For a given healthcare product, the Magnolia Health Plan has a premium of $80 PMPM and a unit variable cost of $30 PMPM. Fixed costs for this product are $30,000 per month. Magnolia can correctly calculate the break-even point for this product to be:
The Longview Hospital contracted with the Carlyle Health Plan to provide inpatient services to Carlyle’s enrolled members. Carlyle provides Longview with a type of stop-loss coverage that protects, on a claims incurred and paid basis, against losses arising from significantly higher than anticipated utilization rates among Carlyle’s covered population. The stop-loss coverage specifies an attachment point of 130% of Longview’s projected $2,000,000 costs of treating Carlyle plan members and requires Longview to pay 15% of any costs above the attachment point. In a given plan year, Longview incurred covered costs totaling $3,000,000.
With regard to the type of stop-loss coverage provided to Longview by Carlyle and to whether this coverage is classified as insurance or reinsurance, the risk transfer approach used in this situation can be described as:
The following information was presented on one of the financial statements prepared by the Rouge health plan as of December 31, 1998:
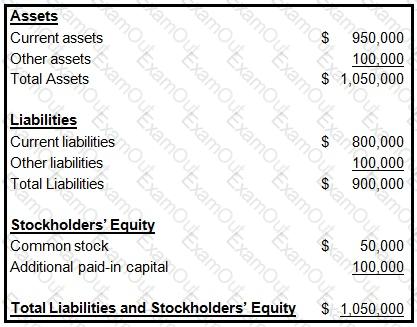
When calculating its cash-to-claims payable ratio, Rouge would correctly divide its:
An investor deposited $1,000 in an interest-bearing account today. That sum will accumulate to $1,200 two years from now. One true statement about this transaction is that:
The Fairway health plan is a for-profit health plan that issues stock. The following data was taken from Fairway's financial statements:
Current assets.....$5,000,000
Total assets.....6,000,000
Current liabilities.....2,500,000
Total liabilities.....3,600,000
Stockholders' equity.....2,400,000
Fairway's total revenues for the previous financial period were $7,200,000, and its net income for that period was $180,000.
From this data, Fairway can determine both its current ratio and its net working capital. Fairway would correctly determine that its
The theory of vicarious liability or ostensible agency can expose a health plan to the risk that it could be held liable for the acts of independent contractors. Factors that may give rise to the assumption that an agency relationship exists between a health plan and its independent contractors include:
Health plans have access to a variety of funding sources depending on whether they are operated as for-profit or not-for-profit organizations. The Verde Health Plan is a for-profit health plan and the Noir Health Plan is a not-for-profit health plan. From the answer choices below, select the response that correctly identifies whether funds from debt markets and equity markets are available to Verde and Noir:
A financial analyst wants to learn the following information about the
Forest health plan for a given financial period:
One typical characteristic of zero-based budgeting (ZBB) is that this budgeting approach
The risk-based capital formula for health plans defines a number of risks that can impact a health plan’s solvency. These categories reflect the fact that the level of risk faced by health plans is significantly impacted by provider reimbursement methods that shift utilization risk to providers. The following statements are about the effect of a health plan transferring utilization risk to providers. Select the answer choice containing the correct statement:

