Which of the following testing standards would be applicable to a lounge chair being specified for a lobby?
Radiant panel
Steiner tunnel
Methenamine pill
Smolder resistance
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
A lounge chair in a lobby, which is a public space, must meet fire safety standards to ensure occupant safety. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and fire safety standards (e.g., from the National Fire Protection Association [NFPA] and the California Technical Bulletin [Cal TB]) outline testing standards for furniture, particularly upholstered furniture, in commercial settings. The question asks for the applicable testing standard for a lounge chair, focusing on its fire performance.
A. Radiant panel: The radiant panel test (ASTM E648) measures the flame spread of flooring materials (e.g., carpet, tile) when exposed to radiant heat. It is not applicable to furniture like a lounge chair, as it tests surface burning characteristics of floor coverings, not upholstered items.
B. Steiner tunnel: The Steiner tunnel test (ASTM E84) measures the flame spread and smoke development of building materials (e.g., wall coverings, ceiling materials) in a tunnel-like apparatus. It is used for interior finishes, not for furniture, so it is not applicable to a lounge chair.
C. Methenamine pill: The methenamine pill test (ASTM D2859) is a flammability test for carpet and rugs, assessing their ignition resistance when exposed to a small flame (a methenamine tablet). This test is specific to floor coverings and is not applicable to upholstered furniture like a lounge chair.
D. Smolder resistance: Smolder resistance testing (e.g., California Technical Bulletin 117-2013 [Cal TB 117-2013]) evaluates the ability of upholstered furniture to resist smoldering ignition, such as from a cigarette. This is a critical test for lounge chairs in public spaces like lobbies, where upholstered furniture poses a risk of smoldering fires. Cal TB 117-2013 tests the foam, fabric, and other components of the chair to ensure they do not ignite or sustain a smoldering fire, making this the most applicable standard for a lounge chair in a lobby.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual emphasizes that smolder resistance testing, such as Cal TB 117, is a key standard for upholstered furniture in commercial settings, ensuring fire safety in public spaces like lobbies.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is D, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 2: Building Codes and Standards): "Smolder resistance testing, such as California Technical Bulletin 117, is applicable to upholstered furniture like lounge chairs in public spaces, ensuring they resist smoldering ignition for fire safety."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that smolder resistance testing is a critical standard for upholstered furniture in commercial settings, such as a lounge chair in a lobby. This test ensures the chair’s materials (e.g., foam, fabric) can resist smoldering ignition, reducing fire risk in public spaces. Other tests like radiant panel, Steiner tunnel, and methenamine pill apply to flooring or finishes, not furniture, making smolder resistance the correct choice.
Objectives:
Understand fire safety testing standards for furniture in public spaces.
Identify the appropriate flammability test for upholstered lounge chairs.
A new reflected ceiling plan communicates location and
Soffit heights
Types of partitions
Type of electrical outlets
Demolition of existing ceiling types
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
A reflected ceiling plan (RCP) is a drawing that shows the ceiling of a space as if it were reflected onto the floor plan, illustrating elements such as lighting fixtures, sprinklers, ceiling materials, and other ceiling features. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual outlines the purpose and content of an RCP in construction documents.
A. Soffit heights: An RCP often includes information about soffits (lowered ceiling sections), such as their location and height, to ensure proper coordination with lighting, HVAC, and other ceiling elements. Soffit heights are critical for understanding vertical clearances and ensuring that the design aligns with code requirements (e.g., minimum ceiling heights). This makes soffit heights a key piece of information communicated in an RCP.
B. Types of partitions: Partition types (e.g., wall construction) are shown on floor plans or partition plans, not on an RCP, which focuses on ceiling elements.
C. Type of electrical outlets: Electrical outlets are shown on power plans or electrical floor plans, not on an RCP, which is concerned with ceiling-mounted electrical elements like lighting fixtures.
D. Demolition of existing ceiling types: Demolition is shown on a separate demolition plan, not on a new RCP, which depicts the proposed ceiling design for construction.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual specifies that an RCP communicates the location of ceiling elements and includes details like soffit heights to ensure proper installation and coordination with other building systems.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is A, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 5: Construction Drawings and Specifications): "A reflected ceiling plan communicates the location of ceiling elements, such as lighting and sprinklers, and includes details like soffit heights to ensure proper coordination and installation."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that an RCP is used to show the design of the ceiling, including the placement of fixtures and features like soffits. Soffit heights are a critical detail because they affect the overall ceiling design, vertical clearances, and coordination with other systems, making this a standard piece of information included in an RCP.
Objectives:
Understand the purpose and content of a reflected ceiling plan.
Identify the types of information communicated in an RCP.
Which certification should the designer look for in the wood specifications if concerned about sustainable sourcing?
EPA
FSC
LEED
USGBC (CAGBC)
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Sustainable sourcing of wood ensures that it comes from responsibly managed forests, reducing environmental impact. The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification is the most recognized standard for sustainable wood sourcing, verifying that the wood is harvested in an environmentally and socially responsible manner. Option A (EPA) is a regulatory agency, not a certification for wood. Option C (LEED) is a green building certification system that may credit FSC-certified wood but is not a wood certification itself. Option D (USGBC/CAGBC) is the organization behind LEED, not a certification for wood.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on sustainable design.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “When concerned about sustainable sourcing of wood, designers should look for FSC certification, which ensures responsible forest management.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum includes sustainable design principles, with FSC certification being the standard for verifying sustainable wood sourcing.
Objectives:
Specify sustainable materials in design (IDFX Objective: Material Selection andSpecification).
The client has expressed a desire for a new space that supports a highly collaborative environment. Which aspect of the design is MOST important?
Ergonomic seating
Furniture placement
Integrated daylighting
Acoustical wall finishes
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
A highly collaborative environment requires a design that facilitates interaction, communication, and teamwork among occupants. Furniture placement is the most important aspect because it directly impacts how people interact—arranging furniture to create open, flexible spaces encourages collaboration by allowing for group discussions, easy movement, and shared work areas. For example, placing tables in a circular or U-shaped arrangement fosters face-to-face interaction. Option A (ergonomic seating) is important for comfort but does not directly address collaboration. Option C (integrated daylighting) enhances the overall environment but is secondary to spatial arrangement for collaboration. Option D (acoustical wall finishes) helps with sound control, which is important but not the primary factor for fostering collaboration.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on human behavior and space planning.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “In collaborative environments, furniture placement is the most critical design aspect to facilitate interaction and teamwork, such as arranging seating to encourage face-to-face communication.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the role of spatial arrangement in supporting specific user activities, with furniture placement being key to creating collaborative spaces.
Objectives:
Design spaces to support user activities and interactions (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
Which of the following symbols would BEST indicate a pendant in a reflected ceiling plan?
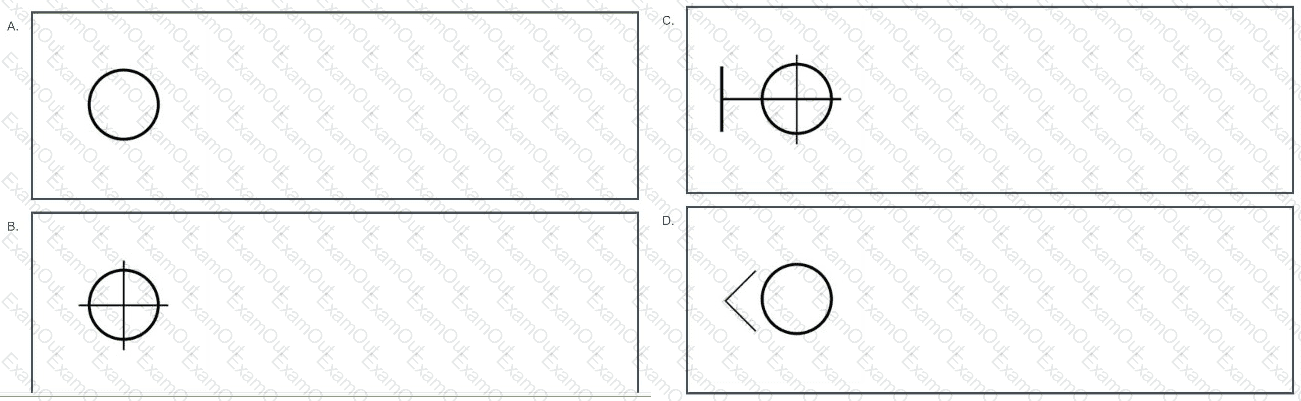
A plain circle
A circle with crosshairs
A circle with crosshairs and a vertical line
A circle with an arrow
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
A reflected ceiling plan (RCP) is a drawing that shows the ceiling of a space as if it were reflected onto the floor, typically used in architectural and interior design to indicate the placement of ceiling elements such as lighting fixtures, sprinklers, and other features. The question asks for the symbol that best indicates a pendant light, which is a type of lighting fixture that hangs from the ceiling, often suspended by a cord, chain, or rod, and is commonly used for ambient or task lighting in spaces like dining areas, kitchens, or lobbies.
To determine the correct symbol, we need to evaluate each option based on standard architectural and interior design drafting conventions, particularly those used in RCPs as outlined in NCIDQ Interior Design Fundamentals.
Option A: A simple circleA simple circle in an RCP typically represents a recessed light or a ceiling-mounted fixture, such as a can light or a flush-mounted light. Pendant lights, however, are not flush with the ceiling; they hang down, and their symbol should reflect this characteristic. A plain circle does not convey the hanging nature of a pendant light, so Option A is not the best choice for a pendant.
Option B: A circle with a crosshair (plus sign) insideIn architectural and interior design drafting standards, a circle with a crosshair (a plus sign) inside is a common symbol for a pendant light in a reflected ceiling plan. The circle represents the fixture itself, and the crosshair indicates that the light is suspended from the ceiling, distinguishing it from recessed or surface-mounted fixtures. This symbol aligns with standard conventions for representing pendant lights in RCPs, making Option B a strong candidate for the correct answer.
Option C: A circle with a crosshair and a small perpendicular line at the topThis symbol is similar to Option B but includes an additional small line at the top of the circle. In some drafting standards, this extra line might indicate a specific type of ceiling fixture, such as a sprinkler head or a ceiling fan, where the line could represent a connection point or a blade. For pendant lights, however, the extra line is not a standard feature in most RCP symbols. The additional line makes this symbol less clear for a pendant light, so Option C is not the best choice.
Option D: A circle with an arrow pointing to the leftThis symbol is not a standard representation for a pendant light. In RCPs, an arrow might be used to indicate direction (e.g., for an exit sign or a directional light), but it is not typically associated with pendant lights. The arrow suggests movement or orientation, which does not align with the static, hanging nature of a pendant light. Therefore, Option D is not appropriate for a pendant light in an RCP.
Based on this analysis, the symbol that best indicates a pendant light in a reflected ceiling plan isa circle with a crosshair inside (Option B), as it aligns with standard drafting conventions for pendant lights in RCPs. The crosshair effectively communicates that the fixture is suspended, which is a key characteristic of a pendant light.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using principles from the NCIDQ Interior Design Fundamentals and standard architectural drafting conventions, which are part of the NCIDQ exam preparation materials.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (a common resource for NCIDQ candidates):
"In a reflected ceiling plan, pendant lights are typically represented by a circle with a crosshair (plus sign) inside to indicate that the fixture is suspended from the ceiling, distinguishing it from recessed or surface-mounted lights."
The NCIDQ guidelines and standard architectural drafting practices specify that a pendant light in a reflected ceiling plan is represented by a circle with a crosshair inside. The circle denotes the fixture, and the crosshair indicates its suspended nature, which is a defining feature of a pendant light. This symbol ensures clarity in the RCP, allowing contractors and designers to understand the type of lighting fixture being specified. Options A, C, and D do not align with this standard convention for pendant lights, as they either lack the crosshair (Option A), include unnecessary elements (Option C), or use an unrelated symbol (Option D).
Objectives:
Understand the purpose and components of a reflected ceiling plan (RCP).
Identify and apply standard architectural symbols for lighting fixtures in RCPs.
Differentiate between symbols for various types of ceiling fixtures (e.g., recessed lights, pendants, sprinklers).
What is the MOST efficient way to distribute balanced daylight and diffused light with minimal glare throughout the changing seasons?
Skylights
Light pipes
Side lights
Clerestories
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Distributing balanced daylight with minimal glare throughout the changing seasons requires a strategy that accounts for the sun’s varying angles. Skylights are the most efficient option because they can be designed with diffusing glazing or shading devices to spread light evenly and reduce glare, while their placement on the roof allows them to capture daylight consistently across seasons. Light pipes (Option B) are effective for bringing light into interior spaces but are less efficient for large-scale distribution and glare control. Side lights (Option C) are windows on vertical walls, which can cause glare and are less effective as the sun’s angle changes. Clerestories (Option D) are high windows that provide good daylight but are less versatile than skylights for consistent, season-long performance.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on daylighting strategies.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Skylights, when designed with diffusing glazing, provide the most efficient way to distribute balanced daylight with minimal glare across seasons.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum covers daylighting as a sustainable design strategy, emphasizing skylights for their ability to provide consistent, diffused light while minimizing glare.
Objectives:
Apply daylighting strategies for sustainable design (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
Which method of dyeing is BEST to use for colorfastness and stain-resistant fibers?
Yarn-dyeing
Piece-dyeing
Solution-dyeing
Stock- or fiber-dyeing
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
Colorfastness (resistance to fading) and stain resistance are critical for textiles in high-traffic environments. Solution-dyeing is the best method because the color is added to the polymer solution before the fiber is extruded, locking the color into the fiber’s core. This makes the fiber highly resistant to fading from UV light, cleaning, or wear, and it also enhances stain resistance because the color is integral, not surface-applied. Option A (yarn-dyeing) dyes the yarn before weaving, offering good colorfastness but less stain resistance. Option B (piece-dyeing) dyes the fabric after weaving, making it more prone to fading and staining. Option D (stock- or fiber-dyeing) dyes loose fibers before spinning, which is less consistent and less resistant to fading than solution-dyeing.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on textile manufacturing and performance.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Solution-dyeing is the best method for colorfastness and stain resistance, as the color is integrated into the fiber during manufacturing, making it highly durable.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum covers textile production methods, with solution-dyeing being the preferred choice for durability and performance in commercial applications.
Objectives:
Understand textile manufacturing methods and their impact on performance (IDFX Objective: Material Selection and Specification).
The relative efficacy of lamps is measured in which of the following?
Luminous flux (lm)
Lumens per watt (lpW)
Foot-candles (fc) [lux (lx)]
Light reflectance value (LRV)
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
The relative efficacy of lamps refers to their efficiency in converting electrical energy into visible light, which is measured in lumens per watt (lpW). Lumens measure the total light output, and watts measure the power consumed, so lpW indicates how much light is produced per unit of energy, a key metric for comparing lamp efficiency. Option A (luminous flux, lm) measures total light output but does not account for energy use, so it’s not a measure of efficacy. Option C (foot-candles or lux) measures illuminance (light intensity on a surface), not lamp efficiency. Option D (light reflectance value, LRV) measures how much light a surface reflects, unrelated to lamp efficacy.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on lighting design and technology.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “The relative efficacy of lamps is measured in lumens per watt (lpW), indicating the efficiency of light output per unit of energy consumed.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum includes lighting principles, emphasizing lumens per watt as the standard measure for lamp efficacy, which is critical for sustainable design and energy efficiency.
Objectives:
Understand lighting metrics and their applications (IDFX Objective: Building Systems and Technology).
What is the most sustainable light source for public spaces?
LED
Daylight
Halogen
Fluorescent
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Sustainability in lighting for public spaces involves considering energy efficiency, longevity, and environmental impact. LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting is the most sustainable option because it has the highest energy efficiency (up to 80% more efficient than traditional lighting), a longlifespan (up to 50,000 hours), and contains no hazardous materials like mercury. Option B (daylight) is sustainable but not a “light source” in the traditional sense, as it relies on natural conditions and cannot be controlled for consistent use in public spaces. Option C (halogen) is energy-inefficient and has a short lifespan. Option D (fluorescent) is more efficient than halogen but less so than LED, and it contains mercury, posing environmental disposal concerns.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on sustainable design and lighting.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “LED lighting is the most sustainable light source for public spaces due to its high energy efficiency, long lifespan, and lack of hazardous materials.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes sustainable design principles, with LED lighting being the preferred choice for energy efficiency and environmental impact in public spaces.
Objectives:
Specify sustainable lighting solutions (IDFX Objective: Building Systems and Technology).
A ceiling with a high NRC rating of 0.95 will sound.
Reflect
Distort
Absorb
Reverberate
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
The Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) is a measure of a material’s ability to absorb sound, with values ranging from 0 to 1. A high NRC rating of 0.95 indicates that the ceiling absorbs 95% of the sound that strikes it, significantly reducing echo and reverberation in the space. Therefore, the ceiling will “absorb” sound. Option A (reflect) would occur with a low NRC rating, where sound bounces back into the room. Option B (distort) refers to altering sound quality, which is not directly related to NRC. Option D (reverberate) means sound continues to bounce, which happens with low sound absorption, not with a high NRC.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on acoustics and material properties.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “A ceiling with a high NRC rating, such as 0.95, will absorb sound, reducing reverberation and improving acoustic quality in the space.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum covers acoustics as part of building systems, emphasizing the role of materials with high NRC ratings in sound absorption to create comfortable environments.
Objectives:
Understand acoustic properties of materials (IDFX Objective: Building Systems and Technology).

