Using the information provided in the additional information, answer the following question on building a change analytics strategy.
Do the measures to be monitored by the CEO represent appropriate ‘leading’, result-oriented measures for the effectiveness of the change interventions?
No, because ‘leading’ metrics must be based on quantitative data.
No, because these metrics are lagging, output-focused indicators.
Yes, because these indicators will identify if UniCo sales continue to decline.
Yes, because these metrics monitor benefits realization at senior management level.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step Explanation:
Context from the UniCo Scenario:
The CEO is tasked with overseeing the change analytics strategy to assess the effectiveness of the transformation program at UniCo. The focus on market share, customer awareness, and sales performance represents metrics primarily indicative of past outcomes rather than predictive trends. These are "lagging indicators" because they measure results that have already occurred rather than helping to predict future performance.
Analysis of the Answer Options:
A. No, because ‘leading’ metrics must be based on quantitative data.
Why Incorrect:While leading indicators are often quantitative, this is not a definitive requirement. Leading indicators can include qualitative metrics, such as customer sentiment or readiness for change, which forecast future outcomes.
B. No, because these metrics are lagging, output-focused indicators.
Why Correct:The CEO's metrics—market share, customer awareness, and sales of mobile applications—are retrospective and assess the outcomes of past strategies rather than providing actionable insights for proactive decision-making. This makes them lagging indicators that are unsuitable as "leading, result-oriented measures." Leading indicators would include forward-looking metrics, such as staff readiness, customer pre-orders, or app engagement metrics.
C. Yes, because these indicators will identify if UniCo sales continue to decline.
Why Incorrect:While these metrics may identify declining sales, they are not suitable for preempting or preventing such issues. They lack predictive value and fail to inform actions needed to drive improvements proactively.
D. Yes, because these metrics monitor benefits realization at senior management level.
Why Incorrect:Although these metrics are useful for benefits realization, they are not sufficient as "leading" indicators. They reflect past performance rather than informing management on whether the change program is on track to achieve its intended future benefits.
Why B Is the Best Answer:
Distinction Between Leading and Lagging Indicators:
Leading indicators provide predictive insights to guide decision-making and corrective actions, while lagging indicators assess outcomes already achieved. The CEO's metrics fall into the latter category, as they focus on market share and customer awareness, which reflect results of past efforts.
Relevance to Change Analytics Strategy:
A robust change analytics strategy must include metrics that enable proactive adjustments. For example, measuring customer engagement during app trials or employee training completion rates would offer actionable insights into the program's progress.
Alignment with AgilePM and Change Management Practices:
AgilePM emphasizes continuous monitoring and adaptation using predictive metrics to guide successful delivery. The CEO's reliance on lagging indicators does not align with this proactive approach.
References to AgilePM Framework:
Metrics in Change Programs:
The AgilePM framework recommends using KPIs that drive decisions, emphasizing early indicators of potential issues. This ensures that leadership can take corrective actions during the program rather than after its completion. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 7: Governance and Control)
Benefits Realization and Leading Indicators:
Leading indicators are essential for tracking progress toward benefits realization. Focusing on lagging metrics risks missing early warning signs of misalignment. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 11: Measuring Success)
Two Sales staff members appear to have lost energy for the change process and did not attend recent change meetings. When questioned, they said they were so overwhelmed by the number of changes in systems, materials, technical knowledge, and processes that they couldn’t deal with any more.
Which 2 actions by the Sales Director are the MOST appropriate when responding to this type of resistance from staff?
Find out which elements could remain unchanged so that future sales are unaffected.
Add personal staff targets to ensure that the changes in the sales operations are continued.
Assign the staff members to projects outside of this change, to prevent them undermining the changes needed.
Consider limiting the changes to those that are related to each other during each iteration of change in sales.
Ensure these staff members are rewarded for raising issues with the implementation.
The Answer Is:
A, DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step Explanation:
1. Analysis of the Scenario: The staff members are experiencing change fatigue due to the overwhelming number of adjustments in systems, processes, and technical knowledge. This fatigue often arises during significant organizational transformations like the one UniCo is undergoing, where staff members feel unprepared or unsupported to handle multiple changes.
Agile Project Management (AgilePM) emphasizes adaptive change management, where incremental changes are planned and staff are supported throughout transitions. The Agile approach also recommends prioritizing manageable changes to prevent burnout.
2. Option Evaluation:
A. Find out which elements could remain unchanged so that future sales are unaffected.
Explanation: Maintaining some consistency during the change process can help overwhelmed staff feel less stressed. By preserving elements that do not directly need alteration, employees can focus on critical areas that need improvement without feeling they are losing their entire work foundation.
Reference from AgilePM: Agile emphasizes incremental delivery and the need to protect stability where possible during change efforts. This is key to balancing innovation with operational continuity.
Why Correct: This approach reduces unnecessary change and helps staff focus on priority areas, reducing resistance and fatigue.
B. Add personal staff targets to ensure that the changes in the sales operations are continued.
Explanation: While setting targets can be a motivational tool, introducing personal targets during a period of resistance or overwhelm can exacerbate stress and lead to further disengagement.
Why Incorrect: AgilePM advocates for team empowerment and reducing pressure during resistance phases. Adding personal targets does not address the root cause of change fatigue.
C. Assign the staff members to projects outside of this change, to prevent them undermining the changes needed.
Explanation: Removing staff from the process entirely may appear to prevent further resistance, but it also excludes them from adapting to and learning the new processes. Such an action can lead to further disengagement and even attrition.
Why Incorrect: AgilePM encourages collaboration and engagement rather than sidelining staff during organizational changes.
D. Consider limiting the changes to those that are related to each other during each iteration of change in sales.
Explanation: By grouping related changes, staff can focus on cohesive elements rather than being overwhelmed by disjointed changes. This iterative approach aligns with AgilePM principles, which emphasize breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable chunks.
Reference from AgilePM: The iterative and incremental approach in Agile ensures that teams manage workload effectively while focusing on high-priority changes.
Why Correct: Limiting and organizing changes into related areas ensures clarity, reduces cognitive load, and builds confidence among the sales staff.
E. Ensure these staff members are rewarded for raising issues with the implementation.
Explanation: Rewarding staff for raising concerns is a positive reinforcement tactic. However, it does not address the root issue of change fatigue. While this could encourage openness, it does not reduce the overwhelming workload or clarify processes.
Why Incorrect: Although AgilePM emphasizes transparency, this approach does not mitigate the resistance caused by change overload.
3. Final Recommendation:
Correct Actions: A and D effectively address the root causes of resistance (overwhelm and fatigue) by maintaining stability where possible and grouping related changes into iterations.
These solutions align with AgilePM's focus on iterative change, manageable workloads, and staff engagement.
Incorrect Actions (B, C, E): These options either fail to address the root problem or risk disengagement further.
References:
AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter on Stakeholder Engagement and Managing Change.
AgilePM Principles: Incremental Delivery and Focus on the Business Need.
Agile Change Management Strategies for Overcoming Resistance.
Using the information provided in the additional information, answer the following question on building a change analytics strategy.
Do the measures to be monitored by the Sales Director represent appropriate measures for assessing change readiness?
No, because change readiness measures should consist of mostly quantitative measures.
No, because change readiness should be monitored using the change programme plan.
Yes, because the Sales Director has identified measures that require new data sources.
Yes, because these metrics provide opinions collected via mostly qualitative methods.
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step Explanation:
Context from the UniCo Scenario:
The Sales Director's metrics focus on assessing the readiness of the sales team to adapt to new systems, such as their confidence levels and ability to demonstrate mobile application features. This ensures that the team is prepared for the transformation UniCo is undertaking. Change readiness is often a combination of quantitative and qualitative insights, especially for understanding how prepared and skilled staff are to adopt the new processes.
Analysis of the Answer Options:
A. No, because change readiness measures should consist of mostly quantitative measures.
Why Incorrect:Change readiness measures are not limited to quantitative methods. Qualitative measures, such as surveys and confidence levels, are essential for evaluating readiness in transformation programs. By relying on both, the organization gets a more holistic understanding.
B. No, because change readiness should be monitored using the change programme plan.
Why Incorrect:The change program plan provides an overarching structure, but it is not the sole method for monitoring readiness. The Sales Director has appropriately identified new data sources and targeted measures (e.g., surveys), which are crucial for assessing readiness directly.
C. Yes, because the Sales Director has identified measures that require new data sources.
Why Correct:The Sales Director’s plan involves surveys to gather fresh data, such as confidence levels and proficiency in new systems. These are leading indicators for change readiness and provide actionable insights into team preparedness. Using new data sources ensures the measures are tailored to the transformation objectives, making them appropriate for assessing readiness.
D. Yes, because these metrics provide opinions collected via mostly qualitative methods.
Why Incorrect:While qualitative methods such as surveys are used, this answer implies an over-reliance on qualitative data. Effective change readiness strategies should balance both qualitative (e.g., confidence levels) and quantitative (e.g., percentage of staff trained) insights.
Why C Is the Best Answer:
Focus on Leading Indicators:
The Sales Director’s identified measures focus on readiness and forward-looking insights, such as proficiency and confidence, which are key aspects of preparing staff for the change.
Incorporating New Data Sources:
The use of surveys as new data sources ensures that the metrics are specific to the change initiative and capture real-time readiness levels, making them highly relevant.
Alignment with AgilePM Principles:
AgilePM emphasizes the importance of gathering real-time, actionable data to monitor progress and adapt strategies. The Sales Director's approach aligns with this principle by introducing targeted metrics for readiness.
References to AgilePM Framework:
Change Readiness Assessment:
AgilePM highlights the importance of continuously assessing readiness to ensure teams can adapt and contribute effectively to change programs. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 7: Governance and Control)
Combining Data Sources:
Balancing qualitative and quantitative methods is a best practice for ensuring that readiness measures are comprehensive and actionable. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 11: Measuring Success)
When receiving instruction on practical skills, which approach is MOST valuable to the learner?
Practicing new skills until consistency is achieved.
Observing repeated demonstrations of the skill by the instructor.
Group discussion of how to learn the new skills.
Presentation of how the new skills relate to the organizational change.
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Practical skill acquisition focuses on hands-on practice to ensure learners achieve mastery and consistency. This is central to Gagné's Nine Events of Instruction, which emphasize active learning strategies.
1. Relevance of Practice in Gagné’s Model:
Gagné's Event 6: Elicit Performance (Practice) highlights that learners must perform the skills themselves to solidify learning.
Practical application is critical to achieving competence, especially for motor or procedural skills. It allows learners to identify gaps and refine their performance through repetition.
2. Why Option A is Correct:
Practicing skills ensures that learners can consistently perform the task correctly. Repeated application:
Reinforces memory.
Builds muscle memory for physical tasks.
Promotes confidence and accuracy.
Consistency is the key indicator of mastery for practical skills.
3. Analysis of Other Options:
Option B: Observing repeated demonstrations of the skill by the instructor.
Observing demonstrations is useful for understanding, but it does not substitute for hands-on practice. Learners must engage actively to develop the skills themselves.
Option C: Group discussion of how to learn the new skills.
Discussion may help learners understand the steps or importance of the skill but does not directly contribute to skill mastery.
Option D: Presentation of how the new skills relate to the organizational change.
While this provides context, it does not help learners physically or cognitively practice the skill.
4. Practical Example:
In a training session for operating new machinery, learners achieve the best outcomes by practicing with the equipment until they can operate it confidently and consistently.
5. Reference to Gagné’s Model:
Event 6: Elicit Performance (Practice) emphasizes the importance of active learner participation to reinforce learning and ensure skill mastery.
Which stakeholder should be placed within the 'primary' segment?
Industry-related professional associations, whose strong opinions and judgments about industry trends reach wide audiences.
The Utilities company, who selected UniCo to provide services but will dictate their specific requirements and operational terms.
The Operations Director, who will consult with others to understand their requirements and decide on the approach.
The UniCo investors, who have provided the finance to support the innovation and improvement needed to recover profitability.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step Explanation:
Understanding Stakeholder Segmentation in Agile Project Management
Stakeholders are segmented based on their level of influence, interest, and involvement in the project. The 'primary' segment consists of stakeholders who are directly impacted by the project’s outcomes or who have the highest influence over its success.
The primary stakeholders often have the power to determine project requirements or outcomes and require significant attention from the project team.
Option Analysis
A. Industry-related professional associations
While their opinions influence industry trends, they are not directly involved in UniCo's project or operational terms. They fall under the secondary segment as their influence is indirect and focuses on broader trends rather than specific deliverables.
Incorrect.
B. The Utilities company
The Utilities company is UniCo’s customer, directly dictating specific requirements and operational terms. As such, they hold significant influence and impact on the project’s success. They represent a key stakeholder group in the primary segment, as satisfying their requirements is essential for UniCo’s strategic goals.
Correct.
C. The Operations Director
The Operations Director is an internal stakeholder involved in decision-making and execution. While they play a crucial role, they are part of the project delivery team rather than an external primary stakeholder. Therefore, they do not belong in the 'primary' segment.
Incorrect.
D. The UniCo investors
Investors are critical for funding and overall company strategy but are not directly involved in defining project requirements or operational terms for this specific initiative. They fall under the key supporting stakeholders rather than the 'primary' segment.
Incorrect.
Why B is the Correct Answer
The Utilities company directly dictates project requirements and operational terms. Their satisfaction is crucial for the project's success and aligns with Agile principles emphasizing delivering value to the customer. This makes them a part of the 'primary' stakeholder segment.
References:
AgilePM Foundation Handbook, Chapter 3: Stakeholder Engagement.
Agile Business Consortium: Stakeholder Influence and Segmentation.
PMBOK Guide, Chapter 13: Stakeholder Management – Primary and Secondary Stakeholders.
Which 'event' BEST offers the opportunity to connect learning to the wider change initiative?
Assess performance, testing whether the instruction has been effective.
Provide guidance to support the learning process, such as real-life examples, stories, and discussion.
Remind the learners of what they already know that is relevant to the current instruction (facts, rules, procedures, or skills).
Provide good learning feedback that allows learners to evaluate their practice.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Gagné's Nine Events of Instruction provide a framework for designing learning activities. When connecting learning to a broader change initiative, the focus should be on guidance and context that ties the learning objectives to real-life applications and organizational goals.
1. Why Guidance is Critical in Change Initiatives:
Providing real-life examples, stories, and discussions enables learners to:
See how the instruction aligns with the organizational changes.
Understand the practical relevance of their learning.
Connect new skills or knowledge to the broader goals of the organization, ensuring alignment with the change initiative.
This corresponds to Event 4: Provide Learning Guidance in Gagné's model, which emphasizes the use of supportive elements to enhance understanding and contextualize learning.
2. Why Option B is Correct:
By incorporating real-life examples and stories, the instruction becomes relatable and directly linked to the learner’s role in the change initiative.
For example, during a training session on new software, discussing how it will streamline workflows within the organization provides clarity and motivation.
3. Analysis of Other Options:
Option A: Assess performance, testing whether the instruction has been effective.
Assessment ensures learning effectiveness but does not inherently connect the learning to the broader change initiative. It focuses on evaluating outcomes rather than providing context.
Eliminate.
Option C: Remind the learners of what they already know that is relevant to the current instruction.
While activating prior knowledge is valuable (Event 3), it focuses on linking new learning to existing knowledge rather than to the broader organizational changes.
Eliminate.
Option D: Provide good learning feedback that allows learners to evaluate their practice.
Feedback helps refine understanding and improve performance (Event 5), but it does not necessarily provide the connection to the wider change initiative.
Eliminate.
4. Practical Example:
Suppose UniCo is training its staff to adopt new processes for mobile applications. The facilitator might include real-life success stories from similar industries, showing how adopting these practices helped achieve growth and customer satisfaction. This ties learning to the organizational change goals.
5. Reference to Gagné’s Model:
Event 4: Provide Learning Guidance emphasizes supporting learners with tools and context that deepen understanding and relevance.
Using the additional information provided for this question in the Scenario Booklet, answer the following question about the actions the Sales Director should
take to develop an effective Sales management team, according to the five dysfunctions that characterize an ineffective team identified by Patrick Lencioni.
Lines 1 to 4 in the table below consist of an assertion statement and a reason statement. For each line identify the appropriate option, from options A to E, that applies.
Each option can be used once, more than once or not at all.

The Answer Is:
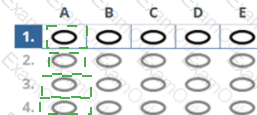
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step Explanation:
1. Assertion: The Sales Director’s plan is an appropriate way to address the team dysfunction exhibited in Point (1).
Reason: Having a clear shared commitment to the outputs required of them is necessary for a team to be truly effective.
Analysis:Patrick Lencioni's first dysfunction is the absence of trust. Point (1) outlines issues of commitment due to internal conflicts and lack of alignment. The Sales Director’s plan addresses these issues by bringing the team together for a shared vision and commitment. This ensures clarity of expectations and alignment.
Since the assertion and reason are true and explain the behavior, the correct answer is A.
2. Assertion: The Sales Director’s plan is an appropriate way to address the team dysfunction exhibited in Point (2).
Reason: Team working is enhanced by taking constructive action to avoid debates that risk damaging team relationships.
Analysis:Dysfunction (2) addresses fear of conflict. The Sales Director plans to clarify individual roles and responsibilities. This proactive action avoids unnecessary debates about overlapping work and ensures constructive conflict resolution, essential for building relationships.
Since the assertion and reason are true and explain the behavior, the correct answer is A.
3. Assertion: The Sales Director’s plan is an appropriate way to address the team dysfunction exhibited in Point (3).
Reason: Team leaders should define the problem-solving and decision-making processes for their teams to support commitment to change tasks.
Analysis:Point (3) highlights a lack of accountability, one of the dysfunctions. The Sales Director’s plan acknowledges unfulfilled tasks and seeks joint agreement on future actions. This creates structured accountability by defining processes and ensuring follow-through on commitments.
Since the assertion and reason are true and explain the behavior, the correct answer is A.
4. Assertion: The Sales Director’s plan is an appropriate way to address the team dysfunction exhibited in Point (4).
Reason: Teams that have trust amongst the members when collaborating, tend to make more efforts to avoid letting other team members down.
Analysis:Dysfunction (4) is inattention to results. Point (4) highlights resistance to adopting the required changes for selling mobile applications. The plan to cross-collaborate with other departments builds trust and understanding among team members, ensuring shared accountability for results.
Since the assertion and reason are true and explain the behavior, the correct answer is A.
References:
Patrick Lencioni's Five Dysfunctions of a Team: A Leadership Fable.
Analysis of team collaboration and management strategies applied to organizational development.
One member of the Customer Services team has been chatting informally to some Sales co-workers. They felt that the Sales process changes are causing more work for Customer Services and that the whole customer experience has now been compromised.
Which 2 actions by the Sales Director are the MOST appropriate when responding to this type of resistance?
Do nothing and allow the informal view to circulate, knowing it will eventually be proved wrong.
Include the member of Customer Services in the planning of the sales process changes to reduce disruption.
Invite Sales staff to help with planning the next phase of internal Sales training for the process changes.
Counter the informal views by inviting the Change Manager to explain the changes at the next Sales staff meeting.
Revisit the Stakeholder mapping work to ensure that the engagement of parties affected by the Sales changes is accurate.
The Answer Is:
B, DExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step Explanation:
Context from UniCo Scenario:
The Sales staff at UniCo are resistant to changes related to the company's new strategic focus on mobile applications. The concern raised here involves Customer Services staff feeling overburdened and Sales staff perceiving the changes as impacting customer experience negatively. This type of resistance reflects miscommunication, lack of engagement, and uncertainty—key elements that require addressing.
Analysis of Each Option:
A. Do nothing and allow the informal view to circulate, knowing it will eventually be proved wrong.
This is not appropriate as it fails to address resistance proactively, which may lead to low morale, increased misunderstandings, and further negativity among teams. The AgilePM framework emphasizes collaboration and communication over passive approaches to resistance management.
Rejected.
B. Include the member of Customer Services in the planning of the sales process changes to reduce disruption.
This approach directly engages the affected parties (Customer Services staff) by involving them in planning. It fosters ownership, reduces resistance, and creates solutions that are practical and inclusive. Aligning this action with AgilePM principles ensures engagement of stakeholders in the change process, which is key to minimizing disruption.
Selected.
C. Invite Sales staff to help with planning the next phase of internal Sales training for the process changes.
While involving Sales staff is useful, the issue here centers around Customer Services staff concerns about disruption and added workload. This option fails to address the root cause of the resistance.
Rejected.
D. Counter the informal views by inviting the Change Manager to explain the changes at the next Sales staff meeting.
This action ensures that informal resistance is addressed through formal communication channels. By providing clarity and transparency about the Sales process changes, this approach prevents misunderstanding and builds alignment across teams. AgilePM emphasizes the importance of clear communication to manage resistance.
Selected.
E. Revisit the Stakeholder mapping work to ensure that the engagement of parties affected by the Sales changes is accurate.
Stakeholder mapping is a strategic action but may not immediately address the informal resistance in question. The issue at hand requires immediate communication and engagement rather than long-term structural adjustments.
Rejected.
Why B and D Are Correct:
Inclusion in Planning (B):
Including Customer Services staff in planning ensures their concerns are heard and integrated into the solutions. This aligns with AgilePM’s focus on stakeholder collaboration and engagement to reduce resistance.
Clear Communication via the Change Manager (D):
Inviting the Change Manager provides an authoritative and transparent explanation of the changes. This aligns with AgilePM’s emphasis on using regular communication to manage resistance and mitigate informal, negative narratives.
References to AgilePM Framework:
Stakeholder Engagement:
AgilePM highlights involving stakeholders in planning as essential for building trust and reducing resistance to change. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 9: Stakeholder Engagement)
Transparent Communication:
AgilePM emphasizes clarity and frequent communication to manage resistance effectively. Using formal channels ensures alignment and prevents misinformation from spreading. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 11: Managing People)
Proactive Resistance Management:
AgilePM promotes proactive actions (like engaging affected staff and using formal communication) rather than passive approaches to manage resistance. (AgilePM Practitioner Guide, Chapter 12: Change Management)
Xan Insurance Company is a friendly company with no separate private offices
for individual managers. Staff members prefer to wander around the office
space and have one-to-one chats rather than use email or have lots of
meetings.
What action should the Project Manager take when planning for effective
communication throughout the Web project?
Identify those individuals with power and influence over the project and
what information they require.
No action is required as the existing form of spontaneous informal
communication is suitable for all project level and Solution Development
Team members.
As this is already common practice, assume all Solution Development
Team members have effective communication skills.
Mandate the use of email so that all communications are recorded for
future reference.
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
The most effective action the Project Manager should take to ensure effective communication throughout the Web project at Xan Insurance Company is:
A. Identify those individuals with power and influence over the project and what information they require.
In any project, especially within an Agile framework, understanding the stakeholders' landscape is crucial for effective communication management. Identifying key individuals with power and influence over the project helps tailor communication strategies to ensure that critical information is shared appropriately, decisions are facilitated efficiently, and stakeholder engagement is maintained. While the company's culture of informal communication can be advantageous for day-to-day interactions, structured communication is essential for project governance, risk management, and decision-making processes. This approach allows the Project Manager to ensure that all stakeholders are kept informed according to their needs and the project's requirements, balancing the informal communication culture with the need for formal communication where necessary.
An external web developer is to be contracted to create the new coffee bar
insurance area on the existing web site. The chosen web developer will only
agree to work on a 'fixed price for a fixed specification' contract.
What action should the Project Manager take?
Ensure the later elements of the project reflect the most valuable features
of the product being built by the contractor.
Agree to a 'fixed price for a fixed specification' contract with a requirement
for the web developer to provide daily progress reports.
Refuse to employ the chosen web developer as this is not an Agile
approach to project management.
Divide the work into component parts to ensure the web developer is
focused on, and is paid to deliver, only what is specified for each
component.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
Dividing the work into smaller, well-defined component parts is a strategic approach when dealing with fixed-price contracts within an Agile framework. This method allows for greater flexibility and adaptability, as each component can be specified in detail, making it clear what the external web developer is responsible for delivering. This approach aligns with Agile principles by enabling incremental development and delivery, allowing for adjustments and refinements to be made as the project progresses and more information becomes available.
References:
In Agile Project Management, particularly when incorporating external resources or contractors, breaking down the project into smaller, manageable parts is a common practice. This not only facilitates better control and tracking of progress but also ensures that the project remains adaptable, with the capacity to respond to changes in requirements or priorities. This approach is in line with Agile methodologies that emphasize iterative development, customer collaboration, and responding to change over following a fixed plan.

