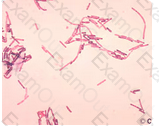
The organisms in this image are demonstrating a gram-variable phenomenon. For the most part, the organisms are staining primarily gram-negative, however, on the tips of some of the rods, there is a gram-positive staining morphology. This can be defined as gram-variable.
Which of the following best describes the organisms seen in this illustration:
Each of the drugs/drug classes listed above have been known to cause drug-induced hemolytic anemia, although cephalosporins are the MOST COMMON cause. Cephalosporins can cause drug-induced hemolytic anemia when a patient produces antibodies to the particular cephalosporin drug in the presence of red blood cells. The drugs can alter the membrane appearance of the red blood cells, causing the body to mistake them as foreign. Complement becomes activated due to these antibodies; red cells are then destroyed causing hemolytic anemia. Dark urine, caused by intravascular hemolysis, is one of the most common symptoms associated with this condition.
Which one of the following drugs/drug classes is the MOST COMMON cause of drug-induced hemolytic anemia?
FFP that has been thawed at 30 - 37oC and maintained at 1 - 6oC must be transfused within 24 hours. In contrast, "Thawed Plasma" can be used for up to 5 days as a replacement therapy for patients requiring stable clotting factors. Keep in mind that these are two different component types and you are asked about FFP.
Blood Bank
FFP that has been thawed at 30 - 37oC and maintained at 1 - 6oC must be transfused within ___________ after it has been thawed.
An automated method for measuring chloride which generates silver ions in the reaction is called:
Isolation and detection of Gardnerella vaginalis from vaginal secretions is improved by which of the following?
This patient is most likely suffering from an immediate-acting coagulation inhibitor; most commonly, lupus anticoagulant. Notice that the addition of normal pooled plasma does not correct upon initial or incubated mix, which means that the inhibitor is not time or temperature-dependent.
Factor VIII is not the correct answer as a factor deficiency would have corrected upon the addition of normal pooled plasma. Factor VII is not the correct answer, as the aPTT assay does not account for factor VII activity or concentration.
The laboratorian completed the mixing study ordered for John Doe. The results are as follows:
Initial aPTT result: 167 seconds
Initial 1:1 Mix with Normal Pooled Plasma: 158 seconds
Incubated 1:1 Mix with Normal Pooled Plasma: 150 seconds
Which of the choices below would most likely explain the results for this patient?
Serum alkaline phosphatase is produced in the bone, intestine, and the placenta- but not in the brain.
Serum alkaline phosphatase activity is derived from all of the following organs except:
The renal threshold is the maximum amount of a substance that the kidney can prevent from entering into the urine.
UA & body fluids
The renal threshold is best described as:
Most anticoagulants in blood collectiong tubes prevent clotting by:
Question options:
These are tyrosine crystals

Urinalysis & Other Body Fluids
True or false? Cystine crystals are present on this slide.
Glucose positive, Maltose positive, Lactose negative and Sucrose negative is the correct answer since Neisseria meningitides causes Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome and it is positive only for glucose and maltose.
An autopsy of a 1-year-old female admitted to the emergency room 4 hours prior to her death revealed Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. Blood and nasopharyngeal cultures taken prior to her death should reveal an oxidase-positive, Gram-negative diplococcus with the following biochemical reactions:
Gram-positive bacteria retain the primary crystal violet stain that is applied in the Gram stain because of the cross-linking of the thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell walls. Their cell walls contain less lipids than that of a gram-negative bacteria, and this reduces the permeability of their cell wall to the organic solvents that are used as a decolorizer. When the counterstain is added, it may enter the gram-positive cell, but does not change the color of the cells.
A thick peptidoglycan is MOST often associated with which of the following types of bacteria?
Angiotensin is an oligopeptide in the blood that causes vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, and release of aldosterone from the adrenals.
A major action of angiotensin II is:
The difference between plasma and serum is that:
Hypochromia can best be described as:

