(You want to configure two static routes: one that references an SD-WAN zone and a second one that references an SD-WAN member that belongs to that zone.
Which statement about this scenario is true? Choose one answer.)
(Refer to the exhibit.
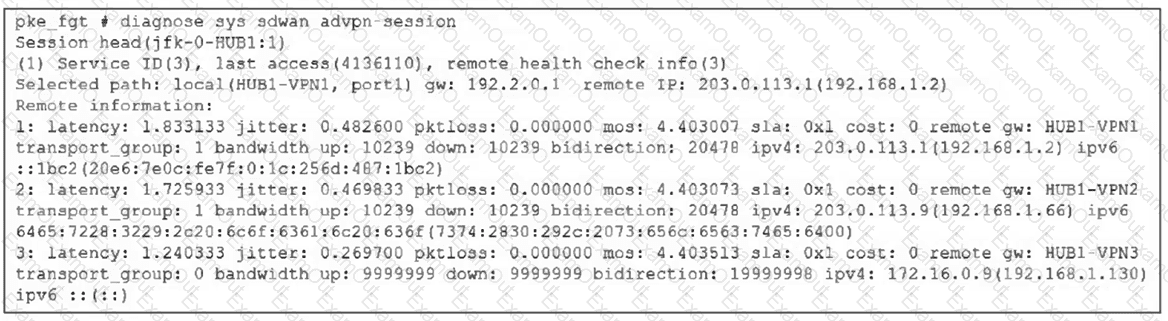
Based on the output shown in the exhibit, what can you conclude about the device role and how it handles health checks? Choose one answer.)
The SD-WAN overlay template helps to prepare SD-WAN deployments. To complete the tasks performed by the SD-WAN overlay template, the administrator must perform some post-run tasks. What are two mandatory post-run tasks that must be performed? (Choose two.)
(In the context of SD-WAN, the terms underlay and overlay are commonly used to categorize links.
Which two statements about underlay and overlay links are correct? Choose two answers.)
(Which two features must you configure before FortiGate can steer traffic according to SD-WAN rules? Choose two answers.)
Refer to the exhibits.
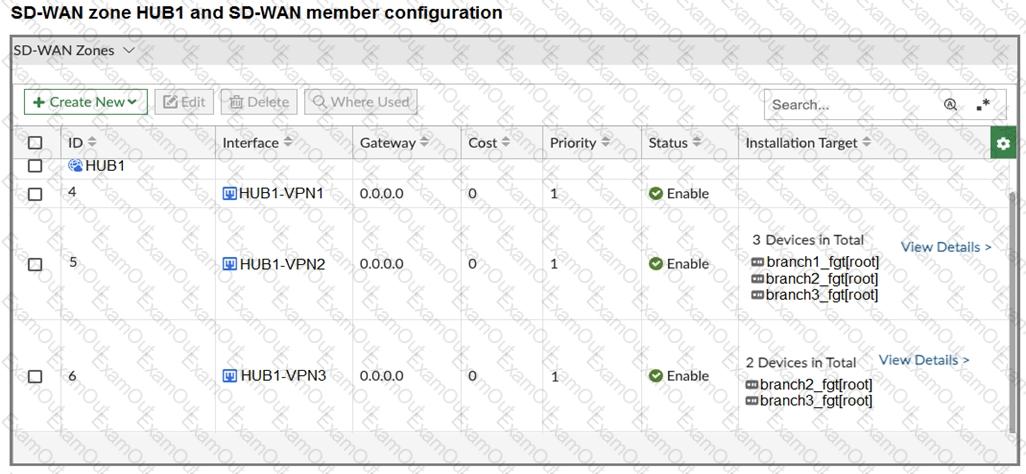
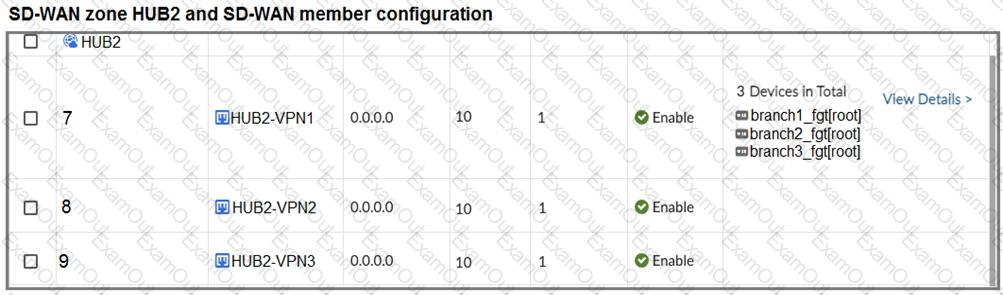
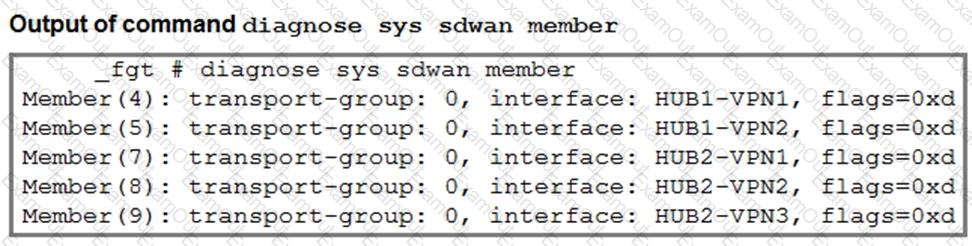
The first exhibit shows the SD-WAN zone HUB1 and SD-WAN member configuration from an SD-WAN template, and the second exhibit shows the output of command diagnose sys sdwan member collected on a FortiGate device.
Which statement best describes what the diagnose output shows?
Refer to the exhibits.
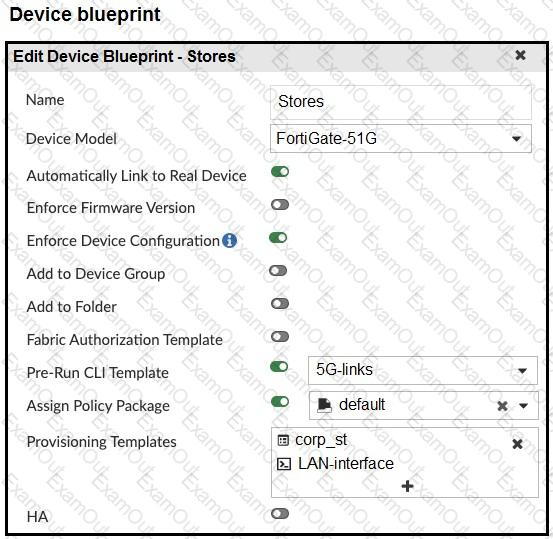
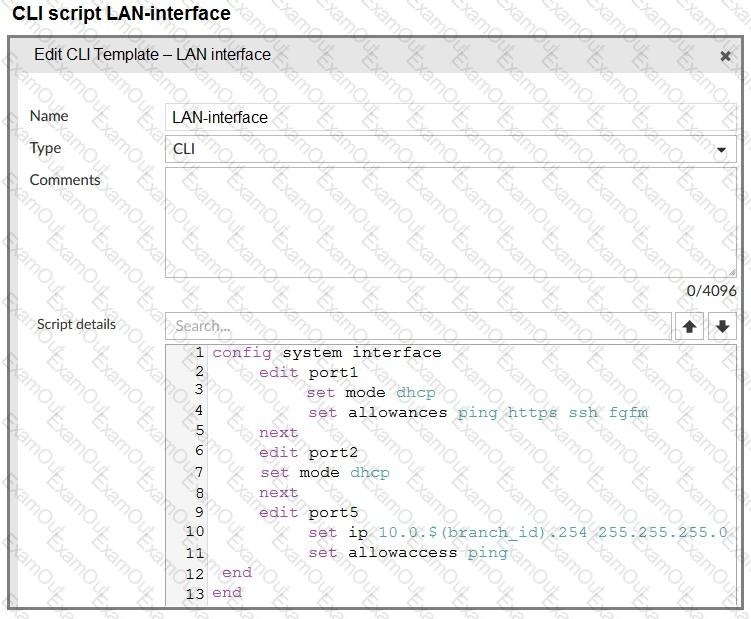
The administrator configured a device blueprint and CLI scripts as shown in the exhibits, to prepare for onboarding FortiGate devices in the company’s stores. Later, a technician prepares a FortiGate 51G with a basic configuration and connects it to the network. The basic configuration contains the port1 configuration and the minimal configuration required to allow the device to connect to FortiManager.
After the device first connects to FortiManager, FortiManager updates the device configuration.
Based on the exhibits, which actions does FortiManager perform?
(Refer to the exhibits.
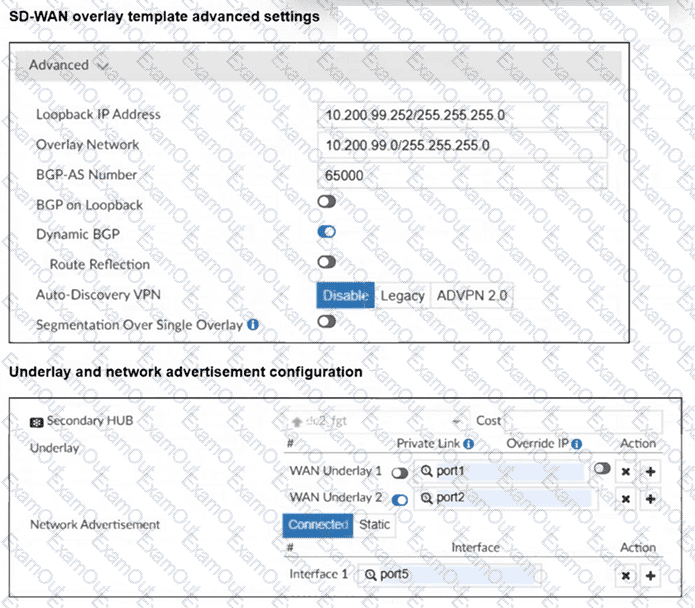
The SD-WAN overlay template advanced settings and the underlay and network advertisement settings are shown. These are the configurations for the secondary hub of a dual-hub SD-WAN topology created with the FortiManager SD-WAN overlay orchestrator.
Which two conclusions can you draw from the information shown in the exhibits? Choose two answers.)
Refer to the exhibit.
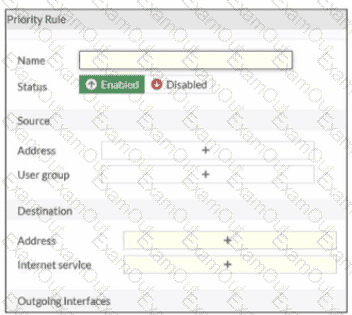
An administrator configures SD-WAN rules for a DIA setup using the FortiGate GUI. The page to configure the source and destination part of the rule looks as shown in the exhibit. The GUI page shows no option to configure an application as the destination of the SD-WAN rule Why?
An administrator is configuring SD-WAN to load balance their network traffic. Which two things should they consider when setting up SD-WAN? (Choose two.)

