A woman in active labor at 8 cm experiences spontaneous rupture of membranes and acute bright red vaginal bleeding. The uterus is soft and nontender to palpation. The fetal monitor tracing has been normal and now shows tachycardia followed by bradycardia with minimal variability. The maternal blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, and the pulse is 86 beats per minute. The most likely cause of these findings is:
Sustained fetal supraventricular tachycardia that goes untreated is most likely to result in:
Interventions undertaken to address fetal tachycardia are targeted at maximizing
A patient presents at 38-weeks gestation with complaints of decreased fetal movement and ruptured membranes. The fetal heart rate is not able to be determined with an external ultrasound monitor. A spiral electrode is placed, and the tracing shows a rate of 90 bpm. What is the next most appropriate action?
A woman at 34-weeks gestation is in active labor after spontaneous rupture of membranes. Accelerations should be documented as
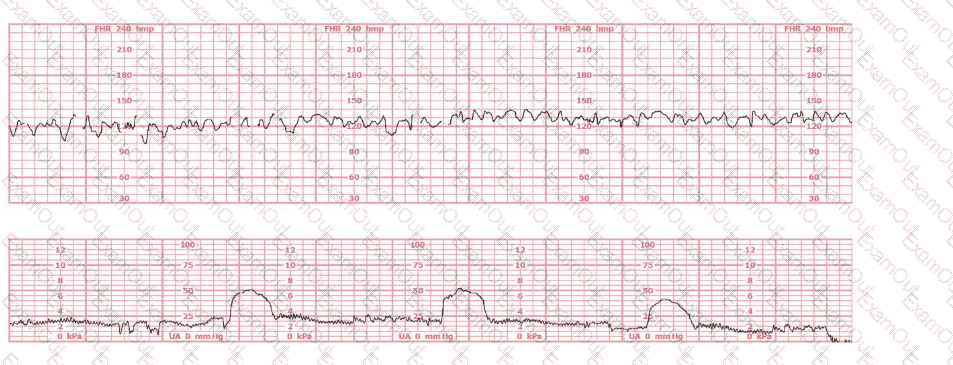
Based on the fetal heart rate tracing shown, the expected fetal pH would be:
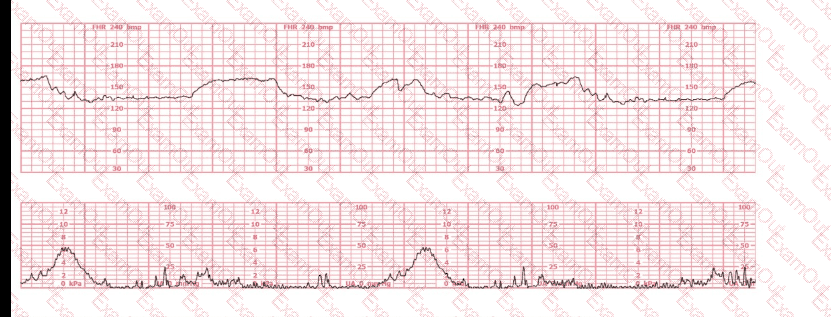
To differentiate a fetal dysrhythmia from artifact, it is important to recognize that artifact appears as deflections that are:
A sentinel or reportable event as defined by the Joint Commission or other regulatory bodies/agencies is one that
An internal electronic fetal monitor tracing continues to record artifact despite equipment troubleshooting and replacement of the spiral electrode. The next action is to:
Maternal-fetal oxygen transfer takes place in the:

