Given the code fragment:

Which code fragment, when inserted at line 7, enables printing 100?
You want to create a singleton class by using the Singleton design pattern.
Which two statements enforce the singleton nature of the design? (Choose two.)
Given:

From what threading problem does the program suffer?
Given:

and the code fragment:

What is the result?
Given:

What is the result?
Given the code fragment:
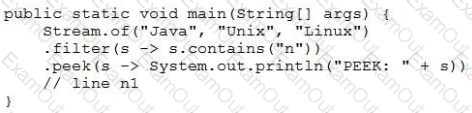
Which two code fragments, when inserted at line n1 independently, result in the output PEEK: Unix?
Given the code fragment:
public void recDelete (String dirName) throws IOException {
File [ ] listOfFiles = new File (dirName) .listFiles();
if (listOfFiles ! = null && listOfFiles.length >0) {
for (File aFile : listOfFiles) {
if (aFile.isDirectory ()) {
recDelete (aFile.getAbsolutePath ());
} else {
if (aFile.getName ().endsWith (“.class”))
aFile.delete ();
}
}
}
}
Assume that Projects contains subdirectories that contain .class files and is passed as an argument to the recDelete () method when it is invoked.
What is the result?
Given:
class Vehicle implements Comparable
int vno;
String name;
public Vehicle (int vno, String name) {
this.vno = vno,;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString () {
return vno + “:” + name;
}
public int compareTo(Vehicle o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
}
and this code fragment:
Set
vehicles.add(new Vehicle (10123, “Ford”));
vehicles.add(new Vehicle (10124, “BMW”));
System.out.println(vehicles);
What is the result?
Given the code fragment:
List
empDetails.stream()
.filter(s-> s.contains(“r”))
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println); //line n1
What is the result?
Which two reasons should you use interfaces instead of abstract classes? (Choose two.)

