When designing a wall with moldings and reveals, what type of detail should be drawn to conveythe depth and profile of the reveals?
Plan detail
Vertical section
Elevation detail
Horizontal section
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Reveals are recessed or projecting features in a wall, often used with moldings to create depth and shadow lines. To convey the depth and profile of reveals, a vertical section is the best type of detail because it shows a cross-sectional view of the wall, illustrating the reveal’s depth, shape, and relationship to the moldings in a vertical plane. This provides contractors with the necessary information to construct the wall accurately. Option A (plan detail) shows a top-down view, which doesn’t convey depth. Option C (elevation detail) shows the wall’s appearance but not the internal profile or depth. Option D (horizontal section) shows a horizontal cut, which is less relevant for vertical features like reveals.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on construction drawings.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “A vertical section is used to convey the depth and profile of wall features such as reveals and moldings, providing a clear view of their construction.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the use of vertical sections to detail wall features, ensuring accurate construction of design elements like reveals.
Objectives:
Develop detailed drawings to communicate wall features (IDFX Objective: Design Communication).
In the image below, which dimension must be changed to meet minimum means of egress requirements?
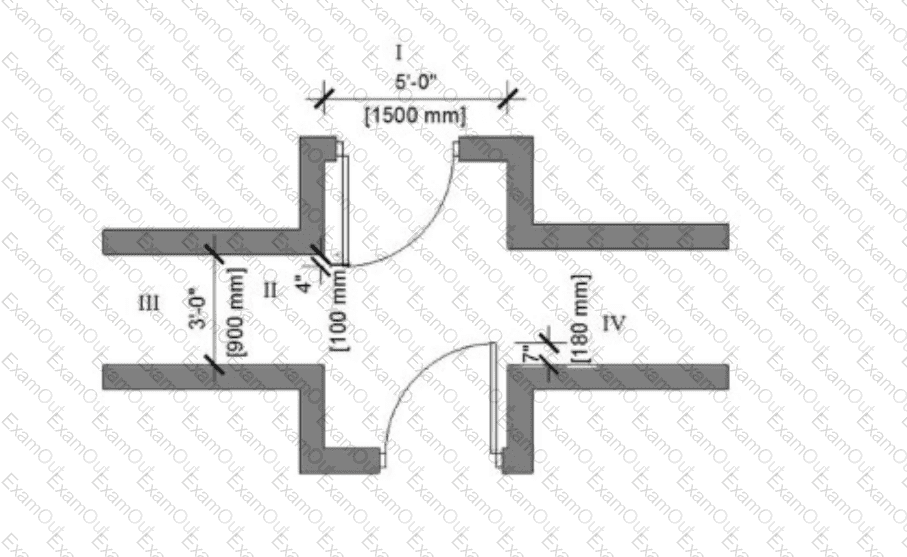
I
II
III
IV
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
The means of egress is a continuous and unobstructed path of travel from any point in a building to a public way, as defined by the IBC. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC Chapter 10 (Means of Egress) specify minimum clear widths for corridors to ensure safe evacuation. For most occupancies, such as business (Group B) or residential (Group R), the minimum clear width for a corridor is 44 inches (1118 mm) in a non-sprinklered building, though it can be reduced to 36 inches (914 mm) in certain cases, such as for smaller occupancies or residential corridors serving fewer than 50 occupants (per IBC Section 1020.2).
Let’s evaluate the dimensions in the image:
Dimension I: 5'-0" [1500 mm]: This is well above the minimum required width of 44 inches (1118 mm) or 36 inches (914 mm), so it meets egress requirements.
Dimension II: 4'-0" [1200 mm]: This is also above the minimum required width, as 4 feet (1200 mm) exceeds both 44 inches and 36 inches.
Dimension III: 3'-0" [900 mm]: This is below the minimum required width. At 3 feet (900 mm), it does not meet the 44-inch (1118 mm) requirement for most corridors, nor the 36-inch (914 mm) minimum for smaller residential corridors. This dimension must be increased to at least 36 inches, and likely 44 inches, depending on the occupancy and number of occupants served.
Dimension IV: 4'-0" [1200 mm]: Like Dimension II, this meets the minimum requirements.
Since Dimension III (3'-0" or 900 mm) does not meet the minimum clear width for a means of egress, it must be changed to comply with building code requirements. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual confirms that corridors must meet these minimum widths to ensure safe evacuation.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is C, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC Section 1020.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 2: Building Codes and Standards): "Corridors must have a minimum clear width of 44 inches (1118 mm) in most occupancies, or 36 inches (914 mm) in certain residential settings, to meet means of egress requirements."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that the minimum clear width for corridors in the means of egress is typically 44 inches, though it can be 36 inches in specific cases. Dimension III (3'-0" or 900 mm) falls below this threshold, making it non-compliant with egress requirements. Increasing this dimension to at least 36 inches, and likely 44 inches depending on the occupancy, ensures safe evacuation.
Objectives:
Understand the minimum clear width requirements for corridors in the means of egress.
Apply building code standards to ensure safe evacuation paths.
If budget is the primary criterion, which method of veneer matching within individual panel faces is best?
Balance match
Running match
Blueprint matched
Balance and center match
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Veneer matching refers to the method used to arrange wood veneer leaves on a panel to achieve a desired aesthetic effect. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and standards from the Architectural Woodwork Institute (AWI) and the Woodwork Institute (WI) outline different veneer matching techniques, each with varying levels of cost and complexity. When budget is the primary criterion, the method that minimizes waste and labor is preferred.
A. Balance match: In a balance match, veneer leaves are matched so that each leaf is of equal width within the panel, creating a symmetrical appearance. This requires careful selection and trimming of veneer leaves to ensure uniformity, which increases labor andmaterial costs due to waste from trimming.
B. Running match: In a running match, veneer leaves are applied sequentially as they come off the flitch (the stack of veneer sheets), without trimming for symmetry. This method allows for slight variations in leaf width and does not require the leaves to be centered or balanced, minimizing waste and labor. It is the least expensive veneer matching method because it uses the veneer as it is cut, making it the best choice when budget is the primary concern.
C. Blueprint matched: Blueprint matching (also called custom matching) involves precisely matching veneer leaves to a specific design or pattern, often across multiple panels or surfaces (e.g., for a seamless look in a high-end conference room). This method is highly labor-intensive and requires custom cutting and sequencing, making it the most expensive option.
D. Balance and center match: This method combines balance matching (equal-width leaves) with center matching (leaves are mirrored around the panel’s centerline). It requires even more precision than a balance match, as the leaves must be both uniform and centered, increasing labor and material costs due to additional trimming and waste.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and AWI standards confirm that a running match is the most cost-effective veneer matching method, as it minimizes waste and labor, making it ideal when budget is the primary criterion.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is B, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles): "A running match is the most cost-effective veneer matching method, as it uses veneer leaves sequentially without trimming for symmetry, minimizing waste and labor costs."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that a running match is the least expensive veneer matching technique because it applies veneer leaves as they come off the flitch, without the need for trimming or precise balancing. This reduces material waste and labor, making it the best choice when budget is the primary concern, compared to more labor-intensive methods like balance match, blueprint matched, or balance and center match.
Objectives:
Understand different veneer matching techniques in interior design.
Select the most cost-effective veneer matching method based on budget constraints.
A designer has been asked to design a chair and table for a preschool. Which human factor is MOST important to consider?
Biometrics
Proxemics
Ergonomics
Anthropometrics
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
Designing furniture for a preschool requires considering the physical dimensions and proportions of young children, which is the focus of anthropometrics—the study of human body measurements. Anthropometrics ensures that the chair and table are appropriately sized for preschool-aged children (e.g., seat height, table height) to promote comfort and safety. Biometrics (Option A) relates to biological identification (e.g., fingerprints), not furniture design. Proxemics (Option B) studies personal space and social distances, which is less critical for sizing furniture. Ergonomics (Option C) focuses on comfort and efficiency but is broader and less specific to sizing than anthropometrics, which is the primary concern for children’s furniture.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on human factors in design.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Anthropometrics is the most important human factor when designing furniture for specific user groups, such as children, to ensure proper sizing and proportion.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes anthropometrics as a key consideration for designing furniture that fits the user’s body, especially for specialized groups like children.
Objectives:
Apply human factors to furniture design (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
A design firm submits a bid for a healthcare project noting that they specialize in healthcare design, when they have only completed education projects that contain one small nurse room per project. This is an example of violating the
Code of ethics
RFP guidelines
Permitting requirements
Health and safety guidelines
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Ethical behavior in interior design is governed by professional codes of conduct, such as the NCIDQ Code of Ethics and codes from organizations like the American Society of Interior Designers (ASID) and the International Interior Design Association (IIDA). These codes emphasize honesty, integrity, and transparency in professional practice.
A. Code of ethics: The NCIDQ Code of Ethics requires designers to be truthful in their professional representations. Claiming to specialize in healthcare design when the firm hasonly completed education projects with minimal healthcare components (e.g., a small nurse room) is a misrepresentation of their expertise. This violates the code of ethics, specifically the principle of honesty, as it could mislead the client about the firm’s qualifications and experience, potentially compromising the project’s outcome.
B. RFP guidelines: A Request for Proposal (RFP) outlines the requirements for submitting a bid, such as project scope and submission format. While misrepresenting expertise might not align with the spirit of an RFP, it is not a direct violation of RFP guidelines unless the RFP explicitly requires proof of healthcare experience, which is not indicated in the question.
C. Permitting requirements: Permitting requirements involve complying with local building codes and regulations to obtain permits for construction. Misrepresenting expertise does not directly violate permitting requirements, as this issue pertains to professional conduct, not regulatory compliance.
D. Health and safety guidelines: Health and safety guidelines relate to designing spaces that protect occupants (e.g., following codes for egress, fire safety). While a lack of healthcare expertise could potentially impact health and safety in a project, the act of misrepresenting expertise is not a direct violation of these guidelines.
The NCIDQ Code of Ethics explicitly prohibits misrepresentation of qualifications, making this a clear violation of ethical standards.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is A, as verified by the NCIDQ Code of Ethics.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ Code of Ethics (Section 1: Responsibility to the Profession): "Interior designers shall not misrepresent their qualifications, experience, or expertise, ensuring honesty in all professional representations to clients and stakeholders."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ Code of Ethics states that designers must be truthful about their qualifications and experience. Claiming to specialize in healthcare design without substantial experience in that area is a misrepresentation, violating the ethical principle of honesty. This could mislead the client and affect the project’s success, making it a clear ethical violation.
Objectives:
Understand ethical standards in interior design practice.
Identify behaviors that violate the NCIDQ Code of Ethics.
A chair requires 6 yards [5.5 m] of fabric. Based on using a COM striped fabric with a 6" [152 mm] horizontal repeat, how is the quantity BEST calculated?
Order 15% more fabric to cover the shortfall.
Have the fabric manufacturer perform the calculation.
Have the furniture manufacturer perform the calculation.
Order 8 yards [7.3 meters] of fabric to cover the shortfall.
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
When calculating fabric quantity for upholstery, especially with a patterned fabric like a striped fabric with a 6" horizontal repeat, the repeat must be accounted for to ensure proper pattern matching. A horizontal repeat means the pattern repeats every 6 inches across the width of the fabric, which can lead to additional fabric waste during cutting to align the stripes correctly on the chair. The base requirement of 6 yards assumes a plain fabric with no repeat, but with a patterned fabric, more fabric is typically needed. The best practice is to have the furniture manufacturer perform the calculation, as they have the expertise to account for the specific chair’s dimensions, the fabric’s repeat, and the cutting layout to minimize waste while ensuring proper pattern alignment. Option A (ordering 15% more) is a rough estimate but not precise. Option B (fabric manufacturer) is incorrect, as they don’t have the chair’s specific details. Option D (ordering 8 yards) is a guess and may not be accurate.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on material calculations and specifications.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “For patterned fabrics with repeats, thefurniture manufacturer should calculate the required yardage to account for pattern matching and cutting requirements.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the importance of accurate material calculations, particularly for patterned fabrics, and recommends relying on the furniture manufacturer for precise yardage estimates.
Objectives:
Calculate material quantities for upholstery (IDFX Objective: Material Selection and Specification).
What is the MOST important reason to review an organization's current furniture standards?
To determine the condition of the furniture for feasibility of reuse
To determine the dimensions of the existing furniture used in the current design
To determine how much furniture will be moved during your remodeling of the space
To determine whether the current furniture is functioning adequately for the client's needs
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Reviewing an organization’s current furniture standards is a critical step in the programming phase to assess whether existing furniture can be reused in the new design, which impacts budget, sustainability, and project timeline. The most important reason is to determine the condition of the furniture for feasibility of reuse, as this directly affects whether the furniture can meet the project’s functional and aesthetic goals. Option B (dimensions) is a secondary concern, as dimensions can bemeasured later if reuse is feasible. Option C (how much furniture will be moved) is logistical, not a primary reason for review. Option D (functioning adequately) is important but less critical than assessing physical condition for reuse, which is a foundational decision.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on programming and furniture assessment.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Reviewing current furniture standards is primarily to assess the condition of existing furniture for potential reuse in the new design.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum highlights the importance of evaluating existing resources during programming to make informed decisions about reuse, aligning with sustainable design practices.
Objectives:
Assess existing conditions during programming (IDFX Objective: Programming and Site Analysis).
A retired couple is renovating their house and wants to plan for aging in place. Which of the following should be recommended?
Flush thresholds, grab bars, and lever handles
ADA-height water closet, 30" [762 mm] clear door width, and walk-in shower
Low-cost, low-maintenance products, low-pile carpeting, and additional grab bars
Wheelchair clearance at master bath, hardwood flooring, and ADA-approved wall sconces
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Aging in place refers to designing a home to allow individuals to live independently as they age, accommodating potential mobility and accessibility challenges. Flush thresholds eliminate tripping hazards, grab bars provide support in areas like bathrooms, and lever handles are easier to operate for those with reduced hand strength or dexterity—key features for aging in place. Option B includes an ADA-height water closet and walk-in shower, which are beneficial, but the 30" clear door width is insufficient (ADA requires 32" minimum). Option C focuses on low maintenance but lacks critical accessibility features like flush thresholds. Option D includes wheelchair clearance and hardwood flooring, but ADA-approved wall sconces are not a primary concern for aging in place.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on universal design and accessibility.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Aging-in-place design includes features such as flush thresholds to eliminate tripping hazards, grab bars for support, and lever handles for ease of use.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes universal design principles, which include features that support aging in place by enhancing safety and accessibility. Flush thresholds, grab bars, and lever handles directly address common aging-related challenges.
Objectives:
Apply universal design principles to residential spaces (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
A material produced without increasing the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere is
Biodegradable
Carbon neutral
Cradle-to-cradle
Low-embodied energy
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Sustainability in interior design involves understanding the environmental impact of materials, including their production, use, and disposal. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and sustainability standards (e.g., from the U.S. Green Building Council [USGBC] and LEED) define key terms related to environmentally responsible materials.
A. Biodegradable: A biodegradable material can break down naturally over time through biological processes, but this does not necessarily mean it is produced without increasing greenhouse gas emissions. The production process might still release significant emissions.
B. Carbon neutral: A carbon-neutral material is produced in a way that results in no net increase in greenhouse gas emissions. This is achieved by balancing emissions (e.g., from manufacturing) with carbon offsets or by using processes that do not emit greenhouse gases. This directly aligns with the definition in the question.
C. Cradle-to-cradle: Cradle-to-cradle refers to a design philosophy where materials are designed to be reused or recycled indefinitely, minimizing waste. While this approach often reduces environmental impact, it does not specifically address greenhouse gas emissions during production.
D. Low-embodied energy: Low-embodied energy materials require less energy to produce, which can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but this term focuses on energy use rather than the net impact on greenhouse gases. A low-embodied energy material might still result in some emissions.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual defines carbon neutrality as a process that does not increase greenhouse gas emissions, making this the most accurate answer for the question. This aligns with sustainability goals in interior design, such as those outlined in LEED certification.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is B, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFXReference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 9: Sustainable Design): "A carbon-neutral material is one that is produced without a net increase in greenhouse gas emissions, either through emission-free production or by offsetting emissions."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that carbon neutrality specifically refers to a material or process that does not contribute to the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which matches the question’s definition. This distinguishes it from other sustainability terms like biodegradable, cradle-to-cradle, and low-embodied energy, which have different focuses.
Objectives:
Understand key sustainability terms in interior design.
Identify materials that align with specific environmental goals, such as carbon neutrality.
A designer was not able to be present during the time of a mock-up walk-through. What can the designer provide to the users to capture their comments and concerns?
Case study
Questionnaire
Summary report
Casual observation
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
A mock-up walk-through involves reviewing a physical or virtual prototype of a design (e.g., a sample room or installation) to gather feedback from users or stakeholders. If the designer cannot be present, they need a method to collect structured feedback from participants. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual outlines methods for gathering user input during the design process, particularly during reviews like mock-ups.
A. Case study: A case study is a detailed analysis of a past project or situation, often used for research or precedent studies. It is not a tool for capturing user feedback during a mock-up walk-through, as it is not interactive or designed for real-time input.
B. Questionnaire: A questionnaire is a structured form with questions designed to gather specific feedback from users. The designer can provide a questionnaire to participants of the mock-up walk-through, asking targeted questions about their experience (e.g., "Does the layout meet your needs?" "Are there any concerns with the materials?"). This allows users to document their comments and concerns in a systematic way, which the designer can review later. It is the most appropriate tool for capturing feedback in the designer’s absence.
C. Summary report: A summary report is a document prepared by the designer or a team member to summarize findings or feedback after an event like a walk-through. It is an output, not a tool for capturing user input, so it is not suitable for this purpose.
D. Casual observation: Casual observation involves informally watching users interact with a space, typically by the designer or a team member. Since the designer is not present during the walk-through, this method is not feasible, and it does not provide a structured way for users to record their feedback.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual recommends using a questionnaire to gather structured feedback from users when the designer cannot be present, ensuring that comments and concerns are documented systematically for later review.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is B, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 3: Programming and Space Planning): "When a designer cannot be present for a mock-up walk-through, providing a questionnaire allows users to capture their comments and concerns in a structured format for later review."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that a questionnaire is an effective tool for collecting user feedback when the designer is absent, as it provides a structured format for users to record their thoughts. This ensures that the designer can gather detailed, actionable input about the mock-up, making it the best method compared to a case study, summary report, or casual observation.
Objectives:
Understand methods for gathering user feedback in the design process.
Identify the appropriate tool for capturing feedback during a mock-up walk-through.

