Where is the initial admin password stored during an installation of IBM Cloud Pak for Integration?
platform-auth-idp-credentials. in the 1AM service installation folder.
platform-auth-idp-credentials, in the ibm-common-services namespace.
platform-auth-idp-credentials, in the /sbin folder.
platform-auth-idp-credentials. in the master-node root folder.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
During the installation of IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I), an initial admin password is automatically generated and securely stored in a Kubernetes secret called platform-auth-idp-credentials.
This secret is located in the ibm-common-services namespace, which is a central namespace used by IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services to manage authentication, identity providers, and security.
The stored credentials are required for initial login to the IBM Cloud Pak platform and can be retrieved using OpenShift CLI (oc).
Retrieving the Initial Admin Password:To view the stored credentials, administrators can run the following command:
sh
Copy
oc get secret platform-auth-idp-credentials -n ibm-common-services -o jsonpath='{.data.admin_password}' | base64 --decode
This will decode and display the initial admin password.
A. platform-auth-idp-credentials in the IAM service installation folder (Incorrect)
The IAM (Identity and Access Management) service does store authentication-related configurations, but the admin password is specifically stored in a Kubernetes secret, not in a local file.
C. platform-auth-idp-credentials in the /sbin folder (Incorrect)
The /sbin folder is a system directory on Linux-based OSes, and IBM Cloud Pak for Integration does not store authentication credentials there.
D. platform-auth-idp-credentials in the master-node root folder (Incorrect)
IBM Cloud Pak stores authentication credentials securely within Kubernetes secrets, not directly in the root folder of the master node.
Analysis of Incorrect Options:
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration - Retrieving Admin Credentials
IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services - Managing Secrets
Red Hat OpenShift - Managing Kubernetes Secrets
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
Select all that apply
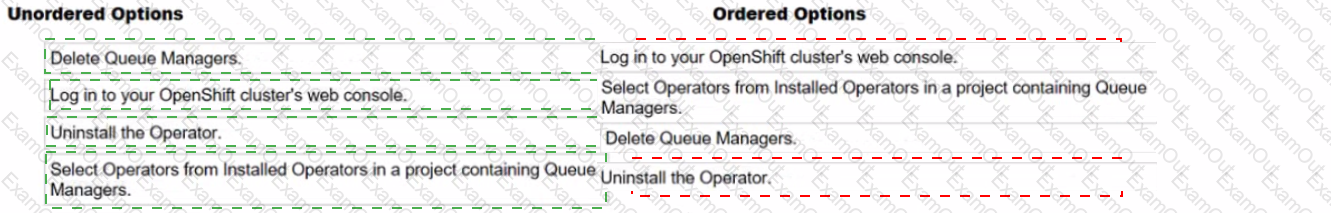
What is the correct sequence of steps to delete IBM MQ from IBM Cloud Pak for Integration?

The Answer Is:
Explanation:
Correct Ordered Steps to Delete IBM MQ from IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I):
1️⃣ Log in to your OpenShift cluster's web console.
Access the OpenShift web console to manage resources and installed operators.
2️⃣ Select Operators from Installed Operators in a project containing Queue Managers.
Navigate to the Installed Operators section and locate the IBM MQ Operator in the project namespace where queue managers exist.
3️⃣ Delete Queue Managers.
Before uninstalling the operator, delete any existing IBM MQ Queue Managers to ensure a clean removal.
4️⃣ Uninstall the Operator.
Finally, uninstall the IBM MQ Operator from OpenShift to complete the deletion process.
To properly delete IBM MQ from IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I), the steps must be followed in the correct order:
Logging into OpenShift Web Console – This step provides access to the IBM MQ Operator and related resources.
Selecting the Installed Operator – Ensures the correct project namespace and MQ resources are identified.
Deleting Queue Managers – Queue Managers must be removed before uninstalling the operator; otherwise, orphaned resources may remain.
Uninstalling the Operator – Once all resources are removed, the MQ Operator can be uninstalled cleanly.
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
IBM MQ in Cloud Pak for Integration
Managing IBM MQ Operators in OpenShift
Uninstalling IBM MQ on OpenShift
How many Cloud Pak for Integration licenses will the non-production environment cost as compared to the production environment when deploying API Connect. App Connect Enterprise, and MQ?
The same amount
Half as many.
More than half as many.
More information is needed to determine the cost.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) licensing follows Virtual Processor Core (VPC)-based pricing, where licensing requirements differ between production and non-production environments.
For non-production environments, IBM typically requires half the number of VPC licenses compared to production environments when deploying components like API Connect, App Connect Enterprise, and IBM MQ.
This 50% reduction applies because IBM offers a non-production environment discount, which allows enterprises to use fewer VPCs for testing, development, and staging while still maintaining functionality.
IBM provides reduced VPC license requirements for non-production environments to lower costs.
The licensing ratio is generally 1:2 (Non-Production:Production), meaning the non-production environment will require half the licenses compared to production.
This policy is commonly applied to major CP4I components, including:
IBM API Connect
IBM App Connect Enterprise
IBM MQ
A. The same amount → Incorrect
Non-production environments typically require half the VPC licenses, not the same amount.
C. More than half as many → Incorrect
IBM’s standard licensing policy offers at least a 50% reduction, so this is not correct.
D. More information is needed to determine the cost. → Incorrect
While pricing details depend on contract terms, IBM has a standard non-production licensing policy, making it predictable.
Why Answer B is Correct?Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Licensing Guide
IBM Cloud Pak VPC Licensing
IBM MQ Licensing Details
IBM API Connect Licensing
IBM App Connect Enterprise Licensing
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
What is the result Of issuing the oc extract secret/platform—auth—idp—credentials --to=- command?
Writes the OpenShift Container Platform credentials to the current directory.
Generates Base64 decoded secrets for all Cloud Pak for Integration users.
Displays the credentials of the admin user.
Distributes credentials throughout the Cloud Pak for Integration platform.
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
The command:
oc extract secret/platform-auth-idp-credentials --to=-
is used to retrieve and display the admin user credentials stored in the platform-auth-idp-credentials secret within an OpenShift-based IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) deployment.
In IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services, the platform-auth-idp-credentials secret contains the admin username and password used to authenticate with OpenShift and Cloud Pak services.
The oc extract command decodes the secret and displays its contents in plaintext in the terminal.
The --to=- flag directs the output to standard output (STDOUT), ensuring that the credentials are immediately visible instead of being written to a file.
This command is commonly used for recovering lost admin credentials or retrieving them for automated processes.
Why Option C (Displays the credentials of the admin user) is Correct:
A. Writes the OpenShift Container Platform credentials to the current directory. → Incorrect
The --to=- option displays the credentials, but it does not write them to a file in the directory.
To save the credentials to a file, the command would need a filename, e.g., --to=admin-creds.txt.
B. Generates Base64 decoded secrets for all Cloud Pak for Integration users. → Incorrect
The command only extracts one specific secret (platform-auth-idp-credentials), which contains the admin credentials only.
It does not generate or decode secrets for all users.
D. Distributes credentials throughout the Cloud Pak for Integration platform. → Incorrect
The command extracts and displays credentials, but it does not distribute or propagate them.
Credentials distribution in Cloud Pak for Integration is handled through Identity and Access Management (IAM) configurations.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services - Retrieving Admin Credentials
OpenShift CLI (oc extract) Documentation
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Identity and Access Management
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
Which command will attach the shell to a running container?
run….
attach….
connect...
shell…
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
In IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2, which runs on Red Hat OpenShift, administrators often need to interact with running containers for troubleshooting, debugging, or configuration changes. The correct command to attach the shell to a running container is:
oc attach
This command connects the user to the standard input (stdin), output (stdout), and error (stderr) streams of the specified container inside a pod.
Alternatively, for interactive shell access, administrators can use:
oc exec -it
or
oc exec -it
if the container supports Bash.
A. run → ❌ Incorrect
The oc run command creates a new pod rather than attaching to an existing running container.
C. connect → ❌ Incorrect
There is no oc connect command in OpenShift or Kubernetes for attaching to a container shell.
D. shell → ❌ Incorrect
OpenShift and Kubernetes do not have a shell command for connecting to a running container.
Instead, the oc exec command is used to start an interactive shell session inside a container.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
OpenShift CLI (oc) Command Reference
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Troubleshooting Guide
Kubernetes attach vs exec Commands
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
How can a new API Connect capability be installed in an air-gapped environ-ment?
Configure a laptop or bastion host to use Container Application Software for Enterprises files to mirror images.
An OVA form-factor of the Cloud Pak for Integration is recommended for high security deployments.
A pass-through route must be configured in the OpenShift Container Platform to connect to the online image registry.
Use secure FTP to mirror software images in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes.
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
In an air-gapped environment, the OpenShift cluster does not have direct internet access, which means that new software images, such as IBM API Connect, must be manually mirrored from an external source.
The correct approach for installing a new API Connect capability in an air-gapped OpenShift environment is to:
Use a laptop or a bastion host that does have internet access to pull required container images from IBM’s entitled software registry.
Leverage Container Application Software for Enterprises (CASE) files to download and transfer images to the private OpenShift registry.
Mirror images into the OpenShift cluster by using OpenShift’s built-in image mirror utilities (oc mirror).
This method ensures that all required container images are available locally within the air-gapped environment.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?Option
Explanation
Correct?
B. An OVA form-factor of the Cloud Pak for Integration is recommended for high-security deployments.
❌ Incorrect – IBM Cloud Pak for Integration does not provide an OVA (Open Virtual Appliance) format for API Connect deployments. It is containerized and runs on OpenShift.
❌
C. A pass-through route must be configured in the OpenShift Container Platform to connect to the online image registry.
❌ Incorrect – Air-gapped environments have no internet connectivity, so this approach would not work.
❌
D. Use secure FTP to mirror software images in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes.
❌ Incorrect – OpenShift does not use FTP for image mirroring; it relies on oc mirror and image registries for air-gapped deployments.
❌
Final Answer:✅ A. Configure a laptop or bastion host to use Container Application Software for Enterprises files to mirror images.
IBM API Connect Air-Gapped Installation Guide
IBM Container Application Software for Enterprises (CASE) Documentation
Red Hat OpenShift - Mirroring Images for Disconnected Environments
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
What are two capabilities of the IBM Cloud Pak foundational services operator?
Messaging service to get robust and reliable messaging services.
Automation assets service to store, manage, and retrieve integration assets.
License Service that reports the license use of the product and its underlying product details that are deployed in the containerized environment.
API management service for managing the APIs created on API Connect.
IAM services for authentication and authorization.
The Answer Is:
C, EExplanation:
The IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services Operator provides essential shared services required for IBM Cloud Pak solutions, including Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I). These foundational services enable security, licensing, monitoring, and user management across IBM Cloud Paks.
The IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services License Service tracks and reports license usage of IBM Cloud Pak products deployed in a containerized environment.
It ensures compliance by monitoring Virtual Processor Cores (VPCs) and other licensing metrics.
This service is crucial for IBM Cloud Pak licensing audits and entitlement verification.
What type of authentication uses an XML-based markup language to exchange identity, authentication, and authorization information between an identity provider and a service provider?
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
IAM SSO authentication
lAMviaXML
Enterprise XML
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based standard used for exchanging identity, authentication, and authorization information between an Identity Provider (IdP) and a Service Provider (SP).
SAML is widely used for Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication in enterprise environments, allowing users to authenticate once with an identity provider and gain access to multiple applications without needing to log in again.
User Requests Access → The user tries to access a service (Service Provider).
Redirect to Identity Provider (IdP) → If not authenticated, the user is redirected to an IdP (e.g., Okta, Active Directory Federation Services).
User Authenticates with IdP → The IdP verifies user credentials.
SAML Assertion is Sent → The IdP generates a SAML assertion (XML-based token) containing authentication and authorization details.
Service Provider Grants Access → The service provider validates the SAML assertion and grants access.
How SAML Works:SAML is commonly used in IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 to integrate with enterprise authentication systems for secure access control.
B. IAM SSO authentication → ❌ Incorrect
IAM (Identity and Access Management) supports SAML for SSO, but "IAM SSO authentication" is not a specific XML-based authentication standard.
C. IAM via XML → ❌ Incorrect
There is no authentication method called "IAM via XML." IBM IAM systems may use XML configurations, but IAM itself is not an XML-based authentication protocol.
D. Enterprise XML → ❌ Incorrect
"Enterprise XML" is not a standard authentication mechanism. While XML is used in many enterprise systems, it is not a dedicated authentication protocol like SAML.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration - SAML Authentication
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) Overview
IBM Identity and Access Management (IAM) Authentication
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
Which two authentication types are supported for single sign-on in Founda-tional Services?
Basic Authentication
OpenShift authentication
PublicKey
Enterprise SAML
Local User Registry
The Answer Is:
B, DExplanation:
In IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2, Foundational Services provide authentication and access control mechanisms, including Single Sign-On (SSO) integration. The two supported authentication types for SSO are:
OpenShift Authentication
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration leverages OpenShift authentication to integrate with existing identity providers.
OpenShift authentication supports OAuth-based authentication, allowing users to sign in using an OpenShift identity provider, such as LDAP, OIDC, or SAML.
This method enables seamless user access without requiring additional login credentials.
Enterprise SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
SAML authentication allows integration with enterprise identity providers (IdPs) such as IBM Security Verify, Okta, Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), and other SAML 2.0-compatible IdPs.
It provides federated identity management for SSO across enterprise applications, ensuring secure access to Cloud Pak services.
A. Basic Authentication – Incorrect
Basic authentication (username and password) is not used for Single Sign-On (SSO). SSO mechanisms require identity federation through OpenID Connect (OIDC) or SAML.
C. PublicKey – Incorrect
PublicKey authentication (such as SSH key-based authentication) is used for system-level access, not for SSO in Foundational Services.
E. Local User Registry – Incorrect
While local user registries can store credentials, they do not provide SSO capabilities. SSO requires federated identity providers like OpenShift authentication or SAML-based IdPs.
Why the other options are incorrect:
IBM Cloud Pak Foundational Services Authentication Guide
OpenShift Authentication and Identity Providers
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration SSO Configuration
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:
An administrator has to implement high availability for various components of a Cloud Pak for Integration installation. Which two statements are true about the options available?
DataPower gateway uses a Quorum mechanism where a global load balancer uses quorum algorithm to choose the active instance.
Queue Manager (MQ) uses Replicated Data Queue Manager (RDQM).
API management uses a quorum mechanism where components are deployed on a minimum of three failure domains.
Platform Navigator uses an Active/Active deployment, where the primary handles all the traffic and in case of failure of the primary, the load balancer will then route the traffic to the secondary.
AppConnect can use a mix of mechanisms - like failover for stateful workloads and active/active deployments for stateless workloads
The Answer Is:
B, CExplanation:
High availability (HA) in IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 is crucial to ensure continuous service availability and reliability. Different components use different HA mechanisms, and the correct options are B and C.
B. Queue Manager (MQ) uses Replicated Data Queue Manager (RDQM).
IBM MQ supports HA through Replicated Data Queue Manager (RDQM), which uses synchronous data replication across nodes.
This ensures failover to another node without data loss if the primary node goes down.
RDQM is an efficient HA solution for MQ in CP4I.
C. API management uses a quorum mechanism where components are deployed on a minimum of three failure domains.
API Connect in CP4I follows a quorum-based HA model, meaning that the deployment is designed to function across at least three failure domains (availability zones).
This ensures resilience and prevents split-brain scenarios in case of node failures.
Correct Answers Explanation:
A. DataPower gateway uses a Quorum mechanism where a global load balancer uses a quorum algorithm to choose the active instance. → Incorrect
DataPower typically operates in Active/Standby mode rather than a quorum-based model.
It can be deployed behind a global load balancer, but the quorum algorithm is not used to determine the active instance.
D. Platform Navigator uses an Active/Active deployment, where the primary handles all the traffic and in case of failure of the primary, the load balancer will then route the traffic to the secondary. → Incorrect
Platform Navigator does not follow a traditional Active/Active deployment.
It is typically deployed as a highly available microservice on OpenShift, distributing workloads across nodes.
E. AppConnect can use a mix of mechanisms - like failover for stateful workloads and active/active deployments for stateless workloads. → Incorrect
While AppConnect can be deployed in Active/Active mode, it does not necessarily mix failover and active/active mechanisms explicitly for HA purposes.
Incorrect Answers Explanation:
IBM MQ High Availability and RDQM
IBM API Connect High Availability
IBM DataPower Gateway HA Deployment
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Documentation
IBM Cloud Pak for Integration (CP4I) v2021.2 Administration References:

