Explain, with examples, the three different ways one can categorise procurement spend: direct vs indirect, capital expenditure vs operational expenditure and stock vs non-stock items. (25 points)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
The knowledge to remember:
 A table with text on it
Description automatically generated
A table with text on it
Description automatically generated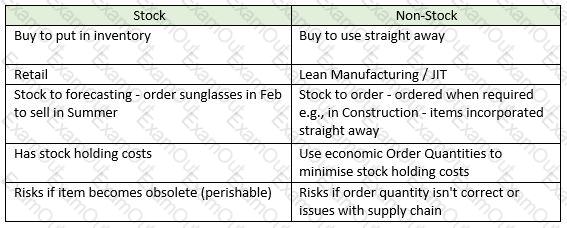
Essay Plan :
Remember to include examples for each of the six categories of spend. This is specifically asked for in the question so it’s important to include as many examples as you can. To do this you could take an example organisation such as a cake manufacturer and explain which of their purchases would fall into each category and why.
Introduction – explain why procurement categorises spend
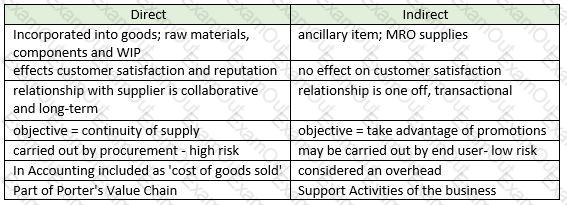
- Direct – these are items that are incorporated into the final goods (the cakes) so would include raw materials such as flour, eggs, sugar etc
- Indirect – these are items that the company needs, but don’t go into the end product. For example, cleaning products and MRO supplies for the machines
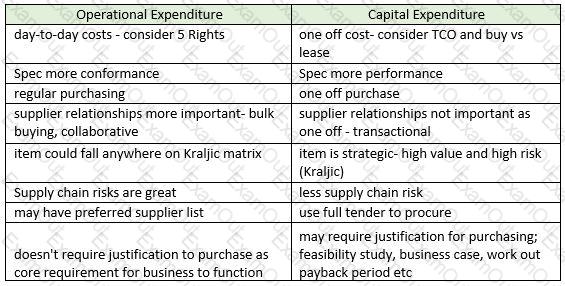
- Capital Expenditure- these are large one-off purchases, such as buying a new piece of equipment such as a giant oven to cook the cakes.
- Operational Expenditure – these are purchases that are required to ensure the business can function day-to-day. They may include PPE for the workers in the factory and cleaning equipment
- Stock items – these are items procured in advance and held in inventory until they are needed. In a cake manufacturing factory this could be PPE for staff such as hairnets and gloves. The organisation will buy these in bulk and keep them in a stock cupboard, using these as and when they are required
- Non- stock items - items that are not stored and used right away. An example would be eggs- these will need to be put directly into the cakes as they would go off if bought in advance.
Conclusion – the categories are not mutually exclusive – an item can be direct and operational, or indirect and stock. Different companies may use different systems to classify items of spend.
Example Introduction and Conclusion
Introduction
Procurement categorizes spend to efficiently manage resources and make strategic decisions. Three primary ways of categorizing procurement spend include distinguishing between direct and indirect spend, classifying expenditures as capital or operational, and categorizing items as stock or non-stock. These distinctions aid organizations in optimizing their procurement strategies for better resource allocation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, categorizing procurement spend into direct vs. indirect, capital vs. operational, and stock vs. non-stock items is essential for strategic resource management. While these categories provide a structured framework, they are not mutually exclusive, as an item can fall into multiple categories. For example, an item may be both direct and operational or indirect and stock. The flexibility of these categories allows organizations to tailor their procurement strategies based on their specific needs, ensuring efficient resource allocation and effective supply chain management. Different companies may adopt varying categorization approaches depending on their industry, size, and operational requirements.
Tutor notes:
- Because you’ve got 6 categories of spend to talk about you’re only going to need 3-4 sentences for each. Providing you’ve said the category, explained what it is and given one example, you’ll absolutely fly through this type of question
- You could also mention that it is useful to use categories of spend as this helps with budgeting. Different categories may also have different processes to follow for procuring the item (this could form part of your introduction or conclusion).
- This subject is LO 1.3.2 it’s quite spread out in the text book but the main info is on p.49
- Note- different companies/ industries classify items of spend differently. Particularly packaging and salaries. Some say they’re direct costs and some say they’re indirect costs. Honestly, it’s a hotly debated subject and I don’t think there is a right or wrong. I’d just avoid those two examples if you can and stick to ones that aren’t as contentious like eggs and PPE.
Discuss 3 areas of regulation relating to competition that a procurement professional should be aware of (25 points)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
How to approach this question
- This question is very vague. Sometimes CIPS do this. It allows for you to be a bit more free in your response, but can also be quite stressful because you don’t 100% know what they’re after.
- For this question we’re looking at competitions, so full tenders where lots of suppliers are invited to bid for an opportunity. This means the type of things we could be discussing include; IP, cartels, merger controls and monopolies.
Example Essay
Procurement professionals operate within a legal framework that regulates competition, aiming to ensure fair business practices and prevent anti-competitive behaviour. Three critical areas of regulation related to competition that procurement professionals should be aware of include intellectual property, cartels, and merger controls.
Intellectual Property (IP):
Intellectual property encompasses creations of the mind, such as inventions, designs, and brand names, protected by law. In the context of procurement, understanding intellectual property is essential when dealing with suppliers' products, technologies, or services that may involve intellectual property rights.
Procurement professionals must be aware of the intellectual property rights associated with the goods or services they are procuring. This includes respecting patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets owned by suppliers. Due diligence is crucial to ensure that the products or services being procured do not infringe on the intellectual property rights of others, requiring verification of legal ownership and legitimacy. An example of something procurement should look out for include ensuring goods are authentic and not counterfeit.
Cartels:
Cartels involve agreements between competitors to control prices, manipulate markets, or restrict competition. For procurement professionals, it is imperative to be vigilant and avoid engaging in or unintentionally supporting cartel activities. Procurement professionals should refrain from participating in anti-competitive behaviour, such as bid-rigging or price-fixing, which are common cartel activities. This involves not colluding with suppliers or competitors to manipulate procurement processes. Maintaining open and fair competition is essential, ensuring that procurement processes remain transparent, competitive, and free from attempts to distort market dynamics, thereby preventing the formation of cartels and promoting a level playing field.
One notable example involved the construction industry in the UK. In 2019, the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) fined three major suppliers to the construction industry for participating in a cartel. The companies, which supplied concrete drainage products, were found to have coordinated their behaviour to share markets, fix prices, and rig bids. The investigation revealed that these companies had breached competition law by engaging in anti-competitive practices that limited competition and negatively impacted customers. The fines imposed were part of the CMA's efforts to deter and penalize such cartel behaviour, emphasizing the importance of fair competition in procurement. The Directors of the companies have also been banned from undertaking the role of Director of any company for 12 years.
Merger Controls:
Merger controls are regulations overseeing the consolidation of companies, mergers, and acquisitions to prevent monopolistic practices and protect fair competition. Procurement professionals need to be aware of these regulations, especially when dealing with suppliers undergoing mergers or acquisitions.
Staying informed about mergers and acquisitions within the supplier base is crucial. If a key supplier undergoes such changes, it may impact the stability of the supply chain or alter market dynamics. Procurement professionals need to be aware of potential changes in supplier relationships, pricing structures, or product/service availability resulting from mergers. Engaging in proactive risk management and contingency planning is necessary to mitigate any negative impacts on procurement operations.
Mergers are actively watched in the UK by the Competition and Markets Authority, and where rules are broken, the CMA can intervene and even prevent mergers from happening. A notable example of this was the attempted merger between JD Sports and Footasylum – the companies were fined millions of pounds for exchanging information and attempting to collude and distort the marketplace.
In conclusion, procurement professionals play a crucial role in navigating these regulatory landscapes effectively. Understanding intellectual property, avoiding cartel activities, and staying informed about merger controls contribute to fostering fair and transparent competition within the marketplace.
Tutor Notes
- The construction example of a cartel can be found here Supply of precast concrete drainage products: civil investigation - GOV.UK (www.gov.uk) but feel free to use your own!
- The JD/ Footasylum one is here: JD Sports and Footasylum fined £4.7m for competition breach - BBC News. Basically, the CMA got involved because the two firms were sharing private information and having secret meetings, with the intention that they could combine. The CMA thought it was super dodgy and that it would distort the trainer / footwear market in the UK so they fined the companies and told them to stop it.
- The study guide is a bit light on this topic, so I would do a bit of extra research and have an example in your back pocket for if you need it. P. 142
If you want an example of IP issues- Shein is a great company to look at- ‘They took my world’: fashion giant Shein accused of art theft | Art and design | The Guardian
Provide a definition of a stakeholder (5 points) and describe 3 categories of stakeholders (20 points).
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
Essay Plan:
Definition of Stakeholder- someone who has a ‘stake’ or interest in the company. A person or organisation who influences and can be influenced by the company.
Categories of stakeholders:
1) Internal Stakeholders- these people work inside the company e.g. employees, managers etc
2) Connected- these people work with the company e.g. suppliers, mortgage lenders
3) External Stakeholders – these people are outside of the company e.g. the government, professional bodies, the local community.
Example Essay:
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or entity that has a vested interest or concern in the activities, decisions, or outcomes of an organization or project. Stakeholders are those who can be affected by or can affect the organization, and they play a crucial role in influencing its success, sustainability, and reputation. Understanding and managing stakeholder relationships is a fundamental aspect of effective organizational governance and decision-making and there are several different types of stakeholders.
Firstly, internal stakeholders are those individuals or groups directly connected to the daily operations and management of the organization. Internal stakeholders are key to success and are arguably more vested in the company succeeding. They may depend on the company for their income / livelihood. Anyone who contributes to the company's internal functions can be considered an internal stakeholder for example:
This category includes
1) Employees: With a direct influence on the organization's success, employees are critical internal stakeholders. Their engagement, satisfaction, and productivity impact the overall performance.
2) Management and Executives: The leadership team has a significant influence on the organization's strategic direction and decision-making. Their decisions can shape the company's future.
Secondly, connected stakeholders are those individuals or groups whose interests are tied to the organization but may not be directly involved in its day-to-day operations. Connected stakeholders work alongside the organisation and often have a contractual relationship with the organisation. For example, banks, mortgage lenders, and suppliers. These stakeholders have an interest in the business succeeding, but not as much as internal stakeholders. It is important to keep these stakeholders satisfied as the organisation does depend on them to some extent. For example, it is important that the organisation has a good relationship with their bank / mortgage provider/ supplier as failing to pay what they owe may result in the stakeholders taking legal action against the organisation.
This category includes:
1) Shareholders/Investors: Holding financial stakes in the organization, shareholders seek a return on their investment and have a vested interest in the company's financial performance.
2) Suppliers and Partners: External entities providing goods, services, or collaboration. Their relationship with the organization impacts the quality and efficiency of its operations.
Lastly external stakeholders are entities outside the organization that can influence or be influenced by its actions. This category includes anyone who is affected by the company but who does not contribute to internal operations. They have less power to influence decisions than internal and connected stakeholders. External stakeholders include the government, professional bodies, pressure groups and the local community. They have quite diverse objectives and have varying ability to influence the organisation. For example, the government may be able to influence the organisation by passing legislation that regulates the industry but they do not have the power to get involved in the day-to-day affairs of the company. Pressure groups may have varying degrees of success in influencing the organisation depending on the subject matter. This category includes:
1) Customers: With a direct impact on the organization's revenue, customers are vital external stakeholders. Their satisfaction and loyalty are crucial for the company's success.
2) Government and Regulatory Bodies: External entities overseeing industry regulations. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for the organization's reputation and legal standing.
In conclusion, stakeholders are diverse entities with a vested interest in an organization's activities. The three categories—internal, connected and external —encompass various groups that significantly influence and are influenced by the organization. Recognizing and addressing the needs and concerns of stakeholders are vital for sustainable and responsible business practices.
Tutor Notes
- The above essay is pretty short and to the point and would pass. If you want to beef out the essay you can include some of the following information for a higher score:
- Stakeholders can be harmed by, or benefit from the organisation (can affect and be affected by the organisation). For example a stakeholder can be harmed if the organisation becomes involved in illegal or immoral practices- e.g. the local community can suffer if the organisation begins to pollute the local rivers. The local community can also benefit from the organisation through increased employment levels.
- CSR argues organisations should respect the rights of stakeholder groups
- Stakeholders are important because they may have direct or indirect influence on decisions
- The public sector has a wider and more complex range of stakeholders as they’re managed on behalf of society as a whole. They’re more likely to take a rage of stakeholder views into account when making decisions. However, these stakeholders are less powerful – i.e. they can’t threaten market sanctions, to withdraw funding, or to quit the business etc.
- The essay doesn’t specifically ask you to Map Stakeholders, but you could throw in a cheeky mention of Mendelow’s Stakeholder Matrix, perhaps in the conclusion. Don’t spend time describing it though- you won’t get more than 1 point for mentioning it. You’d be better off spending your time giving lots and lots of examples of different types of stakeholders.
- Study guide p. 58
Jan is a Contracts Manager at ABC Ltd and has recently awarded a contract to XYZ Ltd. Describe how she can manage the contract and supplier, detailing ways of monitoring performance and adding value for ABC Ltd (25 marks)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
How to approach this question:
- There are 4 sections to this essay, so before you start writing I’d make a couple of notes on each of the points. Then build those notes into separate paragraphs. Your notes may look like this:
How to manage the contract – ensuring contract is fit for purpose, holding XYZ to their responsibilities, ensuring ABC are also fulfilling their responsibilities, issuing contract variations if required, planning for contingencies.
- How to manage the supplier – ensure the right relationship is in place (transactional vs collaborative), communication – open and honest, ensure there is mutual trust and understanding of each other’s goals/ objectives.
- Ways of monitoring performance – use KPIs / SLAs, Supplier Scorecard, Vendor Rating, feedback from customers
- How to add value for ABC – increasing efficiencies (e.g. less product defects), improved quality, assisting with Value Engineering exercises, reduction in time and costs (e.g. through improved processes such as ordering), the supplier delivers ‘extras’ for ABC such as training to staff at no additional cost.
- Ensure each paragraph refers to Jan, ABC and XYZ. The question doesn’t state what the businesses are buying/ selling so you can use this as an opportunity to provide examples: ‘if ABC are procuring raw materials from XYZ such as metal, an effective way to manage performance would include …. If they are procuring a service, it may be more beneficial to use …. methodology’
Example Essay
Jan, the Contracts Manager at ABC Ltd, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the success of the recently awarded contract with XYZ Ltd. Efficient contract and supplier management involves careful planning, communication, performance monitoring, and the continuous addition of value. Here's how Jan can navigate these aspects:
In terms of contract management, Jan must ensure that the terms and conditions of the contract are "fit for purpose," aligning with the specific needs and complexity of the procurement. For instance, a simple goods procurement may necessitate a concise document, while more intricate projects like engineering endeavors may require a detailed contract such as a JCT or NEC contract. Additionally, Jan should vigilantly manage the contract during its lifespan, addressing any potential 'scope creep' that might necessitate amendments. If the contract lacks provisions for such changes, Jan may need to initiate the creation of a new contract to accommodate evolving needs
Clear delineation of responsibilities and contingencies is crucial in the contract to ensure accountability and preparedness for unforeseen circumstances. The inclusion of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and damage clauses, where appropriate, adds a layer of clarity and accountability to the contractual relationship. Planning for contingencies involves having backup strategies in place, especially considering potential challenges that may arise during the collaboration with XYZ Ltd. For example, having other suppliers she can call upon if XYZ fail to deliver on an order.
Turning to supplier management, Jan's role involves fostering a positive and productive relationship with XYZ Ltd. This includes regular meetings to discuss progress, achievements, and future plans. A mobilization meeting is particularly important to ensure a strong start to the contract. Subsequent monthly or quarterly meetings provide a platform to review performance retrospectively and plan for the future. Additionally, effective communication is paramount, with Jan ensuring that both organizations regularly communicate, particularly regarding urgent issues that may require immediate attention. This proactive communication can occur through various channels, such as email or phone calls, facilitating a swift resolution of any emerging concerns.
Trust and honesty form the bedrock of the relationship between ABC Ltd and XYZ Ltd. Jan should work towards fostering mutual trust through both formal and informal activities, recognizing the importance of a transparent and cooperative partnership
In terms of performance monitoring, Jan can employ Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to track performance regularly. These metrics should not be viewed as one-off activities but rather as ongoing tools for assessing and ensuring that performance aligns with expectations. Clear communication regarding the consequences of failing to meet these targets, such as the implementation of a Performance Improvement Plan or potential contract cancellation, is essential for maintaining accountability. Regular performance meetings between ABC Ltd and XYZ Ltd provide an opportunity to discuss achievements, setbacks, and any necessary adjustments. Beyond quantitative metrics, surveys and feedback from customers can provide qualitative insights into performance.
Finally, Jan can contribute to the partnership's success by focusing on adding value. This involves going above and beyond the contractual obligations, such as delivering products more efficiently at no additional cost or improving operational efficiencies. Encouraging XYZ Ltd to participate in Value Engineering exercises and engaging in Early Supplier Involvement to shape and define future requirements would be a good example of this. Additionally, providing 'add-ons' or 'extras' outside the contractual framework, such as training for ABC Ltd staff, further enhances the value derived from the partnership.
In conclusion, Jan's role as Contracts Manager extends beyond the initial awarding of a contract- rather her role involves strategic contract and supplier management throughout the lifetime of the professional relationship. By ensuring the contract is well-suited for its purpose, fostering a positive relationship with the supplier, monitoring performance effectively, and consistently adding value, Jan contributes to the success of the collaboration between ABC Ltd and XYZ Ltd. This comprehensive approach sets the stage for a mutually beneficial and enduring partnership.
Tutor Notes:
- A case study question like this in the real exam is likely to come with more details. They often come with lots and lots of details to be honest, talking about what XYZ supplies to ABC and the names of the people involved. The case study usually gives you some good clues as to what the examiner will be looking for you to include, so do read them carefully.
- You don’t have to include much ‘theory’ on case study questions – the important thing is to reference Jan as much as possible. BUT you could throw in a cheeky mention of the Kraljic matrix. The approach to managing the contract and supplier would depend on the type of item supplied by XYZ – e.g. if it is a bottleneck item the supplier may need to be handled differently to if it is a routine item. You could also mention KPIs and objectives as being ‘SMART’ - Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-Bound
- study guide p.86-90 / p.94 / p.96 -98
Examine FIVE ways in which procurement activities can contribute to achieving BrightAid's organisational objectives. (25 marks)
BrightAid
BrightAid is a medium-sized charity (not-for-profit) with 20 permanent employees and it uses 400 volunteers to deliver aid and services to the individuals and groups it serves. Its main aims are to raise awareness of its cause and bring issues to people's minds to prompt them to donate and/or join campaign activities. The charity depends on these voluntary donations, as without them, it would not be able to function. It also aims for this support to be continued on a regular basis and must engage with a wide range of stakeholders (both internal and external). BrightAid is also considering joining a buying group with several other charities and aims to extend the member's purchasing power and obtain competitive prices for the group members. Recognising that there is increasing competition in the amount and frequency of donations, the charity is now looking at several ways to increase the amount or frequency of donations and make its internal processes more efficient and effective. Up to this point, any procurement activities have been undertaken ad-hoc with no formalised processes.
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
Five Ways Procurement Activities Can Contribute to BrightAid’s Organisational Objectives
Procurement plays a critical role in supporting the operational efficiency and sustainability of a not-for-profit organization like BrightAid. Given its reliance on donations and volunteers, a structured and strategic procurement approach can help maximize resources, reduce costs, and enhance the charity’s impact. Below are five key ways in which procurement can contribute to BrightAid’s organisational objectives.
1. Cost Reduction and Financial Efficiency
How Procurement Helps:
Implementing a formal procurement strategy ensures that goods and services are sourced at the most cost-effective prices.
Joining a buying group with other charities can enhance BrightAid’s purchasing power, securing bulk discounts and reducing overhead costs.
Supplier negotiations and competitive tendering can help maximize value for money on every purchase.
Impact on BrightAid:
More funds can be allocated to core aid and campaign activities.
Lower operational costs mean greater financial sustainability and improved service delivery.
2. Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
How Procurement Helps:
Implementing clear procurement policies and procedures ensures fair supplier selection, minimizing risks of fraud or inefficiencies.
Establishing a procurement audit process ensures compliance with ethical and legal standards.
Open and fair supplier engagement strengthens stakeholder trust (donors, volunteers, and partners).
Impact on BrightAid:
Increases donor confidence, encouraging repeat and larger donations.
Ensures resources are used efficiently and ethically, enhancing the charity’s reputation.
3. Improving Supply Chain Reliability and Efficiency
How Procurement Helps:
Strategic supplier selection ensures consistent delivery of essential goods and services.
Developing long-term supplier relationships can reduce risks of supply disruptions.
Procurement can introduce supplier performance reviews to ensure that services meet BrightAid’s needs effectively.
Impact on BrightAid:
More efficient aid distribution, ensuring beneficiaries receive timely support.
Reduced operational disruptions, allowing volunteers and staff to focus on charitable work instead of supply issues.
4. Supporting Ethical and Sustainable Procurement
How Procurement Helps:
Ethical sourcing policies ensure that supplies (e.g., food, clothing, medical aid) come from responsible and sustainable sources.
Procurement can help BrightAid select suppliers that align with its mission and values (e.g., fair trade suppliers, environmentally friendly packaging).
Working with ethical suppliers enhances CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) partnerships, attracting more donors.
Impact on BrightAid:
Increases public trust and donor support, strengthening brand reputation.
Aligns procurement decisions with the charity’s core mission and sustainability goals.
5. Enhancing Operational Effectiveness and Stakeholder Engagement
How Procurement Helps:
A structured procurement process ensures timely and cost-effective delivery of goods and services, reducing inefficiencies.
Procurement professionals can engage stakeholders (staff, volunteers, donors) to understand their needs and improve sourcing decisions.
Implementing procurement technology or e-procurement systems can streamline purchasing and reduce administrative burdens.
Impact on BrightAid:
Staff and volunteers can focus more on core charitable activities rather than administrative tasks.
Better stakeholder engagement ensures that procurement aligns with donor expectations, strengthening long-term relationships.
Conclusion
By implementing a structured and strategic procurement function, BrightAid can significantly improve its financial efficiency, supply chain reliability, and ethical standards, ultimately enhancing its ability to deliver aid effectively and attract continued donor support. With growing competition for donations, a well-managed procurement process ensures cost savings, improved transparency, and stakeholder trust, directly contributing to the charity’s long-term sustainability and success.
In the supplier selection part of the Procurement Cycle, what criteria can a Procurement Manager use to ensure they award to the best supplier? (25 points)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
How to approach this question:
- This is quite an open question and there are many different things you could mention. One way to approach it would be to use Carter’s 10 Cs- discuss a couple of these. OR just give a couple of criteria in different paragraphs. Some ideas include: Supplier financial status, Reputation / References, Quality, Availability, CSR Policies / Ethics / Environmental considerations, Accreditations, Added Value. This list is not exhaustive.
- If you’re going for Carter’s 10 Cs you could name a couple of these: competency, consistency, capability, control, cost, cash, clean, communication, culture, commitment
- I don’t think either approach is better or worse. Choose the criteria you know the most about and write about those.
- The question doesn’t tell you how many criteria to name, so you have to make a judgement call here. I would aim for 5-6. But if you can only remember 4 that’s fine. The main thing they’re looking for is that you explain for each one 1) what it is 2) how procurement can check 3) why procurement would look at that criteria 4) an example. If you do too many you risk not going into enough detail on each. It’s a balance. 5 is always a good number to aim for if the question doesn’t state.
Example Essay
In the procurement cycle, the supplier selection phase is a critical juncture that demands consideration. Procurement Managers shoulder the responsibility of identifying and awarding contracts to suppliers who not only meet immediate needs, but contribute to the long-term success of the organization. This essay explores various criteria a Procurement Manager can employ to ensure the selection of the best supplier: financial stability, reputation, quality, availability, CSR policies, and added value.
Financial stability is a foundational criterion in supplier selection. Assessing a supplier's financial status involves a multifaceted evaluation, with liquidity and gearing ratio taking center stage. The acid test, comparing short-term assets to liabilities, offers insights into a supplier's ability to settle debts promptly, with a ratio exceeding 1 indicating financial health. Meanwhile, the gearing ratio, reflecting the proportion of capital funded by loans, aids in gauging financial risk, with a ratio below 50% considered low-risk. Relying on published Profit and Loss statements and income statements, along with financial credit checks from platforms like Dun and Bradstreet, empowers Procurement Managers to make informed decisions. This financial scrutiny is imperative to avoid entering contracts with suppliers facing imminent financial struggles, safeguarding against potential disruptions to the supply chain.
Reputation and references are another pivotal criterion. Seeking references from previous contracts allows Procurement Managers to gauge a supplier's track record in successfully delivering on similar commitments. Independent reviews and informal market inquiries supplement this information, providing a holistic understanding of a supplier's performance. However, caution is advised in overreliance on past performance, as variables like personnel changes or contract scale differences may impact outcomes. Recognizing that past shortcomings may have been addressed internally further emphasizes the need for a balanced approach to reference evaluation.
Thirdly, Quality. Beyond the product itself, considerations extend to the supplier's technological capabilities, manufacturing processes, and relevant accreditations such as ISO 9001. Physical visits to supplier sites may be warranted, especially for products like raw materials where samples can be requested. Adhering to recognized safety standards and assessing factors like fire retardancy ensures that the quality of manufactured goods aligns with established benchmarks.
Next, Availability is another important criteria to consider. Procurement Managers must evaluate a supplier's capacity and capability to meet specific requirements. Inquiries about existing contracts and flexibility in response to demand fluctuations provide insights into a supplier's commitment and responsiveness. Assessing the supplier's workload and the significance of the buyer in their client portfolio helps determine the level of attention and service the buyer can expect. A buyer may wish to avoid working for a supplier who is already stretched very thinly with other contracts.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) policies and ethical considerations have gained prominence in supplier selection. Beyond legal compliance, Procurement Managers may scrutinize a supplier's history for convictions or negative press related to corruption, bribery, or fraud. The presence of a Modern Slavery Policy and Environmental Policy, along with relevant accreditations like ISO14001 or Fair Trade certification, attests to a supplier's commitment to ethical and sustainable practices. Procurement would likely seek to appoint a supplier who’s CSR vision aligns with their own company’s.
Lastly, added value is an important criteria to consider. This is particularly so for Public Sector Organizations governed by the Social Value Act. In addition to meeting contractual requirements, suppliers may offer knowledge sharing, training, improved processes, or contribute to social value by employing local community members or providing apprenticeships. This criterion aligns procurement decisions with broader organizational goals, enhancing the overall impact of supplier relationships and benefitting the local community.
In conclusion, a careful combination of financial scrutiny, reputation assessment, quality evaluation, availability considerations, CSR policies, and added value analysis forms the bedrock of effective supplier selection in the procurement cycle. Procurement Managers, armed with a holistic understanding of these criteria, should seek not only to fulfil immediate needs, but also consider the long-term impact of supplier appointments.
Tutor Notes
- A ‘good’ scoring answer (50-70%) will explain the criteria well and give examples. If you’re looking for a distinction level answer (70% +) you could also mention advantages, disadvantages and risks associated with each of the criteria. For example, when looking at references and reputation it’s important to know that a supplier would only ever provide a good reference to you, they would never tell you of a contract that failed. Another example is that financial data may be skewed- a supplier may have a low score if they are just starting up or have recently remortgaged a property. It’s therefore important to get a commentary as well as the figures / scores.
- You could also mention that criteria could be weighted e.g. more importance given to quality than financial status and also consider how easy or difficult it would be to get the information e.g. a supplier may say they have lots of availability to deliver the service you require, but they may just be saying this to win business. How do you know for sure?
- Social Value Act isn’t in this syllabus. If you work in Public Sector procurement it’s something you’ll be very familiar with. If you don’t or you’re outside of the UK do not worry about this. I’ve just included it to show how you can bring in your own knowledge to questions like this. You could think of particular criteria that’s important to your industry and write about that. The Social Value Act: What is it, and why is it important? (samtaler.co.uk)
- Study guide p.77
Explain FIVE possible factors that influence procurement
activities in third sector (not-for-profit) organisations that
Parvinder should research. (25 marks)
Parvinder Kaur works for a leading procurement consultancy, NHB. Her
clients are based all around the world with a diverse range of products
and services. Parvinder specialises in providing procurement advice within
the public sector but she also has two major clients in the private sector.
Before beginning procurement consultancy services with a new client,
parvinder likes to research the organisation and the sector in Which it
operates so that she can understand the type of challenges that the
organisation may face. This work, ahead of the first meeting, has meant
that Parvinder has built an excellent reputation for analysing a business
quickly. It also means she has been able to establish insight into the
aspects which may have a significant impact on the success of the
procurement function in her clients.
NHB has recently won a significant contract to provide procurement
consultancy service to a large third sector (not-for-profit) organisation.
This is an important new client for NHB and the board is keen to assign
Parvinder as the key account manager, even though this is a new area for
her. Parvinder is happy to take on the additional work as she is keen to
develop a greater understanding of this sector.
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
Procurement in third sector (not-for-profit) organisations operates under distinct influences compared to public or private sectors. Understanding these factors is crucial for Parvinder to provide effective consultancy tailored to the sector’s unique challenges and requirements. Below are five key factors that influence procurement activities in third sector organisations:
1. Funding Sources and Financial Constraints
Explanation:Third sector organisations typically rely on donations, grants, fundraising, and government funding rather than sales revenue. This creates tight budgetary controls and unpredictability in funding availability.
Impact on Procurement:Procurement activities must align closely with available funds, often requiring careful prioritisation, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with funders’ conditions. Parvinder should research how the organisation manages fluctuating budgets and whether there are restrictions on how funds can be spent.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Explanation:Not-for-profit organisations are often subject to specific regulatory frameworks and reporting standards, including charity laws, governance codes, and donor-imposed conditions.
Impact on Procurement:These regulations impact supplier selection, contract management, and transparency obligations. Procurement must ensure compliance with these rules to maintain legitimacy, donor confidence, and avoid legal penalties. Parvinder should assess the regulatory environment affecting procurement processes.
3. Social and Ethical Considerations
Explanation:Third sector organisations frequently have missions linked to social good, environmental sustainability, and ethical practices. Procurement decisions are influenced by these values and stakeholder expectations.
Impact on Procurement:Procurement must prioritise suppliers who meet ethical standards, support local communities, and minimize environmental impact. This may limit supplier options but aligns procurement with organisational values and public image. Parvinder should evaluate the organisation’s sustainability and CSR policies.
4. Stakeholder Involvement and Governance
Explanation:Procurement decisions in not-for-profits often involve multiple stakeholders, including trustees, donors, beneficiaries, and volunteers, making the governance structure complex.
Impact on Procurement:This can lengthen decision-making processes, require additional approvals, and demand higher transparency and accountability. Parvinder should investigate who the key stakeholders are and how procurement decisions are governed and communicated.
5. Market and Supplier Availability
Explanation:Depending on the organisation’s geographic location, niche requirements, and mission, there may be limited availability of suitable suppliers, especially those compliant with social and ethical standards.
Impact on Procurement:Limited supplier choice can increase costs and procurement risk. Procurement strategies may need to focus on supplier development, collaboration, or partnerships to meet organisational needs. Parvinder should research supplier markets and potential supply chain risks.
Conclusion:
To effectively advise the new third sector client, Parvinder must research and understand the impact of funding limitations, regulatory compliance, ethical imperatives, stakeholder complexity, and supplier availability on procurement activities. Recognising these factors will enable her to tailor procurement strategies that support the organisation’s mission, ensure transparency, and optimise resource use—key to delivering value in the not-for-profit environment.
Bottom of Form
Top of Form
What is a Code of Ethics? What should an Ethical Policy Contain? What measures can an organisation take if there is a breach of their Ethical Policy? (25 points)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
- Firstly give a short definition of Code of Ethics: a document that sets out moral principles or values about what is right and wrong.
- What an Ethical Policy should contain: Condition of workers, Environment, H+S, Discrimination, Gift / Bribery Policy, Whistleblowing, Confidentiality, Fair Dealings, Declaration of Conflict of Interests. You won’t have time to go into depth on all of these, so pick a few where you want to give an example.
- Measures to take if there is a breach: depending on what the breach is and who breached it this could include: education/ training, sanctions, blacklisting, reporting to authorities, publicise the issue, use a performance improvement plan, issue warnings, dismissal.
Example Essay:
A code of ethics is a formal document or set of principles that outlines the values, ethical standards, and expected conduct for individuals within an organization. It serves as a guide for employees and stakeholders, shaping their behaviour and decision-making to align with the organization's ethical framework. It may take the form of a Mission Statement, Core Values, Specific Guidelines or established reporting mechanisms. The purpose of the Code is to establish standards, promote integrity, mitigate risks and build trust- with both internal and external stakeholders.
A Code of Ethics may contain the following:
- Condition of workers – stating what the company will provide to the employees to make sure the environment is safe. This could include the physical environment but also hours worked, opportunities for breaks etc. Depending on the sector it could detail shift patterns, expectations regarding overtime and compensation.
- Environment – this section would discuss compliance with legislation regarding pollution, disposal of waste materials etc. Depending on the company’s goals- they may have higher commitments to the environment than those imposed by the government. Additional commitments may include NetZero targets or the use of renewable sources of energy.
- H+S- Health and Safety. Ensuring that the working environment is free of hazards and that workers have the training and equipment they need to complete the work safely. E.g. PPE
- Discrimination- a promise not to discriminate based on any characteristic. Aligns with the Equalities Act. Policy should include how the company would handle situations, for example if an employee reports an issue of discrimination or harassment. This may involve the use of a whistleblowing hotline or details on how to contact HR.
- Gift / Bribery Policy – this area of the code of conduct would explain whether the company allows staff members to receive gifts (e.g. from suppliers) and the processes to complete if they do (e.g. return the item, complete an internal document, donate the gift to charity). Different companies and industries will have different rules surrounding this, the Public Sector is much more likely to reject gifts from suppliers for example.
- Declaration of conflict of interests- this explains what staff should do if there is a conflict. For example if they are running a tender and their father owns one of the suppliers who is bidding for the work. The conflict of interest policy will explain what the person should do, how to report it and have mechanisms in place to ensure that nothing untoward could come of the situation. This may be having another member of staff mark the tender to ensure unbiasedness.
Measures to take in case of a breach
A response to a breach will depend on who breached the policy – whether this is an employee or a supplier. It will also depend on the severity of the breach.
Remedies for a supplier breach could include: education / training if the breach is minor. Supplier development if the relationship with the supplier is very important (for example if there are no other suppliers the buyer could turn to) and the breach is minor. If the breach is major such as fraud or misappropriation of funds, a buyer could look to issue sanctions, claim damages and dismiss the supplier. There could be options to claim liquidated damages if this is included in the contract. For very serious offenses the buyer may blacklist the supplier- never use them ever again and could also report the issue to the police if the breech is also criminal (e.g. modern slavery or fraud).
Remedies for an employee breach could include: for minor breaches training may be required, particularly if it was a junior member of the team and it was an innocent mistake like forgetting to fill out a form when they received a Gift. The employee could be carefully monitored and put on an Improvement Plan. If internal issues are found, such as several staff are breaching the Code of Ethics, senior management could look to review policies to make sure issues are being flagged and responded to in the best way. Employees who fail to follow the Ethical Policy, either through routinely failing to adhere to it or through a major breach could be dismissed from the organisation. There would need to be strong evidence of this.
In conclusion it is important for all organisations regardless of size of industry to have an Ethics Policy. Sharing the code of ethics with staff is a fundamental step in embedding ethical principles into the organizational culture. Regular communication and training reinforce these principles, fostering a shared commitment to ethical behaviour across all levels of the organization.
Tutor Notes
- In an essay like this it’s always a good example to use examples. They can be hypothetical – you don’t have to know any company’s Ethics policy off by heart. E.g. If a supplier breached a buyer’s Ethical Policy by employing Child Labour in their factories, an appropriate measure for the buyer to take would be to cancel the contract and find another supplier. This is because not only is Child Labour illegal, the buyer will not want to be associated with this supplier as it will have negative repercussions on their image. The best response would therefore be to distance themselves from the supplier.
- Code of Ethics and an Ethics Policy are the same thing. Just different language. The terms can be used interchangeably
- Study guide p. 128
Explain 5 stages of the sourcing cycle that occur in the pre-contract stage (25 points)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
How to approach this question:
- The Sourcing Cycle is the first half of the CIPS Procurement Cycle and includes these steps:
1) Define Business Need
2) Market Analysis + Make vs Buy
3) Develop Strategy and Plan
4) Pre-Procurement Market Testing
5) Develop Documents and Specification
6) Supplier Selection
7) Issue Tender
8) Bid Evaluation
9) Contract Award and Implementation
Your response should detail 5 of these. It is a good idea to pick the ones you know most about and where there is more to write about. You won’t get any extra points for naming more than 5 so focus on getting as much detail down about 5, rather than explaining more of them.
Essay Plan
Introduction – explain what the sourcing cycle is – the stages of the procurement cycle before a contract is signed. It describes the steps an organisation will take to source/ procures goods or services.
Paragraph 1 – Define the business need
· How is the need identified? E.g. by end user, stores department, ERP system.
· Procurement should challenge this – is it really necessary? Suggest alternatives – this could be a key source of added value
· Put together business case / requisition / project initiation document
· What type of purchase? Straight rebuy, modified rebuy, new purchase
· Decide on what type of specification would be best - Conformance vs performance specification
· This stage may include early supplier involvement
Paragraph 2 – Market Analysis and Make vs Buy Decision
· Create an Analysis by segmenting the market by buyer, product, distribution channel, geography, customer market etc.
· Make vs Buy - use Carter’s Matrix to decide whether the organisation should make vs buy.
· Also consider outsourcing at this stage
Paragraph 3 – Documents and Specification
· Draft documents. These may include a RFQ or ITT, a specification and a proposed form of contract
· Specification may be conformance or performance based
· A contract sets out the roles, rights, responsibilities and obligations of the parties and shows intention to enter into ‘legal relations’
· This stage defines the ‘offer’ which becomes binding once other party accepts
· Documentation may also include proposed KPIs and SLAs
Paragraph 4 – Supplier Selection
· For a new purchase, supplier selection is very important - investigation should be proportionate to the value of the procurement. For rebuys or low-risk purchases you could use the same supplier or a list of pre-approved suppliers.
· You can locate potential suppliers by; catalogues, websites, trade registers, market exchanges and review sites, trade or industry press, fairs and conferences, networking and recommendations/ referrals.
· You can shortlist suppliers by sending out a pre-qualification questionnaire. This adds value by reducing wasted time / costs / risks to entering into a contract with the wrong supplier.
· Other criteria for supplier selection include using Carter’s 10 Cs (competency, consistency, capability, control, cost, cash, clean, communication, culture, commitment), the supplier’s financial standing (e.g. liquidity and gearing), references and considering their CSR policy.
Paragraph 5 – Issue Tender
· Competitive bidding should only be done when there’s sufficient time and resources available, there’s sufficient suppliers in the marketplace, they’re keen to win business (ie that there’s appetite for competition) and there is a strong specification
· Best practice is to issue tenders electronically as it ensures equal treatment of suppliers and transparency
· Consider open vs closed procurement processes
· Use a cross-functional team – particularly when marking responses
Conclusion – you could mention here that different sourcing activities may require more or less effort at each of the stages e.g. procuring a new item may require more market analysis than a re-buy.
Tutor Notes:
- If you want to add in extra details, you could think about ways procurement can add value at each stage
- In the old syllabus, CIPS were a bit obsessed with Michael Porter. In the Market Analysis bit you could talk about using Porter’s 5 forces (buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutions, supplier rivalry) and Porter’s 3 generic strategies for competing (cost leadership, differentiation, niche segment). This has been removed from the study guide so it’s not essential to know this for this module, but if you’ve seen it before it’s a nice one to throw in.
- You could also mention that there are differences between the public and private sector procurement at the different stages. E.g. Public Sector requires open competitions for contracts of a certain value and must follow the rules set out in Public Contract Regulations – the private sector doesn’t have such strict regulations so there is much more flexibility in how tenders are completed. Also in the public sector, the evaluation criteria needs to be agreed beforehand and presented in the ITT- not the same for the private sector.
- Study guide p.71
Describe the key drivers for organisations who operate in the public, private and third sector (25 marks)
The Answer Is:
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Explanation:
- There’s 2 main approaches to layout you could take for this question. Firstly, divide your essay into three sections for the public, private and third sectors and talk about the key drivers for each sector separately. Alternatively, you could select a couple of drivers and form paragraphs around them, explaining in each paragraph whether the driver is strong or weak or even applicable for the different sectors.
- Drivers you could talk about include attitudes towards money, survival in the industry, differentiation, need for transparency, resources available, stakeholders, regulatory compliance
- Your answer should say why these are drivers in each of the industries, whether these drivers are strong or weak and why.
Example essay:
Organizations across the public, private, and third sectors operate within different paradigms, driven by distinct motivations and constraints. Understanding these key drivers is essential for comprehending how these organizations function and achieve their objectives. This essay explores the fundamental drivers of organizations in each of these sectors, focusing on attitudes towards money, survival, differentiation, need for transparency, resource allocation, and stakeholder management.
Attitudes Towards Money:
The approach to profit significantly differentiates the sectors. In the private sector, profit is a primary driver, essential for survival and rewarding shareholders. Conversely, the public sector is not profit-driven; its primary aim is to provide essential services to society, regardless of financial gain. The third sector, often termed 'not-for-profit', also requires profit generation, but uniquely, all profits are reinvested into the organization to further its aims, rather than being distributed as shareholder dividends. The Public-Sector needs to ‘balance the books’ but it is not a profit-generating area of the economy. The priority around money is ensuring that taxpayer money is well spend and that procurement activities represent value for money.
Survival in the Industry:
Survival strategies vary across sectors. Private and third sector organizations must focus keenly on survival, necessitating efficiency and sound business processes. The public sector, by contrast, can continue operating even when inefficient or running at a deficit, as seen in cases like local councils operating with budget shortfalls. This difference underscores a greater urgency for efficient management in the private and third sectors.
Differentiation:
Differentiation is a key driver in the private sector due to competition. Private entities often strive to distinguish their goods or services to gain a competitive edge, either through cost competitiveness or unique offerings. However, differentiation is less of a driver in the public and third sectors, where organizations are often sole providers of certain services or focus on specific social causes without direct competition.
Need for Transparency and Regulatory Compliance:
Transparency and adherence to regulations are paramount in the public and third (not-for-profit) sectors. These sectors are highly regulated, with public organizations adhering to regulations like the Public Contract Regulations 2015 and third sector organizations following guidelines set by bodies like the Charities Commission. The public's right to information through mechanisms like Freedom of Information requests further underscores this need for transparency. In contrast, the private sector faces less pressure for transparency, though it is not entirely exempt from regulatory compliance.
Resource Availability:
The availability and management of resources are different across sectors. Public and third sector organizations often operate with limited funds, making value for money a critical driver. They must achieve their objectives within these financial constraints. In contrast, the private sector generally has greater flexibility in resource acquisition, able to raise funds through loans or share sales, providing them with a broader scope for investment and expansion.
Stakeholder Management:
Stakeholder dynamics vary significantly among sectors. Public and third sector organizations often have a wide range of stakeholders, though these stakeholders may not wield significant power. Conversely, stakeholders in private organizations, like employees, can exert considerable influence, as seen in cases where employees might strike for better working conditions. Therefore, managing and satisfying stakeholders can be a more pressing concern in the private sector compared to the public sector, where actions like strikes can be legally restricted.
Conclusion:
In summary, organizations in the public, private, and third sectors are driven by different motivations and constraints. While profit is a major driver in the private and third sectors, it serves different purposes in each. Survival strategies, the need for differentiation, transparency requirements, resource management, and stakeholder relations all vary significantly across these sectors, reflecting the distinct roles and responsibilities they hold in society. Understanding these key drivers is crucial for anyone looking to navigate or interact with these diverse organizational landscapes effectively.
Tutor Notes:
- If you’re asked about different sectors of the economy it can be difficult to know what to talk about. An easy way to remember topics you can discuss in your essay is the acronym CAROLS which stands for: Competition, Activity, Responsibilities, Objectives, Legal Restrictions and Stakeholders. This acronym may generate some ideas of things you can discuss in your essay.
- This question takes some content from different Learning Outcomes throughout L4. Charities are discussed separately from Public and Private Sectors in LO 4.4 p.230.

