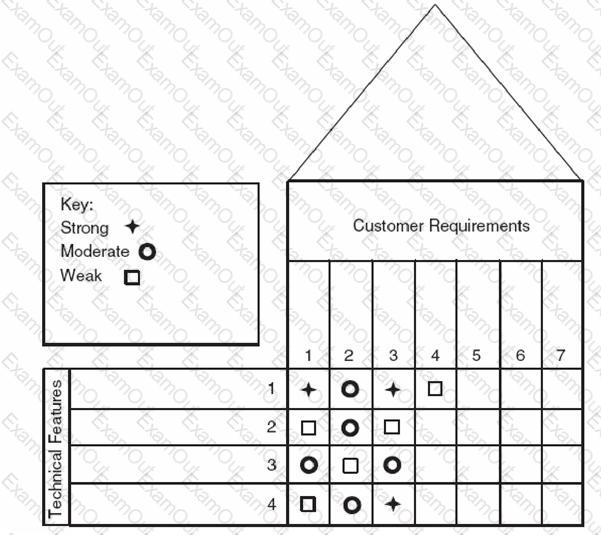
This is an example of part of a:
SWOT is an acronym for:
Perform a risk analysis to determine the expected profit or (loss) from a project which has four possible disjoint outcomes:
Outcome A shows a profit of $340,000 and has a probability of 0.25.
Outcome B shows a profit of $120,000 and has a probability of 0.40.
Outcome C shows a loss of $40,000 and has a probability of 0.10.
Outcome D shows a profit of $100,000 and has a probability of 0.25.
The median is a better choice than the mean for a measure of central tendency if the data:
The support for an important quality initiative was lacking in congress until Reagan’s Secretary of Commerce was killed in a horseback riding accident in 1987. That initiative was:
Samples of size n=36 are randomly selected from a population with mean μ = 125 and variance 12. Find the variance of the distribution of sample means.
(Refer to the previous problem) To estimate the within treatment variance the experimenters would calculate the variances of:
Find the value of (1) in the ANOVA table. Assume:

Find the value of (6) in the ANOVA table. Assume:

The principle disadvantage of fractional factorial experiments is that:

