Which two are true for a dbt clone command?
Choose 2 options.
A developer has updated multiple models in their dbt project, materialized as tables and views.
They want to run and test all models upstream and downstream from the modified models that are materialized as views.
What command will achieve this? Choose 1 option.
What must happen before you can build models in dbt?
Choose 1 option.
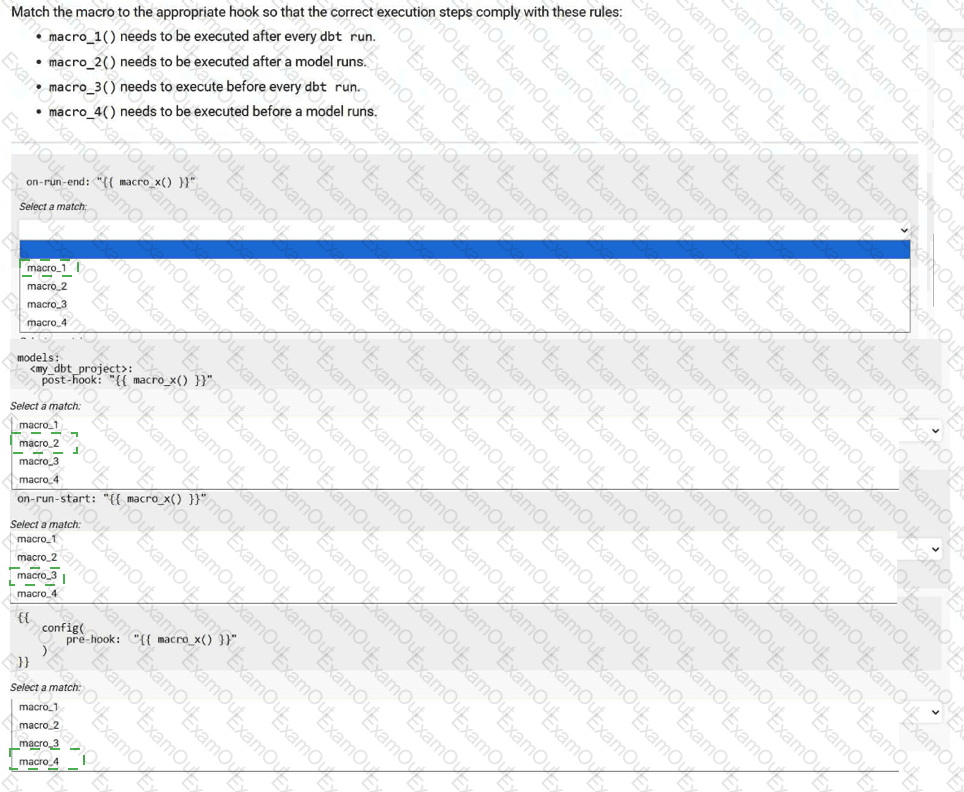
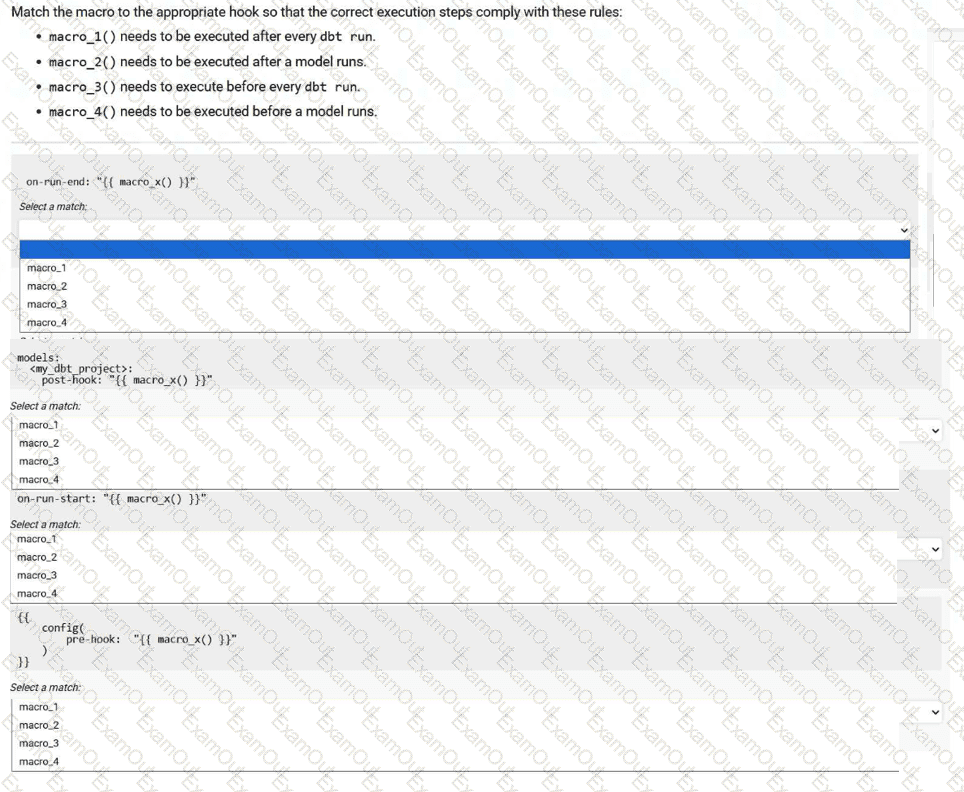
Match the macro to the appropriate hook so that the correct execution steps comply with these rules:
macro_1() needs to be executed after every dbt run.
macro_2() needs to be executed after a model runs.
macro_3() needs to execute before every dbt run.
macro_4() needs to be executed before a model runs.
In development, you want to avoid having to re-run all upstream models when refactoring part of your project.
What could you do to save time rebuilding models without spending warehouse credits in your next command?
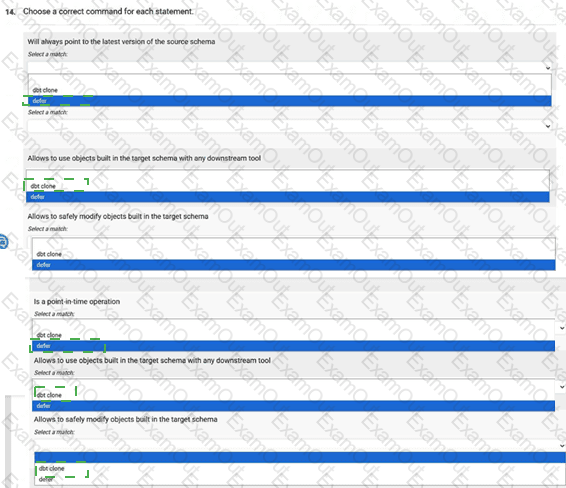
Choose a correct command for each statement.

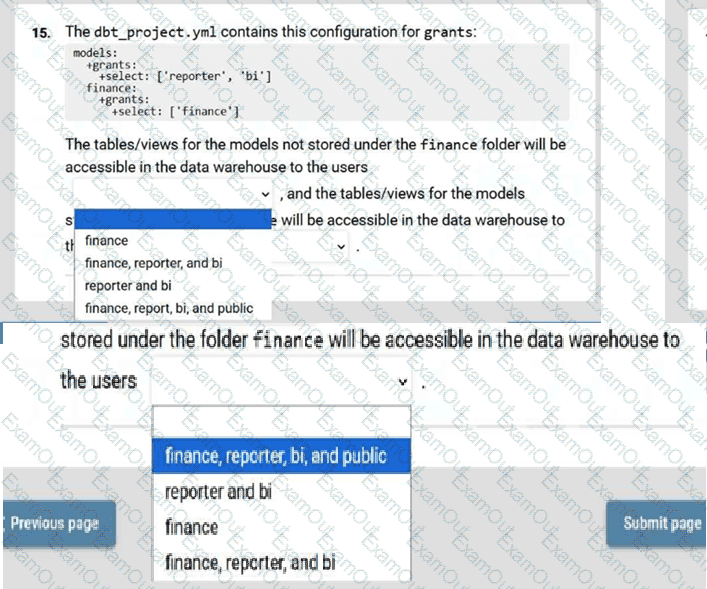
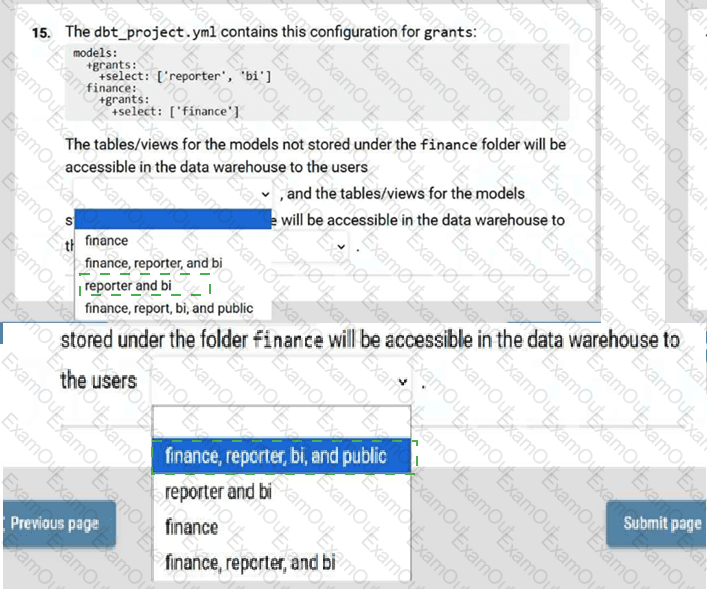
Given this dbt_project.yml:
name: "jaffle_shop"
version: "1.0.0"
config-version: 2
profile: "snowflake"
model-paths: ["models"]
macro-paths: ["macros"]
snapshot-paths: ["snapshots"]
target-path: "target"
clean-targets:
- "logs"
- "target"
- "dbt_modules"
- "dbt_packages"
models:
jaffle-shop:
+materialized: table
…and this warning when compiling your project:
[WARNING]: Configuration paths exist in your dbt_project.yml file which do not apply to any resources.
There are 1 unused configuration paths:
- models.jaffle-shop
What is the root cause?
A run hook in the jaffle_shop project was defined with an incorrect regular expression.
You work at an e-commerce company and a vendor provides their inventory data via CSV file uploads to an S3 bucket.
How do you prep the data for dbt transformations?
Choose 1 option.
Which two configuration items can be defined under models: in your dbt_project.yml file?
Choose 2 options.