Which of the following operators accept integer arguments only? (Choose two.)
What will happen if the memory cannot be allocated?
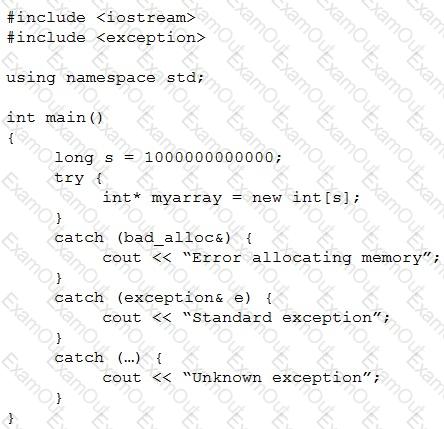
What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?
#include
using namespace std;
int fun(int x) {
return 2*x;
}
int main(){
int i;
i = fun(1) || fun(2);
cout << i;
return 0;
}
What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void fun(int i);
int main()
{
int i=0;
i++;
for (i=0; i<=5; i++)
{
fun(i);
}
return 0;
}
void fun(int i)
{
if (i==3)
return;
cout << i;
}
What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?

What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?
#include
using namespace std;
class First
{
public:
void Print(){ cout<<"from First";}
};
class Second
{
public:
void Print(){ cout<< "from Second";}
};
int main()
{
Second t[2];
for (int i=0; i<2; i++)
t[i].Print();
}
What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class A {
int x;
protected:
int y;
public:
int z;
A() { x=1; y=2; z=3; }
};
class B : public A {
public:
void set() {
y = 4; z = 2;
}
void Print() {
cout << y << z;
}
};
int main () {
B b;
b.set();
b.Print();
return 0;
}
What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?
#include
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void Print(){ cout<<"A";}
};
class C:public A {
public:
virtual void Print()=0;
};
int main()
{
C obj3;
obj3?>Print();
}
What is the output of the program if character “1” is supplied as input?
#include
using namespace std;
int main () {
int c;
cin >> c;
try
{
switch (c)
{
case 1:
throw 20;
case 2:
throw 5.2f;
case 3:
throw 'a';
}
}
catch (int e)
{ cout << "int exception. Exception Nr. " << e; }
catch (float e)
{ cout << "float exception. Exception Nr. " << e; }
catch (...)
{ cout << "An exception occurred."; }
return 0;
}
What happens when you attempt to compile and run the following code?
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int i = 1;
if (--i==1) {
cout << i;
} else {
cout << i-1;
}
return 0;
}

