Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Evaluation of a tracing during oxytocin induction requires analysis of fetal status (baseline, variability, accelerations, decelerations) and uterine activity, with attention to tachysystole and fetal intolerance. NCC, AWHONN, Miller, Menihan, Simpson, and the NICHD guidelines all emphasize that oxytocin must be adjusted based on fetal response and contraction frequency.
Baseline:
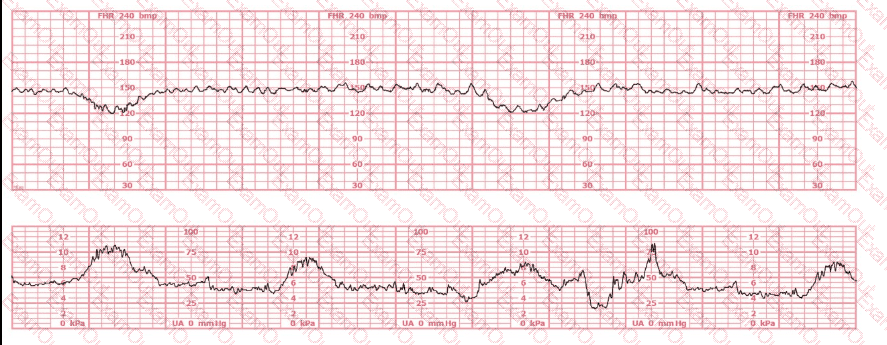
The fetal heart rate baseline is approximately 150 bpm, which is within the normal range of 110–160 bpm.
Variability:
The tracing shows minimal variability (approximately 1–4 bpm amplitude). Minimal variability for a sustained period is categorized as a Category II pattern under NCC/NICHD classification.
Accelerations:
No accelerations are present during the 20-minute representative segment.
Decelerations:
There are no recurrent variable, no recurrent late, and no prolonged decelerations.
Uterine Activity:
The tracing shows very frequent contractions—approximately every 1½ to 2 minutes, which meets the NCC definition of tachysystole when averaged over 10 minutes (more than 5 contractions in 10 minutes).
According to NCC and AWHONN standards, when tachysystole is present with minimal variability, oxytocin must be reduced or discontinued even in the absence of late decelerations.
Clinical decision-making (per NCC principles):
NCC emphasizes that management of Category II patterns during induction starts with intrauterine resuscitative measures, including decreasing or stopping oxytocin when uterine activity is excessive or fetal response is suboptimal. Minimal variability with tachysystole requires correction of uterine stimulation before escalating to invasive monitoring or considering operative birth.
Option B (place a spiral electrode) is not indicated because the pattern is clearly visible and the priority is correcting uterine overstimulation, not refining the tracing.
Option C (operative birth) is not indicated; there is no Category III pattern or recurrent decelerations.
Option A (discontinue oxytocin) is the correct first-line action according to NCC-aligned guidelines when tachysystole and minimal variability occur.
[References:, NCC C-EFM Candidate Guide (2025); NCC Content Outline; NICHD Three-Tier FHR Interpretation System; AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices; Miller’s Fetal Monitoring Pocket Guide; Menihan Electronic Fetal Monitoring; Simpson & Creehan Perinatal Nursing; Creasy & Resnik Maternal–Fetal Medicine., ]