Which must be sent to the license server to generate a new license?
A new BIG-IP VE is deployed with default settings. The BIG-IP Administrator completes the setup utility in the Configuration Utility. The internal self IP address fails to respond to a ping request. What is a possible cause of this issue?
A BIG-IP Administrator configures remote authentication and needs to make sure that users can still
login even when the remote authentication server is unavailable.
Which action should the BIG-IP Administrators in the remote authentication configuration to meet this
requirement?
Which statement accurately describes the difference between two loadbalancing modes specified as "member" and "node"?
Refer to the exhibit.

How are new connections load balanced?
A virtual server is listening at 10.10.1.100:any and has the following iRule associated with it:
when CLIENT_ACCEPTED { if {[TCP::local_port] equals 80 } { pool pool1 } elseif {[TCP::local_port] equals 443} { pool pool2 }
If a user connects to 10.10.1.100 and port 22, which pool will receive the request?
A standard virtual server is defined with a pool and a SNAT using automap. All other settings for the virtual server are at defaults. When client traffic is processed by the BIG-IP, what will occur to the IP addresses?
Assume a client's traffic is being processed only by a NAT; no SNAT or virtual server processing takes place. Also assume that the NAT definition specifies a NAT address and an origin address while all other settings are
left at their defaults. If the origin server were to initiate traffic via the BIG-IP, what changes, if any, would take place when the BIG-IP processes such packets?
Refer to the exhibit.
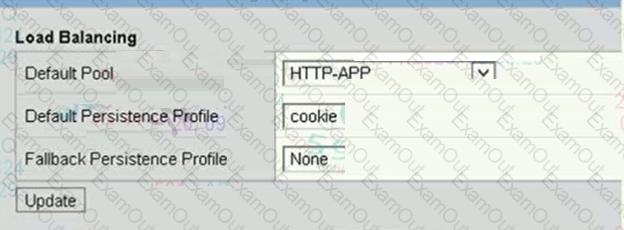
Due to a change in application requirements, a BIG-IP Administrator needs to modify the configuration of a Virtual Server to include a Fallback Persistence Profile.
Which persistence profile type should the BIG-IP Administrator use for this purpose?
Users report that traffic is negatively affected every time a BIG-IP device fails over. The traffic becomes
stabilized after a few minutes.
What should the BIG-IP Administrator do to reduce the impact of future failovers?

