Refer to the exhibit.
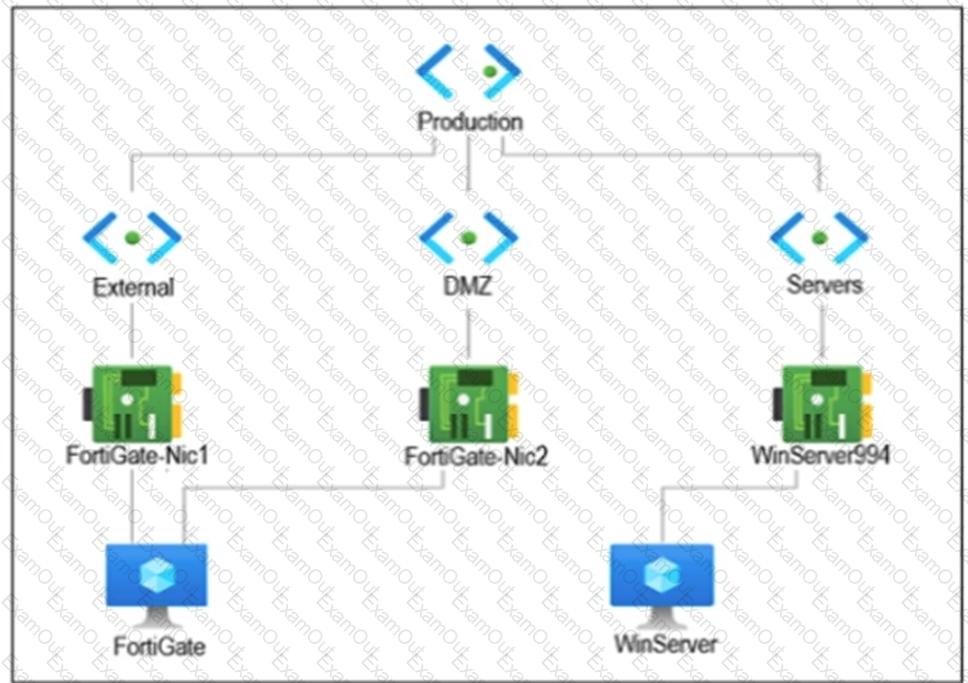
You are troubleshooting a network connectivity issue between two VMs that are deployed in Azure.
One VM is a FortiGate that has one interface in the DMZ subnet, which is in the Production VNet. The other VM is a Windows Server in the Servers subnet, which is also in the Production VNet. You cannot ping the Windows Server from the FortiGate VM.
What is the reason for this?
How are the configurations synchronized between two FortiGate VMs in an active-passive HA with SDN connector failover deployed from the Azure marketplace?
Refer to the exhibits.

A high availability (HA) active-active FortiGate with Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) and Internal Load Balancing (ILB) was deployed with a default setup to filter traffic to a Linux server running Apache server.
Ports 80 and 22 are open on the Linux server, and on FortiGate a VIP and firewall policy are configured to allow traffic through ports 80 and 22. Traffic on port 80 is successful, but traffic on port 22 is not detected by FortiGate.
What configuration changes could you perform to allow SSH traffic?
How does Azure ExpressRoute contribute to achieving predictable latency for network traffic?
A Linux server was deployed in a protected subnet with a dynamic IP address. A FortiGate VM in the internal subnet provides traffic filtering to it. and you must implement a firewall policy using the IP address of the Linux server.
Which feature could help integrate FortiGate using Linux server tags?
Which additional features does Azure Firewall Premium offer compared to Azure Firewall Standard?
What are two characteristics of Azure standard public IP addresses? (Choose two.)
Your organization is in the process of optimizing its Azure network architecture and wants to dynamically manage and exchange routing information between its virtual networks and on-premises networks.
Which Azure service would help to provide a centralized point for efficient route management and dynamic routing?
Which output was taken on a VM running in Azure?
A)

B)

C)

D)

Refer to the exhibit.
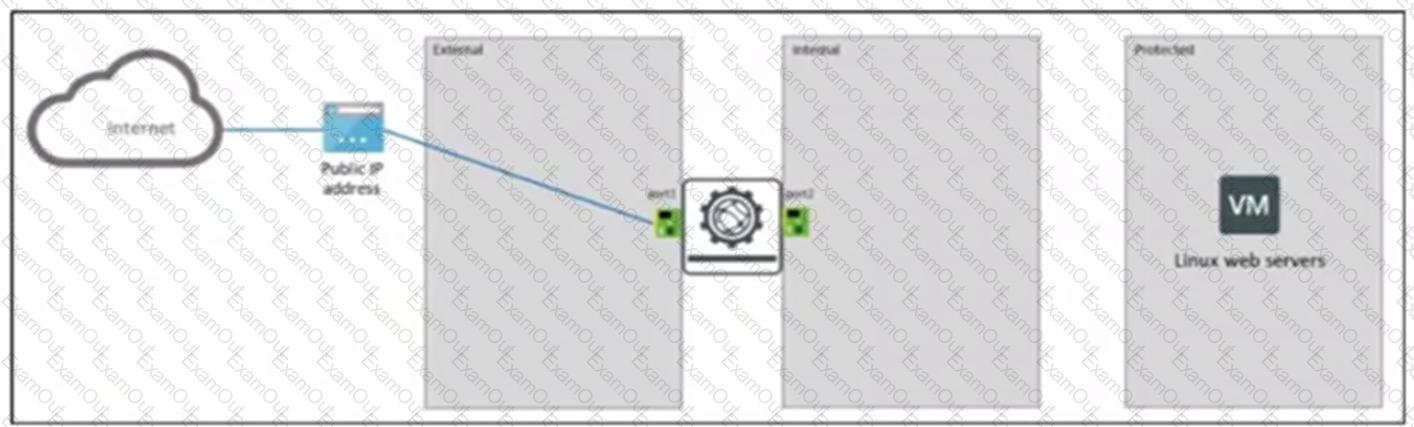
Your company runs front-end web servers in Azure. You need to deploy a Linux VM to be used as a web server.
To protect your web servers with a web application firewall (WAF), you deploy FortiWeb to secure applications from web-based attacks.
Which FortiWeb operation mode can you implement for this scenario?

