Refer to the exhibit.
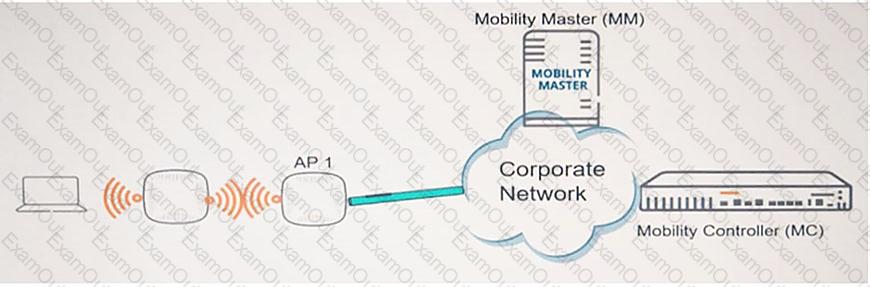
Which role must AP 1 play?
How does WPA2 protect wireless user traffic in the air?
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
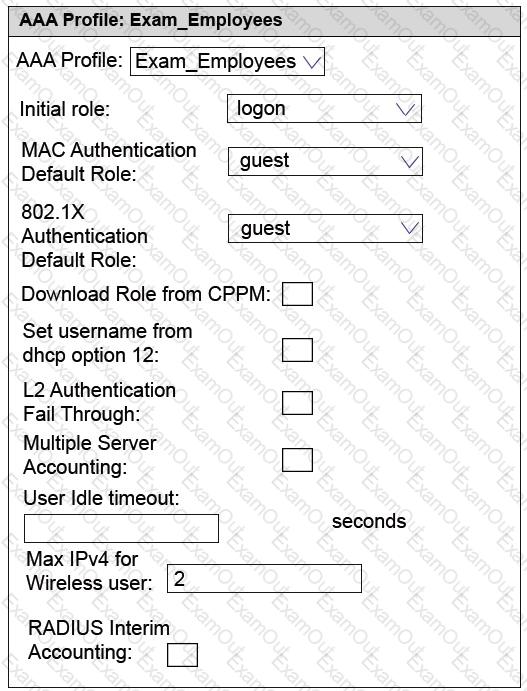
Exhibit 2

An Aruba solution supports a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security. Exhibit 1 shows the AAA policy for the WLAN. Users are supposed to be assigned to different roles after authentication. Network administrators test a connection with the employee user account. Exhibit 2 shows the status for the client after this test.
What is a possible reason for the issue shown in Exhibit 2?
What is one difference between captive portal authentication and 802.1X authentication?
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution. Under which circumstance will an AP radio change channel without the use of the Mobility Master (MM)?
A network administrator reduces an AP radio transmit power from 18 dBm to 15 dBm. This is a loss of 3 dBms.
What is the current power as a percentage of the original power?
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution with a WLAN that assigns users to VLANs 10–19. The company wants the Aruba solution to act at Layer 3 to route wireless user traffic.
What must network administrators configure to permit the solution to forward traffic correctly?
Refer to the exhibit.
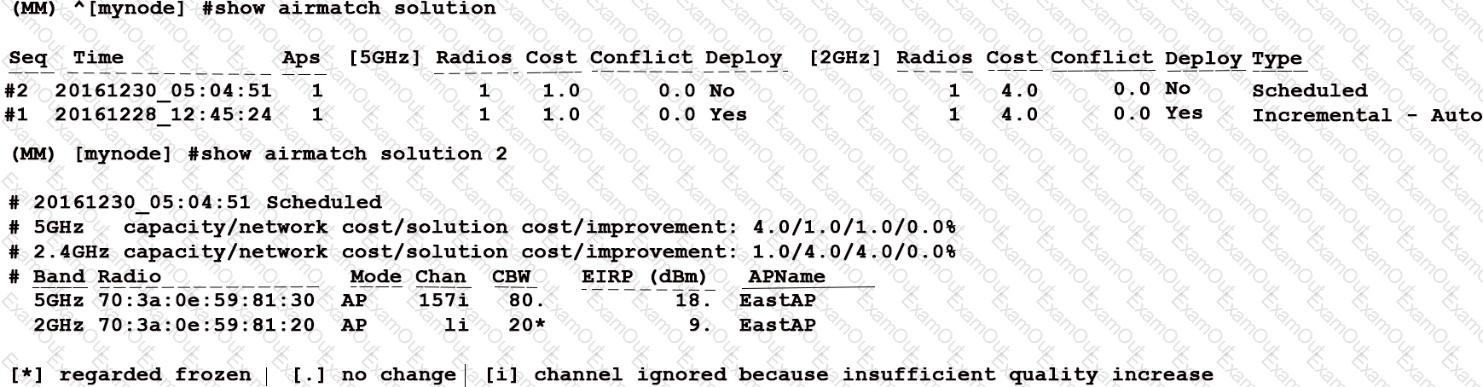
An Aruba solution uses AirMatch with the default AirMatch profile settings. A network administrator sees that a scheduled optimization was completed, but a plan was not deployed.
Based on the exhibit, why did this occur?
What is one difference between how a network administrator can monitor clients in the Mobility (MM) interface and in the AirWave Management Platform?

