A company recently removed administrator rights from all of its end user workstations. An analyst uses CVSSv3.1 exploitability metrics to prioritize the vulnerabilities for the workstations and produces the following information:
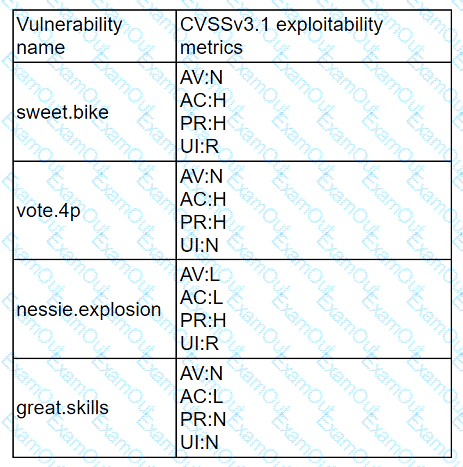
Which of the following vulnerabilities should be prioritized for remediation?
A security team identified several rogue Wi-Fi access points during the most recent network scan. The network scans occur once per quarter. Which of the following controls would best all ow the organization to identity rogue
devices more quickly?
An analyst is reviewing a dashboard from the company’s SIEM and finds that an IP address known to be malicious can be tracked to numerous high-priority events in the last two hours. The dashboard indicates that these events relate to TTPs. Which of the following is the analyst most likely using?
A security analyst needs to mitigate a known, exploited vulnerability related not
tack vector that embeds software through the USB interface. Which of the following should the analyst do first?
Which of the following would help an analyst to quickly find out whether the IP address in a SIEM alert is a known-malicious IP address?
A security analyst has identified outgoing network traffic leaving the enterprise at odd times. The traffic appears to pivot across network segments and target domain servers. The traffic is then routed to a geographic location to which the company has no association. Which of the following best describes this type of threat?
A systems administrator is reviewing after-hours traffic flows from data-center servers and sees regular outgoing HTTPS connections from one of the servers to a public IP address. The server should not be making outgoing connections after hours. Looking closer, the administrator sees this traffic pattern around the clock during work hours as well. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
An older CVE with a vulnerability score of 7.1 was elevated to a score of 9.8 due to a widely available exploit being used to deliver ransomware. Which of the following factors would an analyst most likely communicate as the reason for this escalation?
After conducting a cybersecurity risk assessment for a new software request, a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) decided the risk score would be too high. The CISO refused the software request. Which of the following risk management principles did the CISO select?
A technician is analyzing output from a popular network mapping tool for a PCI audit:
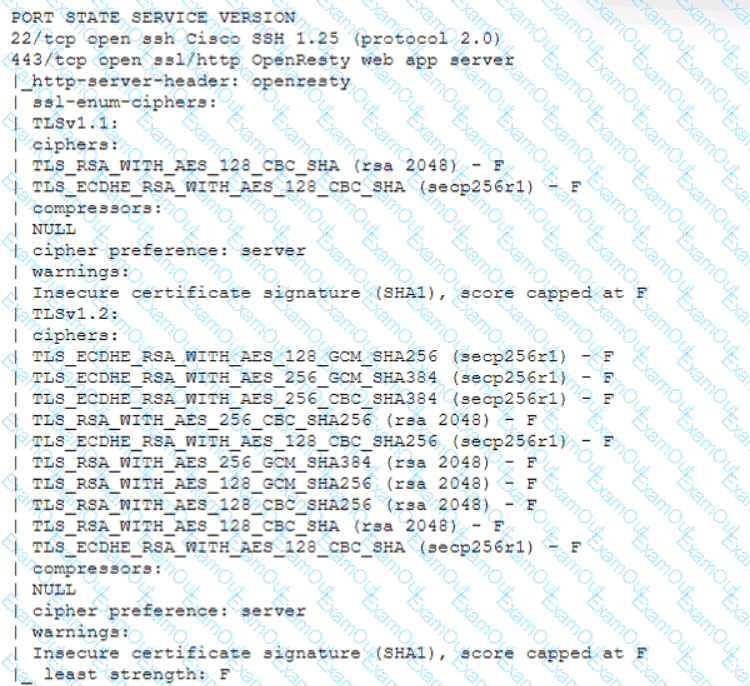
Which of the following best describes the output?

