One of an investment centre's products is sold on an external market. Output is limited because the specialist machine that manufactures the product is operating at full capacity.
Current data for the product are as follows.
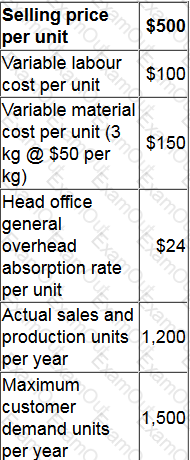
Investigations have identified that more rigorous maintenance of the machine at an annual cost of $5,000 would reduce the number of breakdowns and increase its capacity to 1,300 units per year.
There would be no change in the selling price if more units were sold. Any additional labor hours would be paid a premium of 25%. A discount of 2% of the cost of all materials purchased is available if the company increases its purchases to 3,700 kg or more per year.
What would be the increase in the investment centre's annual controllable profit if more rigorous maintenance is undertaken?
A public sector service organization is considering whether to use a balanced scorecard or a value for money approach based on the three Es to assess its performance.
Which of the following are correct comparisons of the balanced scorecard and value for money based on the three Es as performance measurement frameworks?
Select ALL that apply.
How does beyond budgeting NOT help to resolve the weaknesses of traditional budgeting? Select ALL that apply.
A company has a maximum of $2 million to invest and has identified four viable projects, E, F, G and H.
The initial investment for each of the projects is the maximum amount that can be invested in the project, but any amount up to the maximum can be invested. The projects are divisible.
The projects have been evaluated using net present value, as below. All figures are $ millions.
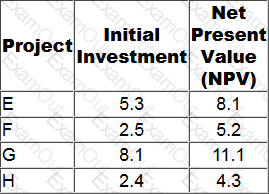
In which project should the company invest $2 million?
The following forecast data relate to the first three years of a five year project.
The project will require an initial investment of $30,000 in non-current assets.
All revenue will be received in the year it is earned and all operating costs will be paid in the year they are incurred. Tax will be paid in the following year.
Tax depreciation will be 25% per annum of the reducing balance.
The taxation rate will be 30% of taxable profits.
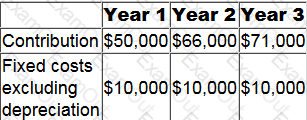
What is the forecast after tax cash flow for year 3 (to the nearest $10)?
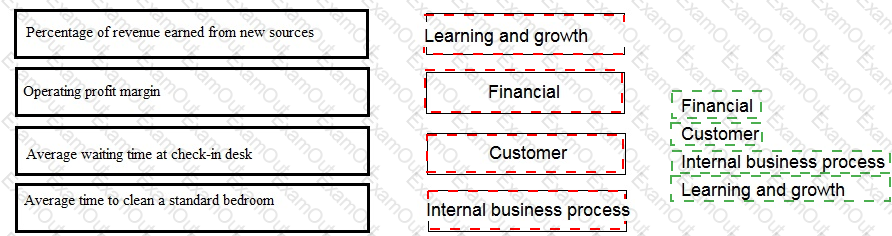
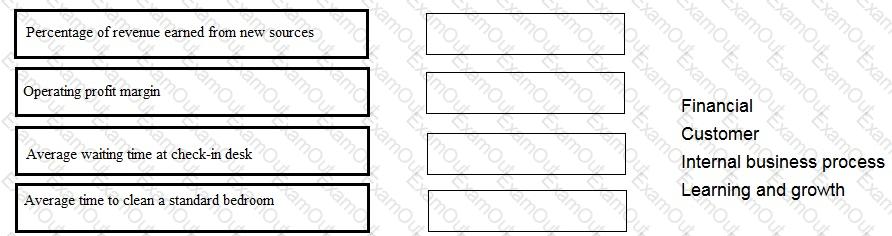
Place each performance measure against the correct perspective of the Balanced Scorecard for a company that operates a chain of hotels.
A project requires an initial investment of $160,000 in an asset for which the annual depreciation charge will be $40,000. The forecast profits from the investment are as follows.
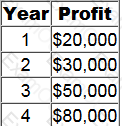
What is the payback period for the project in years? Give your answer to two decimal places.
We have 2 divisions with the following information: Profit before depreciation: B1=$800,000, B2=S1,000,000; Assets: B1 =$2,000,000, B2=S3,000,000; Capital employed: B1 = $1,700,000 and B2 = $2,550,000. 20%
straight-line depreciation is used.
Calculate ROI for each division.
Which of the following statements about modified internal rate of return (MIRR) and internal rate of return (IRR) is correct?
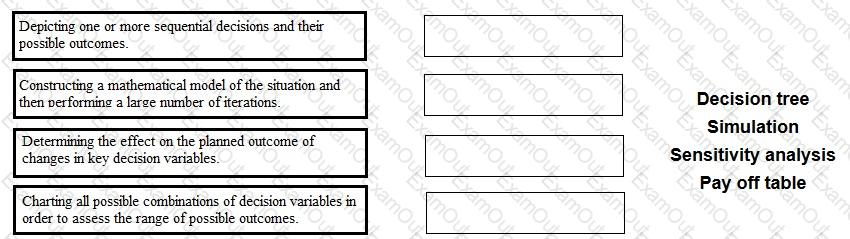
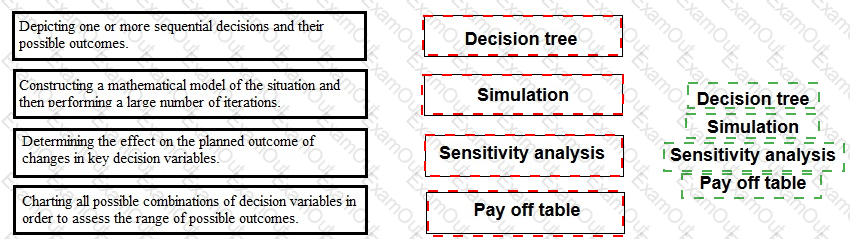
Place each method of analysing risk and uncertainty against the statement that describes it correctly.