You have a mixture of packaged and internally developed applications hosted on a Compute Engine instance that is running Linux. These applications write log records as text in local files. You want the logs to be written to Cloud Logging. What should you do?
Your development team has been tasked with maintaining a .NET legacy application. The application incurs occasional changes and was recently updated. Your goal is to ensure that the application provides consistent results while moving through the CI/CD pipeline from environment to environment. You want to minimize the cost of deployment while making sure that external factors and dependencies between hosting environments are not problematic. Containers are not yet approved in your organization. What should you do?
Your application stores customers' content in a Cloud Storage bucket, with each object being encrypted with the customer's encryption key. The key for each object in Cloud Storage is entered into your application by the customer. You discover that your application is receiving an HTTP 4xx error when reading the object from Cloud Storage What is a possible cause of this error?
You recently developed an application that monitors a large number of stock prices. You need to configure Pub/Sub to receive a high volume messages and update the current stock price in a single large in-memory database The downstream service needs only the most up-to-date prices in the in-memory database to perform stock trading transactions Each message contains three pieces of information
• Stock symbol
• Stock price
• Timestamp for the update
.
How should you set up your Pub/Sub subscription?
You are developing a web application that will be accessible over both HTTP and HTTPS and will run on Compute Engine instances. On occasion, you will need to SSH from your remote laptop into one of the Compute Engine instances to conduct maintenance on the app. How should you configure the instances while following Google-recommended best practices?
The new version of your containerized application has been tested and is ready to deploy to production on Google Kubernetes Engine. You were not able to fully load-test the new version in pre-production environments, and you need to make sure that it does not have performance problems once deployed. Your deployment must be automated. What should you do?
You are a developer working on an internal application for payroll processing. You are building a component of the application that allows an employee to submit a timesheet, which then initiates several steps:
• An email is sent to the employee and manager, notifying them that the timesheet was submitted.
• A timesheet is sent to payroll processing for the vendor's API.
• A timesheet is sent to the data warehouse for headcount planning.
These steps are not dependent on each other and can be completed in any order. New steps are being considered and will be implemented by different development teams. Each development team will implement the error handling specific to their step. What should you do?
You are supporting a business-critical application in production deployed on Cloud Run. The application is reporting HTTP 500 errors that are affecting the usability of the application. You want to be alerted when the number of errors exceeds 15% of the requests within a specific time window. What should you do?
You recently migrated an on-premises monolithic application to a microservices application on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The application has dependencies on backend services on-premises, including a CRM system and a MySQL database that contains personally identifiable information (PII). The backend services must remain on-premises to meet regulatory requirements.
You established a Cloud VPN connection between your on-premises data center and Google Cloud. You notice that some requests from your microservices application on GKE to the backend services are failing due to latency issues caused by fluctuating bandwidth, which is causing the application to crash. How should you address the latency issues?
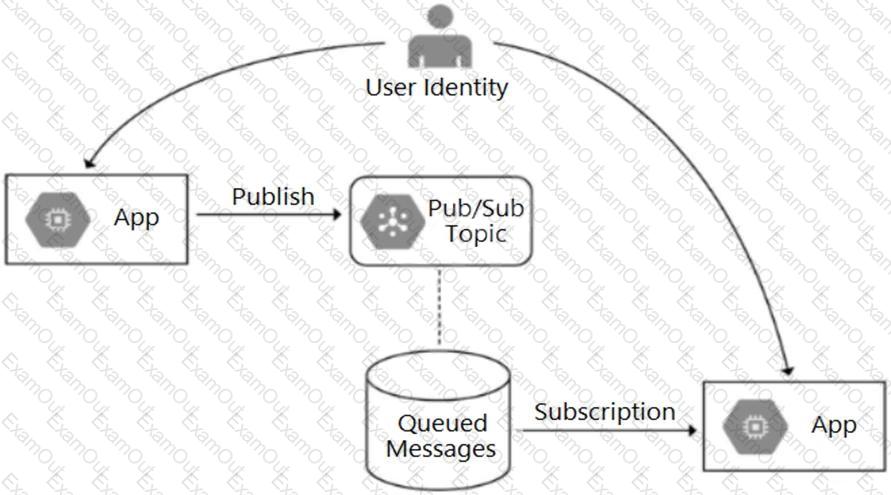
Your team is developing an application in Google Cloud that executes with user identities maintained by Cloud Identity. Each of your application’s users will have an associated Pub/Sub topic to which messages are published, and a Pub/Sub subscription where the same user will retrieve published messages. You need to ensure that only authorized users can publish and subscribe to their own specific Pub/Sub topic and subscription. What should you do?