A data scientist has defined a Pandas UDF function predict to parallelize the inference process for a single-node model:

They have written the following incomplete code block to use predict to score each record of Spark DataFramespark_df:

Which of the following lines of code can be used to complete the code block to successfully complete the task?
The implementation of linear regression in Spark ML first attempts to solve the linear regression problem using matrix decomposition, but this method does not scale well to large datasets with a large number of variables.
Which of the following approaches does Spark ML use to distribute the training of a linear regression model for large data?
What is the name of the method that transforms categorical features into a series of binary indicator feature variables?
Which of the following hyperparameter optimization methods automatically makes informed selections of hyperparameter values based on previous trials for each iterative model evaluation?
A data scientist wants to parallelize the training of trees in a gradient boosted tree to speed up the training process. A colleague suggests that parallelizing a boosted tree algorithm can be difficult.
Which of the following describes why?
A data scientist has written a feature engineering notebook that utilizes the pandas library. As the size of the data processed by the notebook increases, the notebook's runtime is drastically increasing, but it is processing slowly as the size of the data included in the process increases.
Which of the following tools can the data scientist use to spend the least amount of time refactoring their notebook to scale with big data?
A team is developing guidelines on when to use various evaluation metrics for classification problems. The team needs to provide input on when to use the F1 score over accuracy.
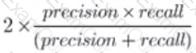
Which of the following suggestions should the team include in their guidelines?
A machine learning engineer would like to develop a linear regression model with Spark ML to predict the price of a hotel room. They are using the Spark DataFrametrain_dfto train the model.
The Spark DataFrametrain_dfhas the following schema:

The machine learning engineer shares the following code block:
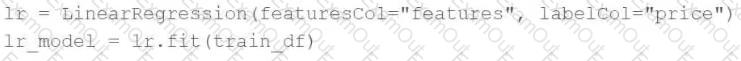
Which of the following changes does the machine learning engineer need to make to complete the task?
Which of the following machine learning algorithms typically uses bagging?
A machine learning engineer is trying to scale a machine learning pipeline by distributing its single-node model tuning process. After broadcasting the entire training data onto each core, each core in the cluster can train one model at a time. Because the tuning process is still running slowly, the engineer wants to increase the level of parallelism from 4 cores to 8 cores to speed up the tuning process. Unfortunately, the total memory in the cluster cannot be increased.
In which of the following scenarios will increasing the level of parallelism from 4 to 8 speed up the tuning process?

