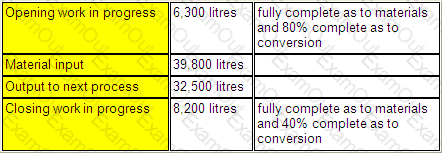
A company operates a process costing system. The following data relates to Process X for the month of September.
Normal loss is 5% of input and all losses occur at the end of the process.
The number of equivalent units, using an average cost basis of valuation, was:
Materials:

