A company operates a full cost system of pricing. Production overheads are absorbed using a pre-determined absorption rate of £3.50 per machine hour. The direct production cost of product A is £15 per unit and it utilises 6 machine hours per unit. The mark-up for non-production costs is 10% of total production cost. The company wants to make a 25% return on sales revenue for all products.
The required selling price for Product A, to two decimal places, is:
Refer to the exhibit.
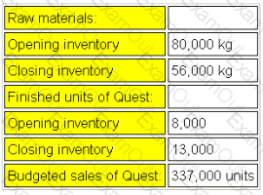
Data for October's budget for product Quest for the month of October are given below:
Each unit of Quest requires 6kg of raw materials. Strict quality control procedures are applied to the manufacturing process and normal rejection levels are 5% of finished units.
The raw materials purchases budget for the month of October is:
The variable overhead expenditure variance is:
A company can increase its margin of safety by which of the following independent actions?
(a) Increasing sales and production
(b) Raising the selling price per unit
(c) Raising the variable cost per unit
(d) Lowering fixed costs
In the process account, the accounting treatment of the value of the abnormal gain is:
Fixed costs can best be described as:
Each finished carton of product P contains 15 litres of liquid L. During the production process there is an unavoidable loss of 20% of the liquid input. The standard price of liquid L is $2 per litre.
The standard ingredient cost for liquid L shown on the standard cost card for one carton of product P will be
A company’s cash budgetary plans show that there will be surplus cash for three months of the forthcoming year.
Which THREE of the following would be appropriate management actions in this situation?
Each unit of product GM requires 4 labour hours to be produced. 25% of the units will be completed during overtime hours.
Sales of 24,000 units are planned and finished goods inventory is budgeted to rise by 2,000 units.
If the wage rate is £6 per hour and the overtime premium is 50%, what is the budgeted labour cost?
A company wishes to compare the variability of its monthly sales revenue in country A with that of country B. The two countries use different currencies.
The monthly sales revenue for the last 48 months in country A (which is measured in $) has been analysed as follows.
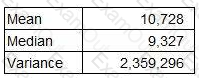
What is the coefficient of variation of this data?
Give your answer as a percentage to one decimal place.

