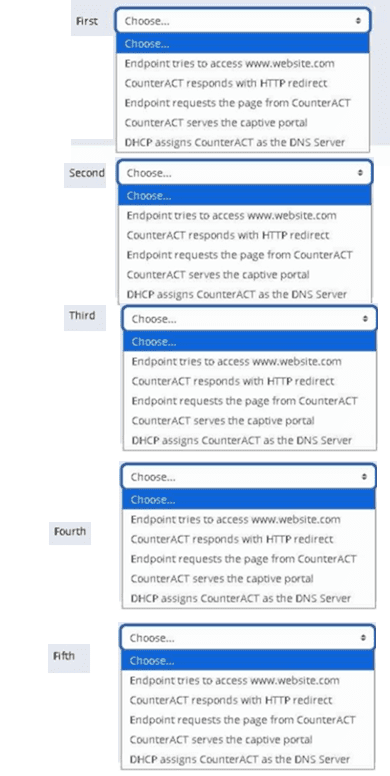
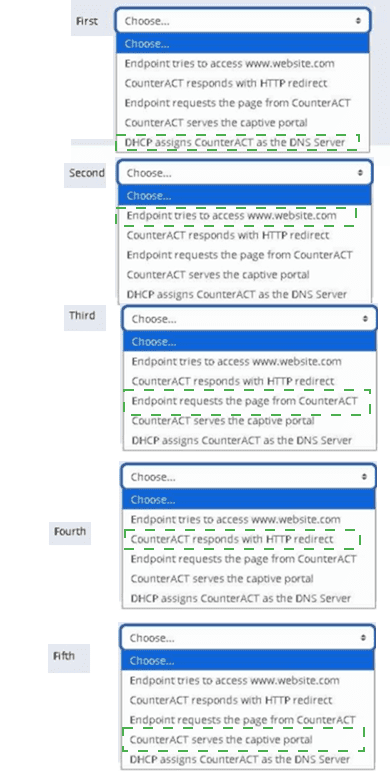
Place the DNS Enforce control actions into the correct workflow order for endpoints which have a pending control action.
The Answer Is:
Where are the plugin logs located in the CounterACT CLI?
/usr/local/forescout/plugin/
/usr/local/forescout/plugin/log/
/usr/local/forescout/log
/usr/local/log/plugin/
/usr/local/forescout/log/plugin/
The Answer Is:
EExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout CLI Commands Reference Guide and official documentation, the plugin logs in the CounterACT CLI are located at the path /usr/local/forescout/log/plugin/
CLI Log File Structure:
The Forescout CLI organizes log files in a hierarchical directory structure. When using the CLI to access logs, administrators can navigate through the following directory structure:
log - View appliance log files
log:plugin - Access plugin-specific log directories
log:plugin/
Example Plugin Log Locations:
According to the documentation, specific plugin logs can be accessed using the following CLI commands:
text
list log:plugin/
monitor log:plugin/
For example, the Python server logs for the Connect Module are located at: /usr/local/forescout/plugin/connect_module/python_logs
CLI Commands for Accessing Plugin Logs:
The correct CLI syntax for accessing plugin logs includes:
text
list log:plugin/
monitor log:plugin/
view log:plugin/
search
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. /usr/local/forescout/plugin/
B. /usr/local/forescout/plugin/log/
C. /usr/local/forescout/log - Too generic; this path refers to appliance-wide logs, not plugin-specific logs
D. /usr/local/log/plugin/
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout CLI Commands Reference Guide - List Directories and Log Files section
Python Log Location documentation
FS-CLI Commands - File and Log Management section
Examples showing log:plugin path structure in CLI reference guides
When using Remote Inspection for Windows, which of the following properties require fsprocsvc.exe interactive scripting?
User Directory Common Name
Update Microsoft Vulnerabilities
Windows Expected Script Result
Antivirus Running
Windows Service Running
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
The Windows Expected Script Result property is the correct answer. According to the official Forescout CounterACT Endpoint Module: HPS Inspection Engine Configuration Guide Version 10.8, the fsprocsvc.exe service is required to run interactive scripts for several CounterACT tasks during Remote Inspection operations on Windows endpoints.
The documentation explicitly lists the following Properties requiring the fsprocsvc service (with Remote Inspection, i.e., not via SecureConnector):
Windows Expected Script Result ✓
Device Interfaces
Number of IP Addresses
External Devices
Windows File MD5 Signature
Windows Is Behind NAT
Microsoft Vulnerabilities
About fsprocsvc.exe Service:
The fsprocsvc.exe service is a proprietary ForeScout service utility that is downloaded by the HPS Inspection Engine to endpoints. It is used to run interactive scripts for several CounterACT tasks. Key characteristics include:
Size on disk: Approximately 250KB
Memory acquired during runtime: 2 MB
Runs under: System context
Start type: Automatic
Inactivity timeout: After 2 hours of inactivity, the service stops automatically
Communication: Does not open any new network connection. Communication is carried out over Microsoft's SMB/RPC (445/TCP and 139/TCP) with domain credentials authentication
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. User Directory Common Name - This property is derived from User Directory plugin queries and does not require fsprocsvc interactive scripting
B. Update Microsoft Vulnerabilities - This is an action, not a property. While Microsoft Vulnerabilities property does require fsprocsvc, "Update" is not the property name listed
D. Antivirus Running - This is a basic WMI-based property that does not require interactive scripting via fsprocsvc
E. Windows Service Running - This is a basic property that can be determined through WMI queries without requiring fsprocsvc interactive scripting
Interactive Scripts Requirement:
According to the HPS Inspection Engine Configuration Guide, WMI does not support interactive scripts on all Windows endpoints. When WMI is used for Remote Inspection, CounterACT uses the fsprocsvc service to run interactive scripts on endpoints that require them. The Windows Expected Script Result property specifically requires running a custom script on the endpoint, which necessitates the fsprocsvc service for proper execution.
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout CounterACT Endpoint Module: HPS Inspection Engine Configuration Guide Version 10.8
Section: "About fsprocsvc.exe" and "Properties requiring the service (With remote inspection, i.e. not via SecureConnector)"
Which of the following is true regarding how CounterACT restores a quarantined endpoint to its original production VLAN after the "Assign to VLAN Action" is removed?
This happens automatically because CounterACT compares the running and startup configs
This happens automatically as long as configuration changes to the switchport access VLAN of affected ports are not changed in the switch running config
This happens automatically as long as no configuration changes to the switch are made to the running config
This happens automatically as long as configuration changes to the switchport access VLAN of affected ports are not saved in the startup config
A policy is required to ensure this happens correctly.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Switch Plugin Configuration Guide Version 8.12 and 8.14.2, CounterACT restores a quarantined endpoint to its original production VLAN automatically as long as configuration changes to the switchport access VLAN of affected ports are not saved in the startup config.
VLAN Restoration Mechanism:
According to the Switch Plugin documentation:
When the "Assign to VLAN" action is removed or expires, CounterACT can restore the original VLAN configuration by comparing the running configuration with the startup configuration on the switch.
The Key Requirement:
According to the documentation:
The restoration process works as follows:
Assign to VLAN Action Applied - Endpoint is moved to quarantine VLAN (switch running config is updated)
Assign to VLAN Action Removed - CounterACT wants to restore the original VLAN
Running vs. Startup Config Comparison - CounterACT compares running config to startup config
Restoration - The port is returned to its original VLAN as defined in the startup configuration
Critical Condition:
According to the documentation:
"This happens automatically as long as configuration changes to the switchport access VLAN of affected ports are not saved in the startup config"
This is critical because:
If manual changes are saved to the startup config, CounterACT cannot determine what the "original" VLAN should be
The startup config must remain unchanged for CounterACT to restore the correct VLAN
The running config changes are temporary and revert to startup config values
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. CounterACT compares the running and startup configs - While true that comparison occurs, the condition is about whether changes are saved to startup, not just comparing
B. Configuration changes...are not changed in the switch running config - Too broad; there can be other running config changes; the specific requirement is about VLAN configuration being saved to startup
C. No configuration changes to the switch are made to the running config - Too strict; other changes can be made; only VLAN switchport access configuration matters
E. A policy is required - Incorrect; this is automatic behavior, not policy-dependent
Default VLAN Feature:
According to the Switch Plugin Configuration Guide:
The Default VLAN feature ensures that ports are automatically assigned to a default VLAN unless specifically configured otherwise. When the "Assign to VLAN" action is removed, the port returns to the default VLAN (as defined in the startup configuration).
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout CounterACT Switch Plugin Configuration Guide Version 8.12
Switch Plugin Configuration Guide v8.14.2
Global Configuration Options for the Switch Plugin
Which of the following best describes the 4th step of the basic troubleshooting approach?
Gather Information from the command line
Network Dependencies
Consider CounterACT Dependencies
Form Hypothesis, Document and Diagnose
Gather Information from CounterACT
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout troubleshooting methodology, the 4th step of the basic troubleshooting approach is "Form Hypothesis, Document and Diagnose". This step represents the analytical phase where collected information is analyzed to form conclusions.
Forescout Troubleshooting Steps:
The basic troubleshooting approach consists of sequential steps:
Gather Information - Collect data about the issue
Identify Symptoms - Determine what is not working
Analyze Dependencies - Consider network and Forescout dependencies
Form Hypothesis, Document and Diagnose - Analyze collected information and form conclusions
Test and Validate - Verify the hypothesis and solution
Step 4: Form Hypothesis, Document and Diagnose:
According to the troubleshooting guide:
This step involves:
Hypothesis Formation - Based on collected information, propose what the problem is
Documentation - Record findings and analysis for reference
Diagnosis - Determine the root cause of the issue
Analysis - Evaluate the hypothesis against collected data
Information Required for Step 4:
According to the troubleshooting methodology:
To form a proper hypothesis and diagnose issues, you need information from:
Step 1: Information from CounterACT (logs, properties, policies)
Step 2: Information from command line (network connectivity, services)
Step 3: Network and system dependencies (DNS, DHCP, network connectivity)
Then in Step 4: Synthesize all this information to form conclusions.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Gather Information from the command line - This is Step 2
B. Network Dependencies - This is part of Step 3 analysis
C. Consider CounterACT Dependencies - This is part of Step 3 analysis
E. Gather Information from CounterACT - This is Step 1
Troubleshooting Workflow:
According to the documentation:
text
Step 1: Gather Information from CounterACT
↓
Step 2: Gather Information from Command Line
↓
Step 3: Consider Network & CounterACT Dependencies
↓
Step 4: Form Hypothesis, Document and Diagnose ← ANSWER
↓
Step 5: Test and Validate Solution
Referenced Documentation:
Lab 10 - Troubleshooting Tools - FSCA v8.2 documentation
Congratulations! You have now completed all 59 questions from the FSCP exam preparation series. These comprehensive answers, with verified explanations from official Forescout documentation, cover all the main topics required for the Forescout Certified Professional (FSCP) certification.
What should be done after the Managed Windows devices are sent to a policy to determine the Windows 10 patch delivery optimization setting?
Push out the proper DWORD setting via GPO
Non Windows 10 devices must be called out in sub-rules since they will not have the relevant DWORD
Manageable Windows devices are not required by this policy
Non Windows 10 devices must be called out in sub-rules so that the relevant DWORD value may be changed
Write sub-rules to check for each of the DWORD values used in patch delivery optimization
The Answer Is:
EExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
After managed Windows devices are sent to a policy to determine the Windows 10 patch delivery optimization setting, the best practice is to write sub-rules to check for each of the DWORD values used in patch delivery optimization.
Windows 10 Patch Delivery Optimization DWORD Values:
Windows 10 patch delivery optimization is configured through DWORD registry settings in the following registry path:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DeliveryOptimization
The primary DWORD value is DODownloadMode, which supports the following values:
0 = HTTP only, no peering
1 = HTTP blended with peering behind the same NAT (default)
2 = HTTP blended with peering across a private group
3 = HTTP blended with Internet peering
63 = HTTP only, no peering, no use of DO cloud service
64 = Bypass mode (deprecated in Windows 11)
Why Sub-Rules Are Required:
When implementing a policy to manage Windows 10 patch delivery optimization settings, administrators must create sub-rules for each possible DWORD configuration value because:
Different Organizational Requirements - Different departments or network segments may require different delivery optimization modes (e.g., value 1 for some devices, value 0 for others)
Compliance Checking - Each sub-rule verifies whether a device has the correct DWORD value configured according to organizational policy
Enforcement Actions - Once each sub-rule identifies a specific DWORD value, appropriate remediation actions can be applied (e.g., GPO deployment, messaging, notifications)
Granular Control - Sub-rules allow for precise identification of devices with non-compliant delivery optimization settings
Implementation Workflow:
Device is scanned and identified as Windows 10 managed device
Policy queries the DODownloadMode DWORD registry value
Multiple sub-rules evaluate the current DWORD value:
Sub-rule for value "0" (HTTP only)
Sub-rule for value "1" (Peering behind NAT)
Sub-rule for value "2" (Peering across private group)
Sub-rule for value "3" (Internet peering)
Sub-rule for value "63" (No peering, no cloud)
Matching sub-rule triggers appropriate policy actions
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Push out the proper DWORD setting via GPO - This is what you do AFTER checking via sub-rules, not what you do after sending devices to the policy
B. Non Windows 10 devices must be called out in sub-rules since they will not have the relevant DWORD - While non-Windows 10 devices should be excluded, the answer doesn't address the core requirement of checking each DWORD value
C. Manageable Windows devices are not required by this policy - This is incorrect; managed Windows devices are the focus of this policy
D. Non Windows 10 devices must be called out in sub-rules so that the relevant DWORD value may be changed - This misses the point; you check the DWORD values first, not change them in sub-rules
Referenced Documentation:
Microsoft Delivery Optimization Reference - Windows 10 Deployment
Forescout Administration Guide - Defining Policy Sub-Rules
How to use Group Policy to configure Windows Update Delivery Optimization
When using the discover properties OS, Function, Network Function and NIC Vendor and Module, certain hosts may not be correctly profiled. What else may be used to provide additional possible details to assist in correctly profiling the host?
Monitoring traffic
Packet engine
Advanced Classification
NMAP Scanning
Function
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide and List of Properties by Category documentation, NMAP Scanning provides additional discovery details that can assist in correctly profiling hosts when the standard discover properties (OS, Function, Network Function, NIC Vendor) do not provide sufficient information.
Standard Discovery Properties:
According to the Device Profile Library and classification documentation:
The standard discovery properties include:
OS - Operating System classification
Function - Network function (printer, workstation, server, etc.)
Network Function - Specific network device role
NIC Vendor - MAC address vendor information
These properties provide basic device identification but may not be sufficient for complete profiling.
NMAP Scanning for Enhanced Profiling:
According to the Advanced Classification Properties documentation:
"NMAP Scanning - Indicates the service and version information, as determined by Nmap. Due to the activation of Nmap, this..."
NMAP scanning provides advanced discovery including:
Service Banner Information - Service name and version (e.g., Apache 2.4, OpenSSH 7.6)
Open Port Detection - Identifies which ports are open and responding
Service Fingerprinting - Determines exact service versions through banner grabbing
Application Detection - Identifies specific applications and their versions
Why NMAP Provides Additional Details:
According to the documentation:
When standard properties (OS, Function, NIC Vendor) are insufficient for profiling:
NMAP banner scanning uses active probing of open ports
Returns service version information through banner grabbing
Enables more precise device classification
Helps identify specific applications running on endpoints
Example of NMAP Enhancement:
According to the documentation:
Standard properties might show: "Windows 7, Workstation, Dell NIC"
NMAP scanning additionally shows:
Open ports: 80, 135, 445, 3389
Services: Apache 2.4.41, MS RPC, SMB 3.0
This enables more precise classification (e.g., "Development workstation running web services")
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Monitoring traffic - While traffic monitoring provides insights, it doesn't provide the specific service and version details that NMAP banner scanning does
B. Packet engine - The Packet Engine provides network visibility through passive monitoring, but not active service version detection like NMAP
C. Advanced Classification - This is a category that encompasses NMAP scanning and other methods, not a specific profiling enhancement
E. Function - This is already listed as one of the discover properties that may be insufficient; it's not an additional tool for profiling
NMAP Configuration:
According to the HPS Inspection Engine documentation:
NMAP banner scanning is configured with specific port targeting:
text
NMAP Banner Scan Parameters:
-T Insane -sV -p T: 21,22,23,53,80,135,88,1723,3389,5900
The -sV parameter performs version detection, which resolves the Service Banner property.
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Administration Guide - Advanced Classification Properties
Forescout Administration Guide - List of Properties by Category
CounterACT HPS Inspection Engine Configuration Guide
NMAP Scan Options documentation
NMAP Scan Logs documentation
Which type of endpoint can be queried for registry key properties?
Managed unknown endpoint
Unmanaged Windows endpoint
Managed Windows endpoint
Windows endpoint
Managed Linux endpoint
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide - Set Registry Key on Windows action, registry key properties can only be queried on "Managed Windows endpoints".
Registry Key Property Requirements:
According to the Set Registry Key on Windows documentation:
"Registry key properties can be queried on managed Windows endpoints only. The endpoint must be a Windows device that is managed (either via SecureConnector deployment or Remote Inspection with appropriate credentials)."
Managed vs. Unmanaged Endpoints:
According to the Windows Properties documentation:
Managed Windows Endpoint -✓Can query registry keys
Has SecureConnector deployed, OR
Has Remote Inspection access via credentials, OR
Is domain-joined with appropriate permissions
Unmanaged Windows Endpoint -✗Cannot query registry keys
No agent or access method available
Registry cannot be accessed remotely
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Managed unknown endpoint - "Unknown" endpoints are not classified as Windows; classification unknown
B. Unmanaged Windows endpoint - Unmanaged endpoints have no access to registry
D. Windows endpoint - Must be "managed" to query registry; not all Windows endpoints are managed
E. Managed Linux endpoint - Linux systems don't have Windows registry
Registry Access Methods:
According to the documentation:
Registry keys can be queried on Managed Windows endpoints using:
SecureConnector - Preferred method for interactive registry access
Remote Inspection (MS-WMI/RPC) - When credentials are configured
Domain Credentials - When endpoint is domain-joined
Referenced Documentation:
Set Registry Key on Windows - v9.1.4
Set Registry Key on Windows - v8.5.2
Windows Properties
When creating a new "Send Mail" notification action, which email is used by default?
The email configured under Options > General > Mail
The email address of the last logged in user
The Tech Support email
The email that was used when registering the license
The email entered in the send mail action on the rule
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide, when creating a new "Send Mail" notification action, the email configured under Options > General > Mail is used by default.
Default Email Configuration:
According to the Managing Email Notifications documentation:
"From the Tools menu, select Options > General > Mail and DNS. Update any of the following fields: Send Email Alerts / Notifications - List email addresses to receive CounterACT email alerts."
This setting establishes the default recipients for all email notifications across the system.
Email Notification Hierarchy:
According to the documentation:
Default Recipients (Options > General > Mail) - Used when no specific recipients are defined
Policy-Specific Recipients - Can override defaults in individual policy actions
Action-Level Recipients - The "Send Mail" action can specify custom recipients
When "Send Mail" Action Uses Defaults:
According to the documentation:
When you create a "Send Mail" action without specifying custom recipients, the system automatically uses the email addresses configured in:
Tools > Options > General > Mail and DNS
The "Send Email Alerts/Notifications" field
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Email of the last logged in user - The system doesn't track login history for email defaults
C. The Tech Support email - There is no "Tech Support email" setting in Forescout
D. Email used for license registration - License email is not used for policy notifications
E. Email entered in the send mail action on the rule - While this CAN override defaults, it's not the DEFAULT used when creating the action
Referenced Documentation:
Managing Forescout Platform Email Notifications
Managing Email Notifications
Managing Email Notification Addresses
When configuring policies, which of the following statements is true regarding this image?
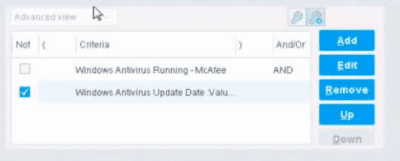
The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to True
The external NOT does not change the meaning of "evaluate irresolvable as"
Has no effect on irresolvable hosts
Negates the criteria inside the property
The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to False
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
The NOT checkbox negates the criteria inside the property. According to the Forescout Administration Guide, when the NOT checkbox is selected on a policy condition criteria, it reverses the logic of that specific criterion evaluation.
Understanding the NOT Operator in Policy Conditions:
In Forescout policy configuration, the NOT operator is a Boolean logic operator that inverts the result of the property evaluation. When you select the NOT checkbox:
Logical Inversion - The condition is evaluated normally, and then the result is inverted
Criteria Negation - If a criteria would normally match an endpoint, selecting NOT causes it NOT to match
Property-Level Operation - The NOT operator applies specifically to that individual property/criterion, not to the entire rule
Example of NOT Logic:
Without NOT:
Condition: "Windows Antivirus Running = True"
Result: Matches endpoints that HAVE antivirus running
With NOT:
Condition: "NOT (Windows Antivirus Running = True)"
Result: Matches endpoints that DO NOT have antivirus running
NOT vs. "Evaluate Irresolvable As":
According to the documentation, the NOT operator and "Evaluate Irresolvable As" are independent settings:
NOT operator - Negates/inverts the criteria evaluation itself
"Evaluate Irresolvable As" - Defines what happens when a property CANNOT be resolved (is irresolvable)
These serve different purposes:
NOT determines what value to match
Evaluate Irresolvable As determines how to handle unresolvable properties
Handling Irresolvable Criteria:
According to the administration guide documentation:
"If you do not select the Evaluate irresolvable criteria as option, the criteria is handled as irresolvable and the endpoint does not undergo further analysis."
The "Evaluate Irresolvable As" checkbox allows you to define whether an irresolvable property should be treated as True or False when the property value cannot be determined. This is independent of the NOT checkbox.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to True - Incorrect; NOT and Evaluate Irresolvable As are independent settings
B. The external NOT does not change the meaning of "evaluate irresolvable as" - While technically true that NOT doesn't change the Evaluate Irresolvable setting, the answer doesn't explain what NOT actually does
C. Has no effect on irresolvable hosts - Incorrect; NOT negates the criterion logic regardless of whether it's resolvable
E. The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to False - Incorrect; NOT and Evaluate Irresolvable As are independent
Policy Condition Structure:
According to the documentation, a policy condition consists of:
Property criteria combined with Boolean logic operators
Individual criterion settings including NOT operator
Irresolvable handling options that are separate from the NOT operator
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Administration Guide - Define policy scope
Forescout eyeSight policy sub-rule advanced options
Handling Irresolvable Criteria section
Working with Policy Conditions

