Audit methods can be either with or without interaction with individuals representing the auditee. Which two of the following methods are with interaction?
Scenario 6: Cyber ACrypt is a cybersecurity company that provides endpoint protection by offering anti-malware and device security, asset life cycle management, and device encryption. To validate its ISMS against ISO/IEC 27001 and demonstrate its commitment to cybersecurity excellence, the company underwent a meticulous audit process led by John, the appointed audit team leader.
Upon accepting the audit mandate, John promptly organized a meeting to outline the audit plan and team roles This phase was crucial for aligning the team with the audit's objectives and scope However, the initial presentation to Cyber ACrypt’s staff revealed a significant gap in understanding the audit's scope and objectives, indicating potential readiness challenges within the company
As the stage 1 audit commenced, the team prepared for on-site activities. They reviewed Cyber ACrypt's documented information, including the information security policy and operational procedures ensuring each piece conformed to and was standardized in format with author identification, production date, version number, and approval date Additionally, the audit team ensured that each document contained the information required by the respective clause of the standard This phase revealed that a detailed audit of the documentation describing task execution was unnecessary, streamlining the process and focusing the team's efforts on critical areas During the phase of conducting on-site activities, the team evaluated management responsibility for the Cyber Acrypt's policies This thorough examination aimed to ascertain continual improvement and adherence to ISMS requirements Subsequently, in the document, the stage 1 audit outputs phase, the audit team meticulously documented their findings, underscoring their conclusions regarding the fulfillment of the stage 1 objectives. This documentation was vital for the audit team and Cyber ACrypt to understand the preliminary audit outcomes and areas requiring attention.
The audit team also decided to conduct interviews with key interested parties. This decision was motivated by the objective of collecting robust audit evidence to validate the management system’s compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 requirements. Engaging with interested parties across various levels of Cyber ACrypt provided the audit team with invaluable perspectives and an understanding of the ISMS's implementation and effectiveness.
The stage 1 audit report unveiled critical areas of concern. The Statement of Applicability (SoA) and the ISMS policy were found to be lacking in several respects, including insufficient risk assessment, inadequate access controls, and lack of regular policy reviews. This prompted Cyber ACrypt to take immediate action to address these shortcomings. Their prompt response and modifications to the strategic documents reflected a strong commitment to achieving compliance.
The technical expertise introduced to bridge the audit team's cybersecurity knowledge gap played a pivotal role in identifying shortcomings in the risk assessment methodology and reviewing network architecture. This included evaluating firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and other network security measures, as well as assessing how Cyber ACrypt detects, responds to, and recovers from external and internal threats. Under John's supervision, the technical expert communicated the audit findings to the representatives of Cyber ACrypt. However, the audit team observed that the expert s objectivity might have been compromised due to receiving consultancy fees from the auditee. Considering the behavior of the technical expert during the audit, the audit team leader decided to discuss this concern with the certification body.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Question:
Which criteria for evaluating documented information was NOT validated by the audit team? (Refer to Scenario 6)
Which two of the following statements are true?
You are performing an ISMS audit at a residential nursing home called ABC that provides healthcare services.
The next step in your audit plan is to verify the information security on ABC's healthcare mobile app
development, support, and lifecycle process. During the audit, you learned the organization outsourced the
mobile app development to a professional software development company with CMMI Level 5, ITSM (ISO/IEC
20000-1), BCMS (ISO 22301) and ISMS (ISO/IEC 27001) certified. The IT Manager presented the software
security management procedure and summarised the process as follows:
The mobile app development shall adopt "security-by-design" and "security-by-default" principles, as a
minimum. The following security functions for personal data protection shall be available:
Access control.
Personal data encryption, i.e., Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm, key lengths: 256 bits; and
Personal data pseudonymization.
Vulnerability checked and no security backdoor
You sample the latest Mobile App Test report - details as follows:
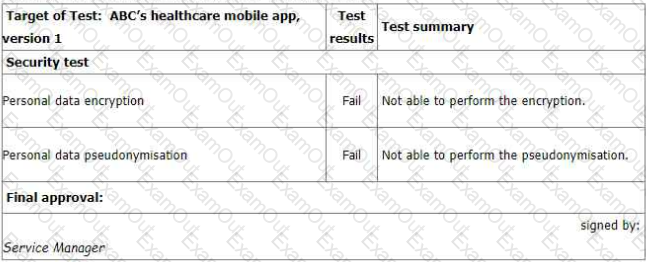
You ask the IT Manager why the organisation still uses the mobile app while personal data
encryption and pseudonymization tests failed. Also, whether the Service Manager is authorized to
approve the test.
The IT Manager explains the test results should be approved by him according to the software
security management procedure. The reason why the encryption and pseudonymization functions
failed is that these functions heavily slowed down the system and service performance. An extra
150% of resources are needed to cover this. The Service Manager agreed that access control is
good enough and acceptable. That's why the Service Manager signed the approval.
You sample one of the medical staff's mobile and found that ABC's healthcare mobile app, version
1.01 is installed. You found that version 1.01 has no test record.
The IT Manager explains that because of frequent ransomware attacks, the outsourced mobile app
development company gave a free minor update on the tested software, performed an emergency
release of the updated software, and gave a verbal guarantee that there will be no impact on any
security functions. Based on his 20 years of information security experience, there is no need to re-
test.
You are preparing the audit findings Select two options that are correct.
You are performing an ISMS audit at a residential nursing home that provides healthcare services. The next step in your audit plan is to verify the information security incident management process. The IT Security Manager presents the information
security incident management procedure (Document reference ID: ISMS_L2_16, version 4) and explains that the process is
based on ISO/IEC 27035-1:2016.
You review the document and notice a statement "any information security weakness, event, and incident should be reported
to the Point of Contact (PoC) within 1 hour after identification". When interviewing staff, you found that there were differences
in the understanding of the meaning of "weakness, event, and incident".
The IT Security Manager explained that an online "information security handling" training seminar was conducted 6 months
ago. All of the interviewed persons participated in and passed the reporting exercise and course assessment.
You are preparing the audit findings. Select two options that are correct.
Which one of the following options describes the main purpose of a Stage 1 audit?
Scenario 5: Cobt. an insurance company in London, offers various commercial, industrial, and life insurance solutions. In recent years, the number of Cobt's clients has increased enormously. Having a huge amount of data to process, the company decided that certifying against ISO/IEC 27001 would bring many benefits to securing information and show its commitment to continual improvement. While the company was well-versed in conducting regular risk assessments, implementing an ISMS brought major changes to its daily operations. During the risk assessment process, a risk was identified where significant defects occurred without being detected or prevented by the organizations internal control mechanisms.
The company followed a methodology to implement the ISMS and had an operational ISMS in place after only a few months After successfully implementing the ISMS, Cobt applied for ISO/IEC 27001 certification Sarah, an experienced auditor, was assigned to the audit Upon thoroughly analyzing the audit offer, Sarah accepted her responsibilities as an audit team leader and immediately started to obtain general information about Cobt She established the audit criteria and objective, planned the audit, and assigned the audit team members' responsibilities.
Sarah acknowledged that although Cobt has expanded significantly by offering diverse commercial and insurance solutions, it still relies on some manual processes Therefore, her initial focus was to gather information on how the company manages its information security risks Sarah contacted Cobt's representatives to request access to information related to risk management for the off-site review, as initially agreed upon for part of the audit However, Cobt later refused, claiming that such information is too sensitive to be accessed outside of the company This refusal raised concerns about the audit's feasibility, particularly regarding the availability and cooperation of the auditee and access to evidence Moreover, Cobt raised concerns about the audit schedule, stating that it does not properly reflect the recent changes the company made It pointed out that the actions to be performed during the audit apply only to the initial scope and do not encompass the latest changes made in the audit scope
Sarah also evaluated the materiality of the situation, considering the significance of the information denied for the audit objectives. In this case, the refusal by Cobt raised questions about the completeness of the audit and its ability to provide reasonable assurance. Following these situations, Sarah decided to withdraw from the audit before a certification agreement was signed and communicated her decision to Cobt and the certification body. This decision was made to ensure adherence to audit principles and maintain transparency, highlighting her commitment to consistently upholding these principles.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Question:
Based on the role of Sarah described in Scenario 5, which of the following should NOT be part of her responsibilities?
Scenario 8: EsBank provides banking and financial solutions to the Estonian banking sector since September 2010. The company has a network of 30 branches with over 100 ATMs across the country.
Operating in a highly regulated industry, EsBank must comply with many laws and regulations regarding the security and privacy of data. They need to manage information security across their operations by implementing technical and nontechnical controls. EsBank decided to implement an ISMS based on ISO/IEC 27001 because it provided better security, more risk control, and compliance with key requirements of laws and regulations.
Nine months after the successful implementation of the ISMS, EsBank decided to pursue certification of their ISMS by an independent certification body against ISO/IEC 27001 .The certification audit included all of EsBank’s systems, processes, and technologies.
The stage 1 and stage 2 audits were conducted jointly and several nonconformities were detected. The first nonconformity was related to EsBank’s labeling of information. The company had an information classification scheme but there was no information labeling procedure. As a result, documents requiring the same level of protection would be labeled differently (sometimes as confidential, other times sensitive).
Considering that all the documents were also stored electronically, the nonconformity also impacted media handling. The audit team used sampling and concluded that 50 of 200 removable media stored sensitive information mistakenly classified as confidential. According to the information classification scheme, confidential information is allowed to be stored in removable media, whereas storing sensitive information is strictly prohibited. This marked the other nonconformity.
They drafted the nonconformity report and discussed the audit conclusions with EsBank’s representatives, who agreed to submit an action plan for the detected nonconformities within two months.
EsBank accepted the audit team leader's proposed solution. They resolved the nonconformities by drafting a procedure for information labeling based on the classification scheme for both physical and electronic formats. The removable media procedure was also updated based on this procedure.
Two weeks after the audit completion, EsBank submitted a general action plan. There, they addressed the detected nonconformities and the corrective actions taken, but did not include any details on systems, controls, or operations impacted. The audit team evaluated the action plan and concluded that it would resolve the nonconformities. Yet, EsBank received an unfavorable recommendation for certification.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Which action illustrated in scenario 8 is unacceptable in an external audit?
You are conducting a third-party surveillance audit when another member of the audit team approaches you seeking clarification. They have been asked to assess the organisation's application of control 5.7 - Threat Intelligence. They are aware that this is one of the new controls introduced in the 2022 edition of ISO/IEC 27001, and they want to make sure they audit the control correctly.
They have prepared a checklist to assist them with their audit and want you to confirm that their planned activities are aligned with the control's requirements.
Which three of the following options represent valid audit trails?

