Consider the following relation definition:
STUDENT(
Student_Number: integer NOT NULL
Name: variable length character string length 20 NOT NULL)
Primary Key Student_Number
HOUSING(
Housing_ID: integer NOT NULL
Student_Number: integer NOT NULL
Building: variable length character string length 25 NOT NULL)
Primary Key Housing_ID
Foreign Key Student_Number References
STUDENT(Student_Number)
ON DELETE NO CHECK
ON UPDATE
Which integrity constraint is violated in this relation definition?
Consider the Information Engineering diagram shown in the exhibit. Building_ID, R_ID, Room_Count and Room_Num are integer numbers, whereas Bldg_Name and Res_Name are represented by variable-length strings with a maximum of 20 characters. Location can be up to 50 characters long, and no building has more than 600 rooms. Which SQL statement best implements the BUILDING relation shown in this diagram?

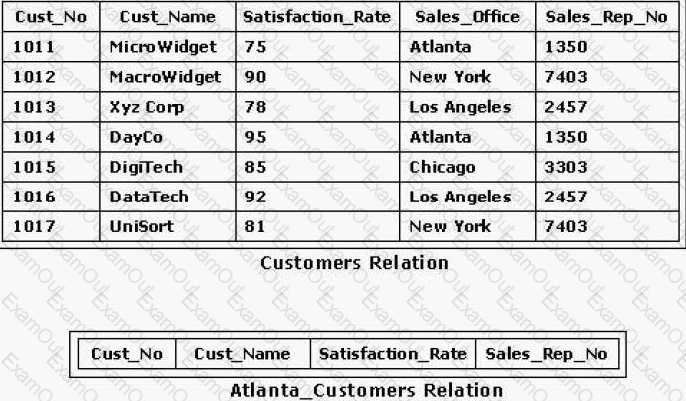
Consider the relations shown in the exhibit. Which of the following SQL statements would enter data from the Customers relation into the Atlanta_Customers relation?
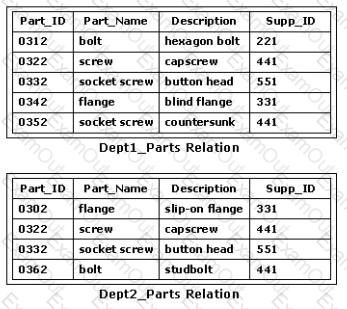
Consider the Dept1_Parts and Dept2_Parts relations shown in the exhibit. Which of the following SQL statements would create an intersection of the two relations with the widest variety of Structured Query Language dialects?
FROM Registration WHERE
Consider the following relational algebraic expression: Which of the following SQL Course_Code = 'A4343';
statements is equivalent to this relational algebraic expression?
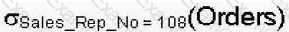
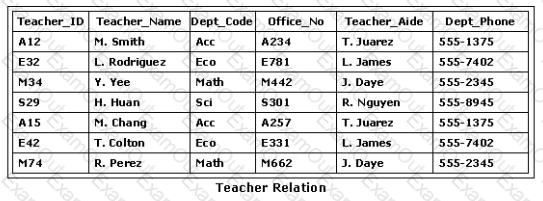
What is the highest normal form of the relation(s) shown in the exhibit?
NULL) Primary Key Class_Num
Consider the Information Engineering diagram shown in the exhibit. Which DBDL definition best describes this diagram?

Which of the following is a characteristic of the three-tier database architecture?
Consider the Information Engineering diagram in the exhibit showing a conceptual data model of the relations BUILDING and RESIDENT. What is the next step in refining the data model?

Consider the Stu_Act and Act_Fee tables shown in the exhibit. Which relational algebraic operation would yield the Activity Relation table in the exhibit?

