Examine the structure of the ora1.depts table:

Now, examine these statements issued by user ora1 which execute successfully:
Create or replace view dep_vu as select * from depts;
Alter table depts add dep_email varchar2(20);
Finally, examine this block of code executed by user ora1:

Which is true?
Which three are true about the procedure overloading feature? (Choose three.)
Examine the EMPLOYEES table structure:

Now, examine this code:
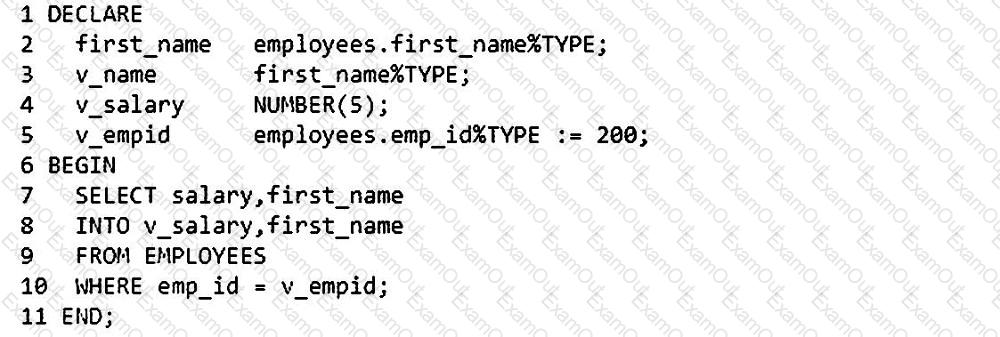
Which statement is true about the result of executing this block?
Examine these statements and output:

The procedure is created successfully.

User ora2 has password ora2 in pdb1.
Which script will execute successfully?
Which three statements can process a dynamic multi-row query? (Choose three.)
Which three statements are true about passing parameters to subprograms? (Choose three.)
Which two blocks of code display a numerical zero? (Choose two.)
Which three are true about DDL triggers? (Choose three.)
Examine this row of data from the EMPLOYEES table:

Now, examine this block of code which executes successfully:

What is the value of v_commission?
In one of your databases, table HR.EMPLOYEES includes the columns FIRST_NAME and EMPLOYEE_ID.
A row exists with EMPLOYEE_ID 201.
Examine these packages created by user HR:
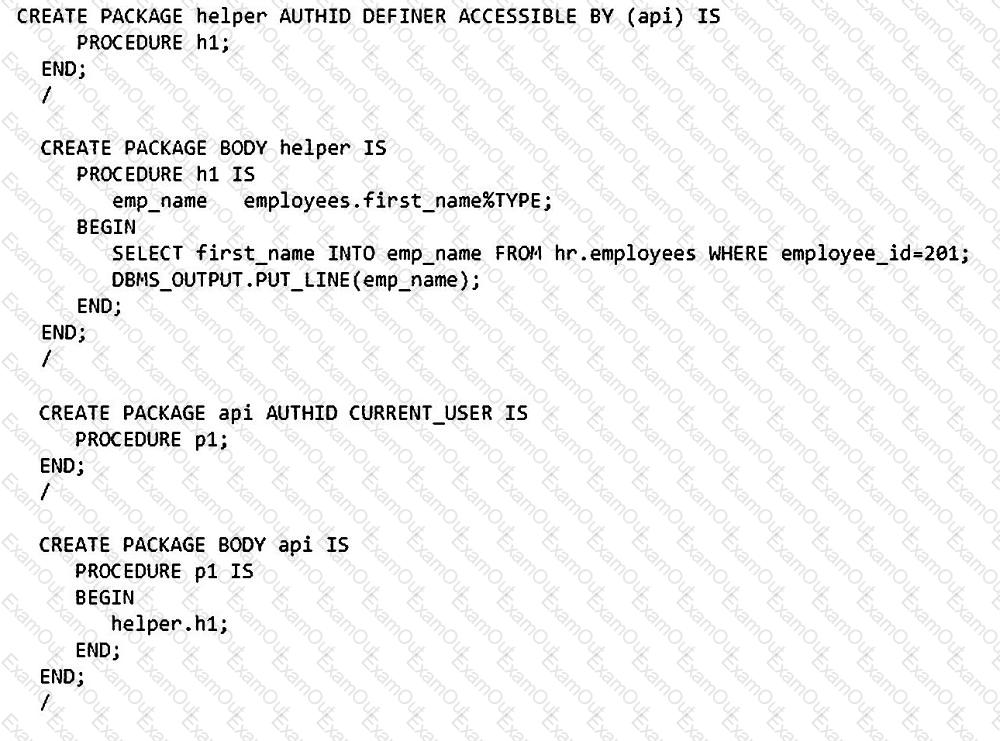
EXECUTE privilege is granted to user SH, on the HR.API and HR.HELPER packages.
Which two will execute successfully? (Choose two.)









