Refer to the exhibit.

SP, a manufacturing company, uses a standard costing system. The standard variable production overhead cost is based on the following budgeted figures for the year:
During the month of September, 5,300 actual hours were worked and 5,600 standard hours of output were produced. Total variable production overhead costs in September were $8,600.
What was the variable production overhead expenditure variance in September?
Which of the following entries to record the direct and indirect labour costs in the month are correct?
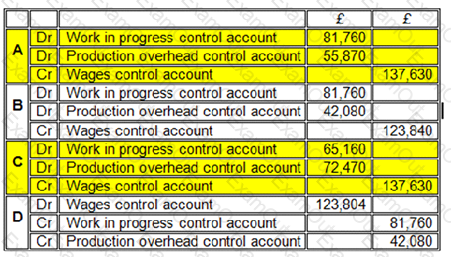
The correct entry is
Budgets are produced:
(a) For planning purposes
(b) For control purposes
(c) To be published with the annual accounts
(d) To comply with international accounting standards
An increase in variable costs per unit, where selling price and fixed costs remain constant, will result in which of the following:
Refer to the exhibit.
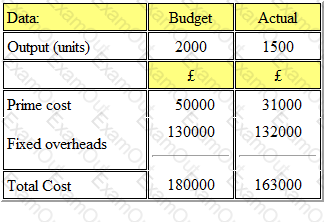
A company issued its production budget based on an anticipated output of 2000 units. The actual output for the period was 1500 units. The details of the costs are shown below:
What was the budget expenditure variance?
It is company policy that the closing inventory of finished goods must be equal to 20% of the following month's budgeted sales. The budget sales for November and December are 6,000 and 7,000 units respectively.
The budgeted production for November will be
When preparing the material purchases budget, the quantity to be purchased equals:
What is the purpose of performing an NPV?
A new range of clothing is very unique and will not appeal everyone. You are aware that if you were to equally distribute all the units there is a chance that they would not all sell.
You decide that the best option would be to select specific stores in which to sell the items, making them rare and desirable. This way they will become highly sought after.
However, whilst this has the potential to be very profitable it also has the lowest probability.
By making this decision you are considered to be_______.
A service company provides accountancy training courses. Which THREE of the following would be classified as variable costs of the company?

