Which of the following would NOT be a common metric used for monitoring test preparation and execution?
Which of the following optionsBESTexplain the pesticide paradox principle of testing?
Which option BEST describes how the level of risk is determined?
Which of the following does NOT represent one of the three triggers for maintenance testing an operational system?
Which of the following is NOT a valid use of decision coverage?
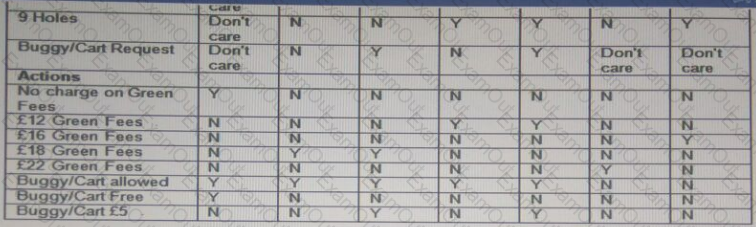
The decision table above reflects a golf club's pricing structure for green fees and buggy/cart hire.
What is the expected result (actions) for each of the following two test cases (TC1 and TC2)?
* TC 1 - Paul is not a full member, is a Loyalty Card holder and requests to play 18 holes with a buggy/cart
* TC 2 - Cheryl is not at full member, doesn't have a Loyalty Card and requests to play 9 holes with a buggy/cart
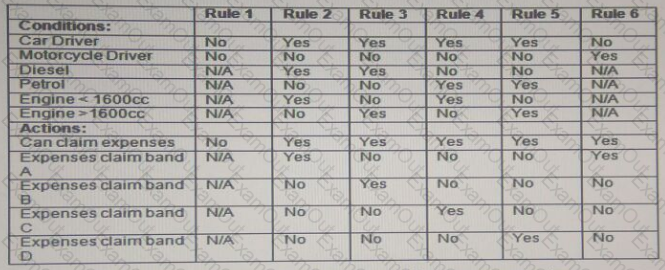
The decision table above shows a company's fuel expenses structure.
Which of the following Test Cases based on the decision table are Valid?
Test Case 1:
An employee who is not a car or motorcycle driver attempts to claim fuel expenses. Expected result: Expense claim not allowed.
Test Case 2:
An employee who drives a 1700cc diesel car attempts to claim fuel expenses. Expected result: Expense claim accepted at band C.
Test Case 3:
An employee who rides a motorcycle attempts to claim fuel expenses. Expected result: Expense claim accepted at band A.
The five parts of the fundamental test process have a broad chronological order. Which of the options gives three different parts in the correct order?
Code Coverage is used as a measure of what?
Which of the following statements about risks is most accurate?

