You want to write a query that prompts for two column names and the WHERE condition each time it is executed in a session but only prompts for the table name the first time it is executed.
The variables used in your query are never undefined in your session.
Which query can be used?
Examine this command and some partial output:

Why does the DB01.abc.com service show unknown status?
Which four statements are true regarding primary and foreign key constraints and the effect they can have on table data? (Choose four.)
Which two actions can you perform using DBCA for an existing database?
Evaluate these commands which execute successfully:
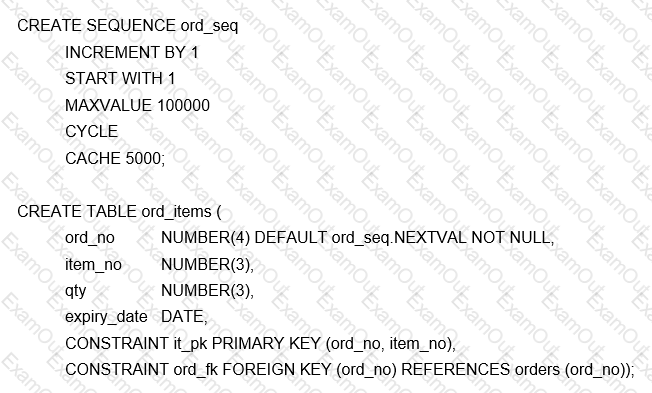
Which two statements are true about the ORD_ITEMS table and the ORD_SEQ sequence? (Choose two.)
Which two statements are true about the PMON background process? (Choose two.)
Which three are types of segments in an Oracle Database? (Choose three.)
In the spfile of a single instance database, LOCAL_LISTENER is set to LISTENER_1.
The TNSNAMES.ORA file in $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin in the database home contains:

Which statement is true?
Which two statements are true about substitution variables?
Table ORDER_ITEMS contains columns ORDER_ID, UNIT_PRICE and QUANTITY, of data type NUMBER.
Examine these SQL statements:
Statement 1:
SELECT MAX(unit_price * quantity) “Maximum Order”
FROM order_items;
Statement 2:
SELECT MAX(unit_price * quantity) “Maximum Order”
FROM order_items
GROUP BY order_id;
Which two statements are true?

