Which option below is NOT a role of the audit team leader?
You are an experience ISMS audit team leader carrying out a third-party certification audit of an organization specialising in the secure disposal of confidential documents and removable media. Both documents and media are shredded in military grade devices which make it impossible to reconstruct the original.
The audit has gone well and you are just about to start to write the audit report, 30 minutes before the closing meeting. At
this point one of the organization's employees knocks on your door and asks if they can speak to you. They tell you that when things get busy her manager tells her to use a lower grade industrial shredder instead as the organisation has more of these and they operate faster. You were not informed about the existence or use of these machines by the auditee.
Select three options for how you should respond to this information.
CMM stands for?
You are conducting an ISMS audit in the despatch department of an international logistics organisation that provides shipping services to large organisations including local hospitals and government offices. Parcels typically contain pharmaceutical products, biological samples, and documents such as passports and driving licences. You note that the company records show a very large number of returned items with causes including misaddressed labels and, in 15% of cases, two or more labels for different addresses for the one package. You are interviewing the Shipping Manager (SM).
You: Are items checked before being dispatched?
SM: Any obviously damaged items are removed by the duty staff before being dispatched, but the small profit margin makes it uneconomic to
implement a formal checking process.
You: What action is taken when items are returned?
SM: Most of these contracts are relatively low value, therefore it has been decided that it is easier and more convenient to simply reprint the label and re-send individual parcels than it is to implement an investigation.
You raise a nonconformity. Referencing the scenario, which three of the following Annex A controls would you expect the auditee to have implemented when you conduct the follow-up audit?
Which six of the following actions are the individual(s) managing the audit programme responsible for?
You are the audit team leader conducting a third-party audit of an online insurance organisation. During Stage 1, you found that the organisation took a very cautious risk approach and included all the information security controls in ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Appendix A in their Statement of Applicability.
During the Stage 2 audit, your audit team found that there was no evidence of the implementation of the three controls (5.3 Segregation of duties, 6.1 Screening, 7.12 Cabling security) shown in the extract from the Statement of Applicability. No risk treatment plan was found.
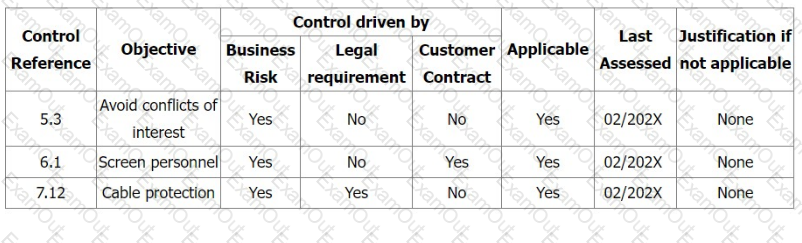
Select three options for the actions you would expect the auditee to take in response to a
nonconformity against clause 6.1.3.e of ISO/IEC 27001:2022.
Which of the options below presents a minor nonconformity?
OrgXY is an ISO/IEC 27001-certified software development company. A year after being certified, OrgXY's top management informed the certification body that the company was not ready for conducting the surveillance audit. What happens in this case?
What is the difference between a restricted and confidential document?
You are the audit team leader conducting a third-party audit of an online insurance company. During Stage 1, you found that the organization took a very cautious risk approach and included all the information security controls in ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Appendix A in their Statement of Applicability.
During the Stage 2 audit, your audit team found that there was no evidence of a risk treatment plan for the implementation of the three controls (5.3 Segregation of duties, 6.1 Screening, 7.12 Cabling security). You raise a nonconformity against clause 6.1.3.e of ISO 27001:2022.
At the closing meeting, the Technical Director issues an extract from an amended Statement of Applicability (as shown) and asks for the nonconformity to be withdrawn.
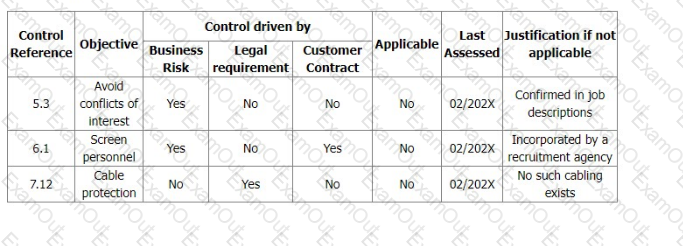
Select three options of the correct responses of an audit team leader to the request of the Technical Director.

